Method for preparing novel phenolic amine resin demulsifier
A technology of phenalkamine resin and demulsifier, which is applied in the field of preparation of new phenalkamine resin demulsifier, can solve the problems of low molecular weight, unseen, few polyether branches, etc., and achieves low oil content and fast oil-water separation speed. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
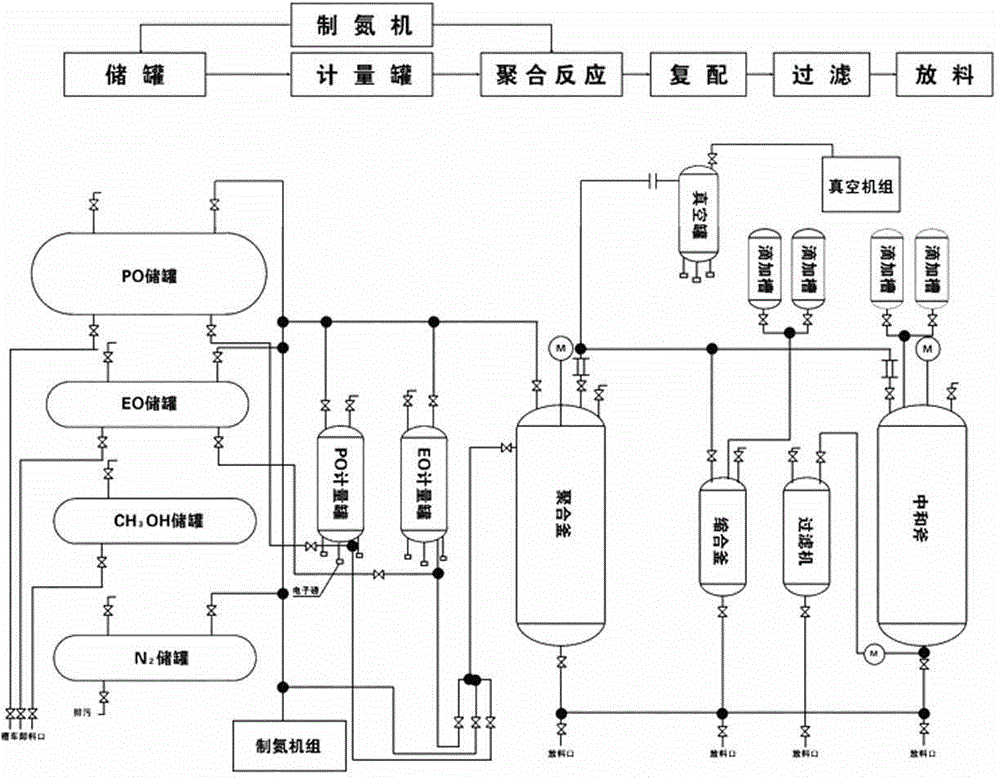
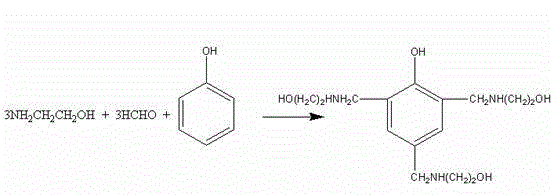
[0026] The first step is to synthesize phenalkamine resin
[0027] Put phenol and monoethanolamine into the reactor according to the claimed molar ratio 1:3, phenol is 188kg, monoethanolamine is 369.7kg, raise the temperature to 40℃~60℃, slowly add 486.5kg of formaldehyde solution (formaldehyde content is 37%) ), the temperature is controlled during the dripping process, and the temperature is kept at 50~60℃ to prevent local overheating due to violent reaction. After the addition, the temperature is raised to 90°C for aging for 1 hour, and the temperature is raised to 100°C to 160°C for vacuum dehydration. After the anhydrous is evaporated, the reaction is completed, cooled and discharged for later use.
[0028] The second step: phenolic amine resin polymerization of propylene oxide
[0029] Add the above 300kg phenalkamine resin and 6kg KOH catalyst into the polyether reactor, turn on the stirring, heat the material to 100℃~110℃, vacuum dehydration (about 20min), and close the vacu...
Embodiment 2
[0034] The first step is to synthesize phenalkamine resin
[0035] Put phenol and diethanolamine into the reactor according to the claimed molar ratio 1:3, phenol is 188kg, diethanolamine is 636.7kg, raise the temperature to 40℃~60℃, slowly drop 486.5kg of formaldehyde solution (formaldehyde content is 37% ), the temperature is controlled during the dripping process, and the temperature is kept at 50~60℃ to prevent local overheating due to violent reaction. After the addition, the temperature is raised to 90°C for aging for 1 hour, and the temperature is raised to 100°C to 160°C for vacuum dehydration. After the anhydrous is evaporated, the reaction is completed, cooled and discharged for use.
[0036] The second step: phenolic amine resin polymerization of propylene oxide
[0037] Add the above 250kg phenalkamine resin and 5.5kg KOH catalyst into the polyether reactor, turn on the stirring, heat the material to 100℃~110℃, vacuum dehydration (about 20min), close the vacuum valve whe...
Embodiment 3
[0042] The first step is to synthesize phenalkamine resin
[0043] Put phenol and triethanolamine into the reactor according to the claimed molar ratio of 1:3, phenol is 94kg, triethanolamine is 525.9kg, raise the temperature to 40℃~60℃, slowly drip 243kg formaldehyde solution (formaldehyde content is 37%) , The temperature is controlled during the dripping process, and the temperature is kept at 50~60℃ to prevent local overheating due to violent reaction. After the addition, the temperature is raised to 90°C for aging for 1 hour, and the temperature is raised to 100°C to 160°C for vacuum dehydration. After the anhydrous is evaporated, the reaction is completed, cooled and discharged for use.
[0044] The second step: phenolic amine resin polymerization of propylene oxide
[0045] Add the above 300kg phenalkamine resin and 6kg KOH catalyst into the polyether reactor, turn on the stirring, heat the material to 100℃~110℃, vacuum dehydration (about 20minh), and close the vacuum valve w...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| dehydration rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| dehydration rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| dehydration rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com