A low-power two-way real-time wireless sensing method
A technology of wireless sensing and low power consumption, applied in the field of wireless sensing, can solve the problems of poor real-time performance, high power consumption, no receiving unit, etc., and achieve the effect of real-time performance improvement, low power consumption, and low power consumption performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the drawings.
[0029] In order to help clearly explain the technical solution of the present invention, the technical terms involved are first explained as follows:
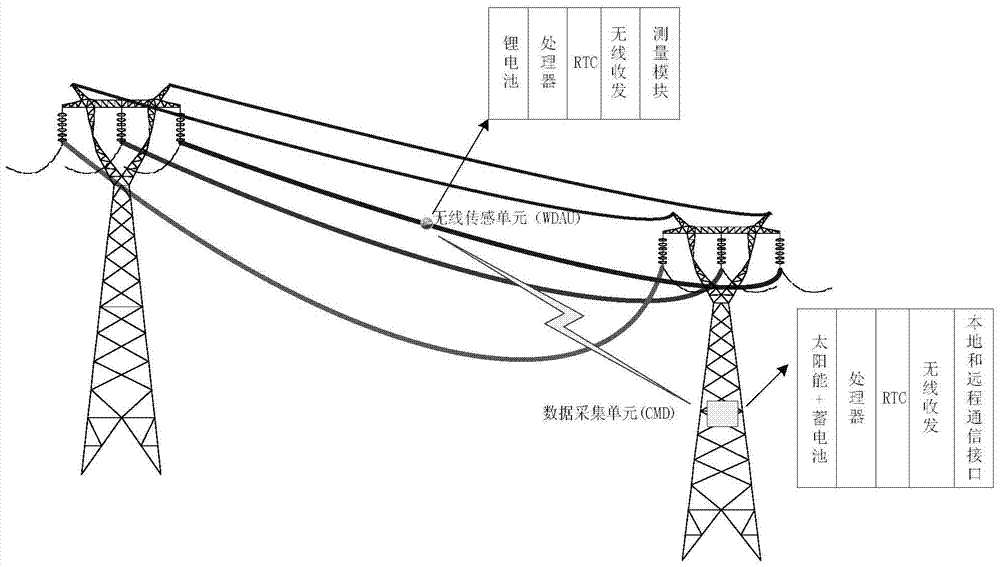
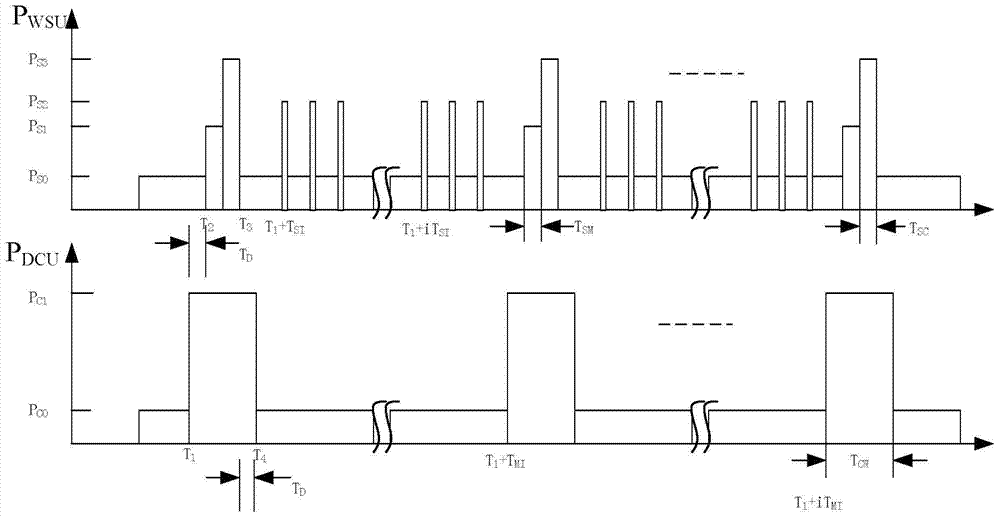
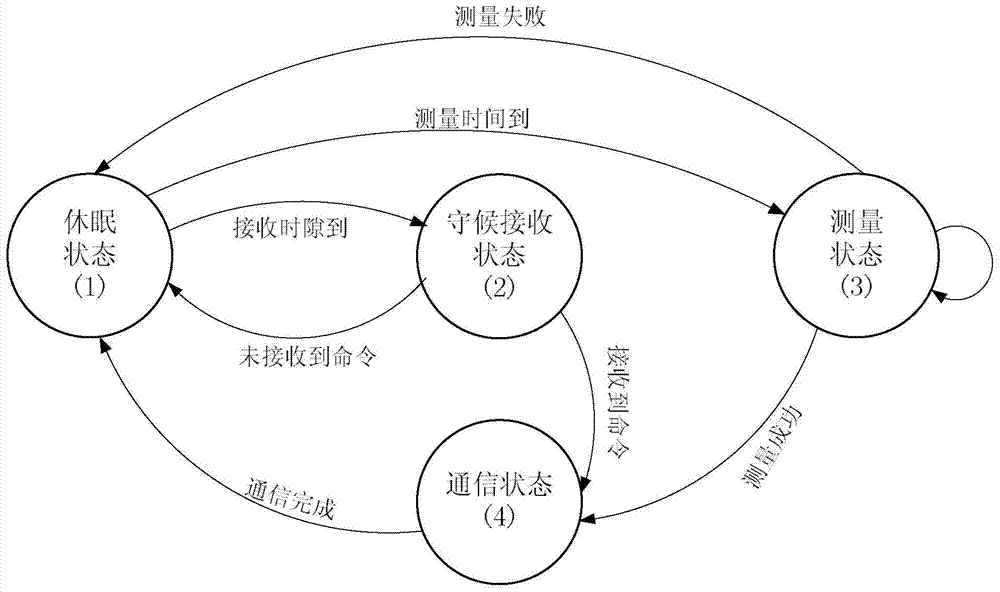
[0030] RTC (Real-Time Clock): Real-time clock. The main function is to provide a stable clock signal for subsequent circuits. The main functions are: clock & calendar, alarm clock, periodic interrupt output, 32KHz clock output.
[0031] Power Line Supervisory: Power Line Supervisory is a general term that uses advanced technology to automatically monitor and scientifically manage transmission lines, and is also one of the important foundations for the realization of smart grids. On-line monitoring of transmission lines is a complex system project. It takes the on-line monitoring system of transmission lines as the core, and involves the supporting requirements for the primary grid and equipment of the transmission grid, the comp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com