Residual magnetism control expansion satellite solar wing and test verification method thereof
An unfolding, solar technology, applied in general control systems, control/regulation systems, testing/monitoring control systems, etc., can solve problems such as large remanence, inability to conduct solar wing magnetic tests, and theoretical calculations that cannot represent actual values, etc. achieve low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
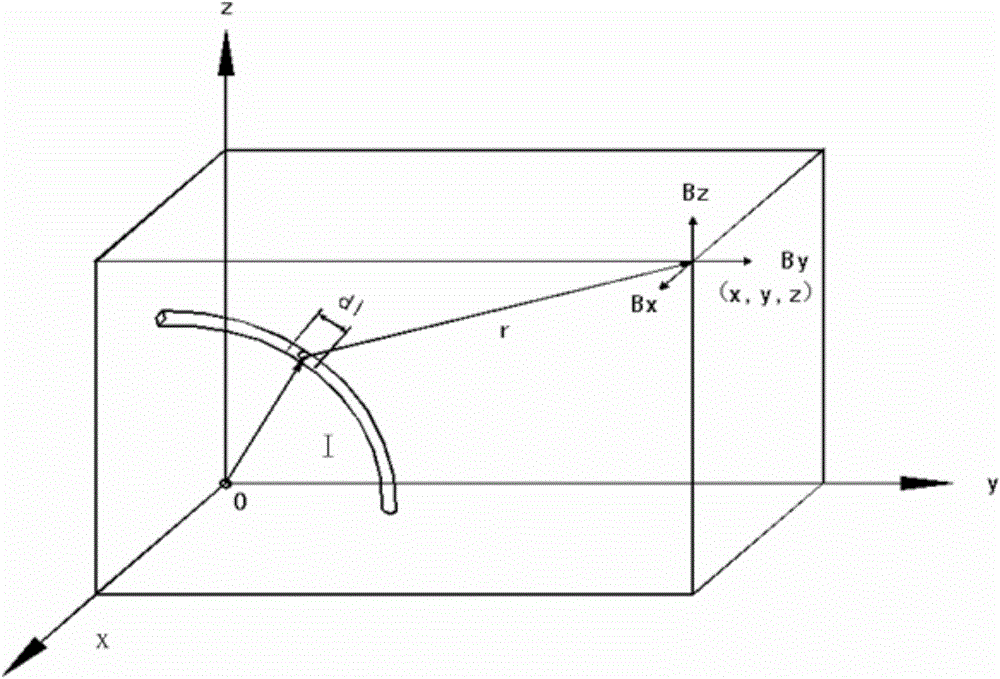
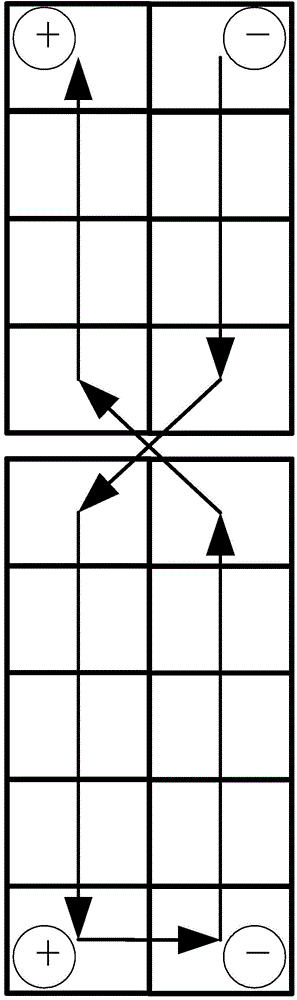
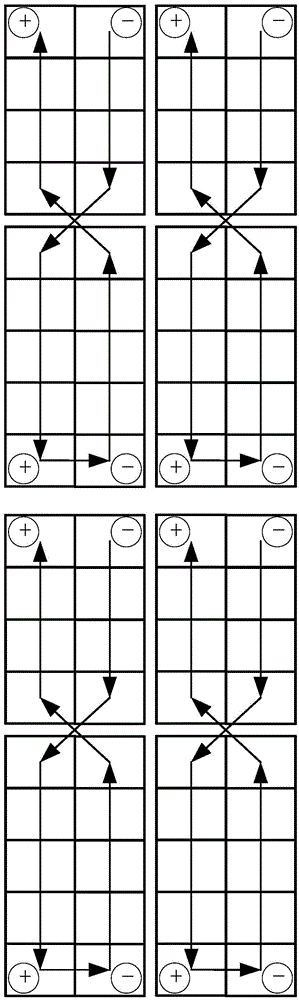
[0040] The basic idea of the present invention is: on the principle of reducing the area of the current loop generated when the solar wing is irradiated by sunlight to generate electricity in orbit, it provides a deployable satellite solar wing with a residual magnetism control design, and the establishment of a solar wing capable of Simulate the test simulation piece of the magnetic field state generated when it works in orbit, and design experiments to verify that the residual magnetism state generated by the deployed satellite solar wing designed with residual magnetism control meets the requirements when it works in orbit.
[0041] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
[0042] Deployable satellite solar wing designed with residual magnetism control:
[0043] Due to the limitation of the satellite configuration, an outrigger needs to be installed on the -Y side of the sate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com