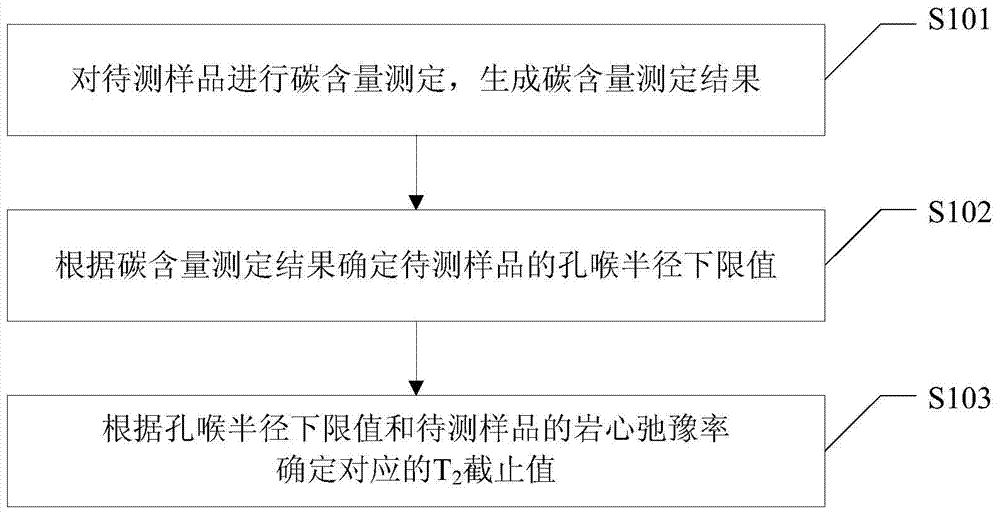
Method for determining nuclear magnetic resonance T2 cutoff value and fluid saturation of tight oil, and apparatus thereof
A technology of nuclear magnetic resonance and determining methods, which is applied in the field of oil exploration, and can solve problems such as inaccuracy and difficult quantitative correspondence of centrifugal force
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
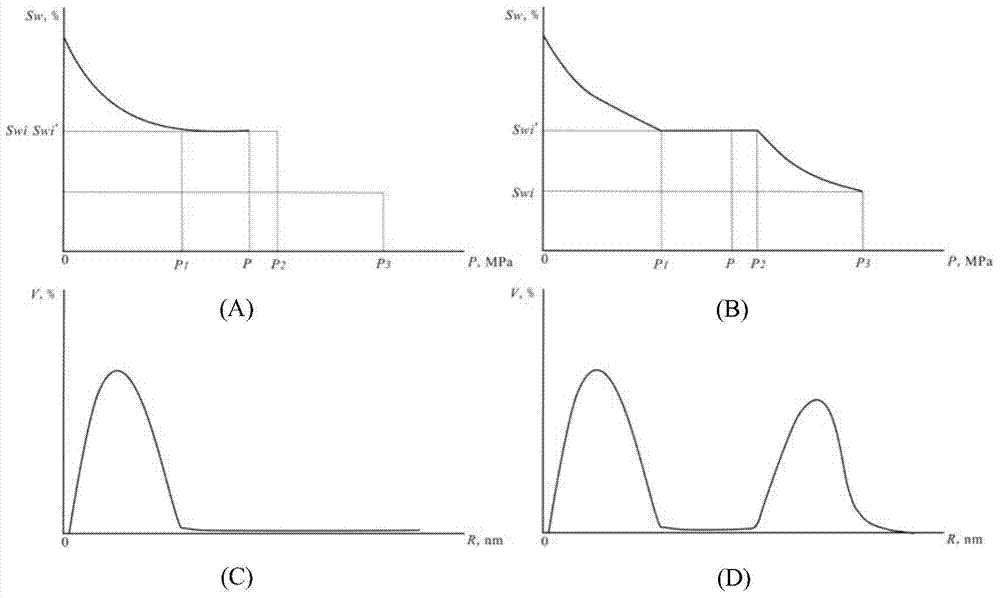
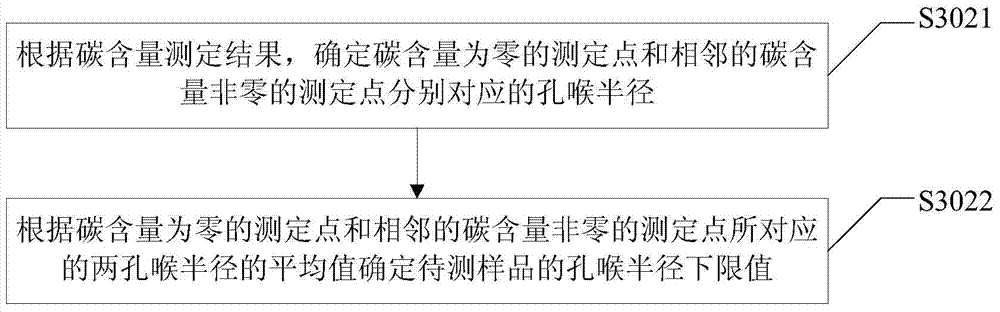
[0080] The experiment of tight oil well R59 well S121 in Fuyu reservoir of Jilin Oilfield was taken as an example. The experimental data of the lower limit value of the pore throat radius of movable fluid in tight oil are as follows: point 1: roar radius 110nm, carbon content 36%; point 2: roar radius 88nm, carbon content 24%; point 3: roar radius Radius 76nm, carbon content 15%; No. 4 point: radius 42nm, carbon content 7%; Point 5: radius 18nm, carbon content 0%. The average value of 42nm and 18nm, 30nm, is taken as the lower limit of the pore throat radius of the movable fluid in tight oil. NMR T 2 The spectral core relaxation rate is taken as 15 μm / s, and the core relaxation rate is generally an empirical value. The empirical value of relaxation rate of sandstone is generally 15 μm / s.
[0081] The lower limit of the pore throat radius is 30nm, and the corresponding T2 cut-off value is 1.5ms ( Image 6 ).
[0082] Predecessors against T 2 The cut-off values are exten...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com