Self-adaption quasi-PRD control method for photovoltaic grid-connected inverter
A control method and inverter technology, applied in photovoltaic power generation, AC network circuits, single-network parallel feeding arrangements, etc., can solve problems such as poor adaptability to grid impedance changes and poor stability of photovoltaic grid-connected systems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
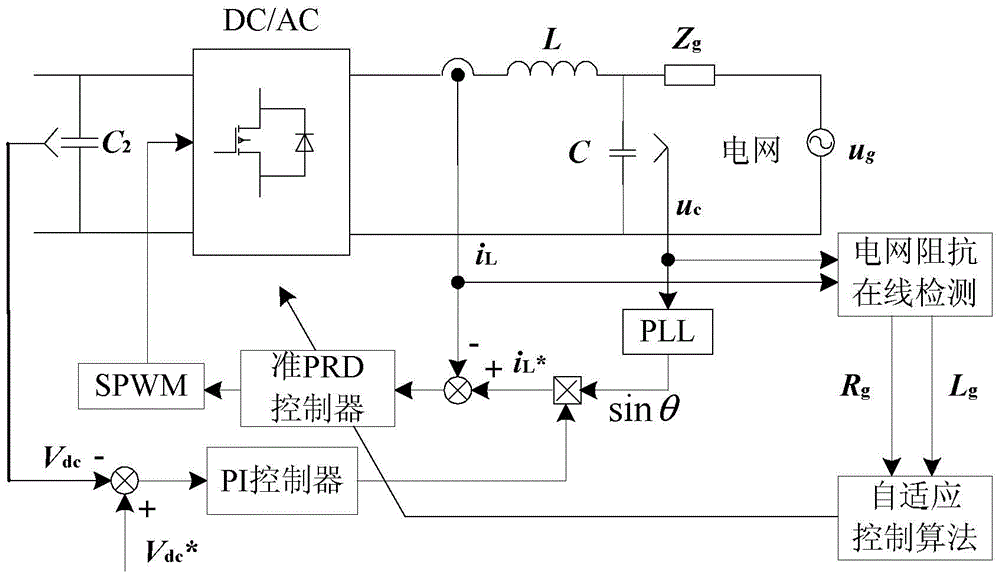
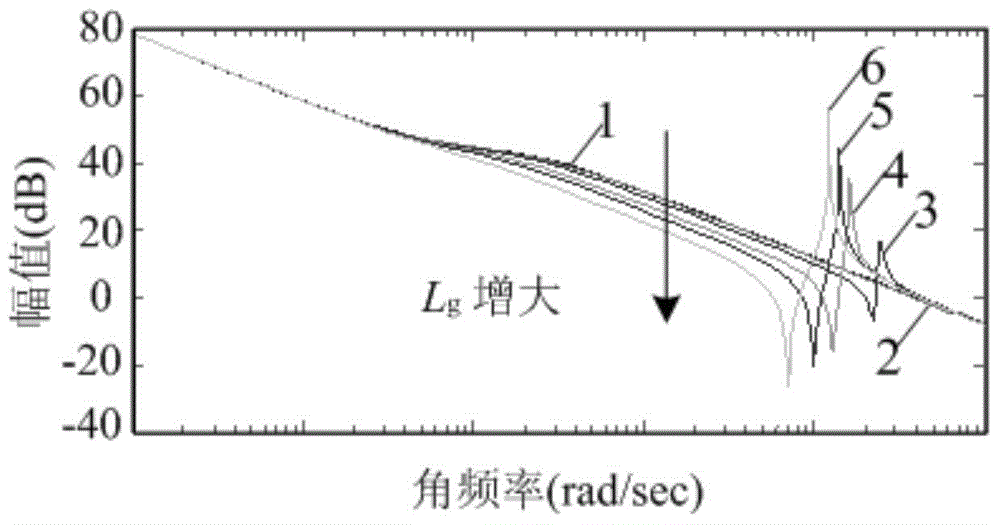
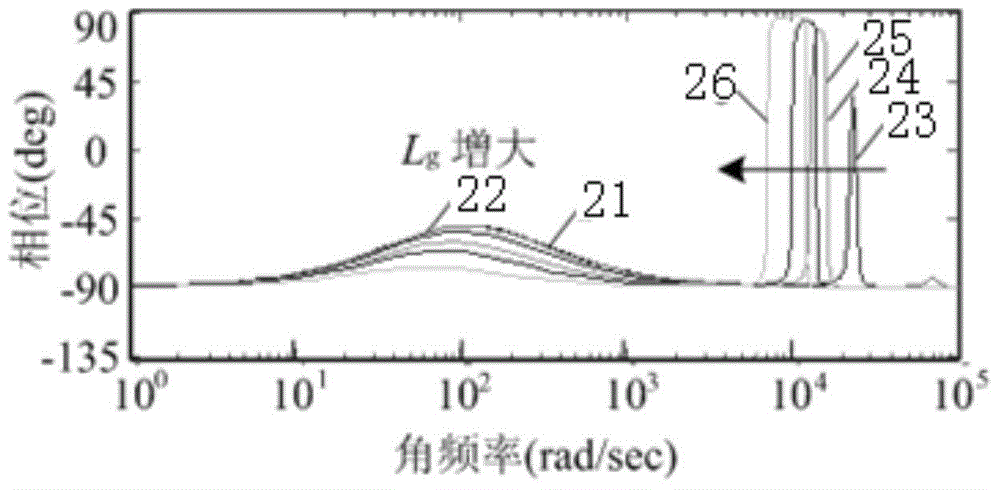
[0044] Specific implementation mode one: refer to Figure 1 to Figure 11 , Figure 18 to Figure 21 Specifically explain this embodiment, the photovoltaic grid-connected inverter adaptive quasi-PRD control method described in this embodiment, it includes the following steps:
[0045] Step 1. Inject a disturbance current of a set frequency into the power grid through the disturbance current injection method through the inverter, and then use the detection element to detect the voltage and current response at the grid-connected point, and then combine the signal processing technology to separate the injected specific subharmonic The modulus value of the wave component, according to which the equivalent grid resistance R is obtained g and grid inductance L g ,
[0046] Step 2. The sinusoidal PWM voltage output by the inverter bridge arm is equivalent to a voltage source, and according to the grid resistance R obtained in step 1 g and grid inductance L g , to establish the tra...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0065] Specific implementation mode two: refer to Figure 12 to Figure 17 Describe this embodiment in detail. This embodiment is a further description of the self-adaptive quasi-PRD control method for photovoltaic grid-connected inverters described in Embodiment 1. In this embodiment, in step 1, the disturbance current injection method uses Double harmonic current disturbance injection method, that is, the injected disturbance current contains harmonics of two frequencies, the frequencies are respectively 400Hz and 600Hz harmonic current, the location of disturbance injection is a given point of grid-connected current, and the way of disturbance injection For intermittent injection into the grid.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0066] Specific embodiment 3: This embodiment is to further explain the adaptive quasi-PRD control method of photovoltaic grid-connected inverter described in specific embodiment 1 or 2. In this embodiment, the equivalent grid resistance is obtained according to the modulus R g and grid inductance L g The process is:
[0067] Since there is the following relationship between the impedance of the grid at different frequencies:
[0068] Z 1 2 = R g 2 + ω 1 2 · L g 2 Z ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com