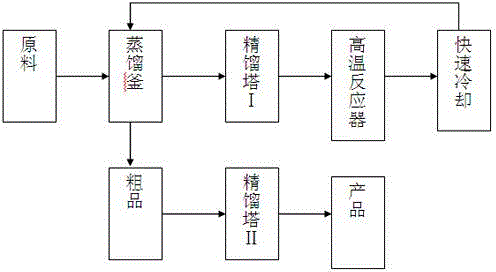
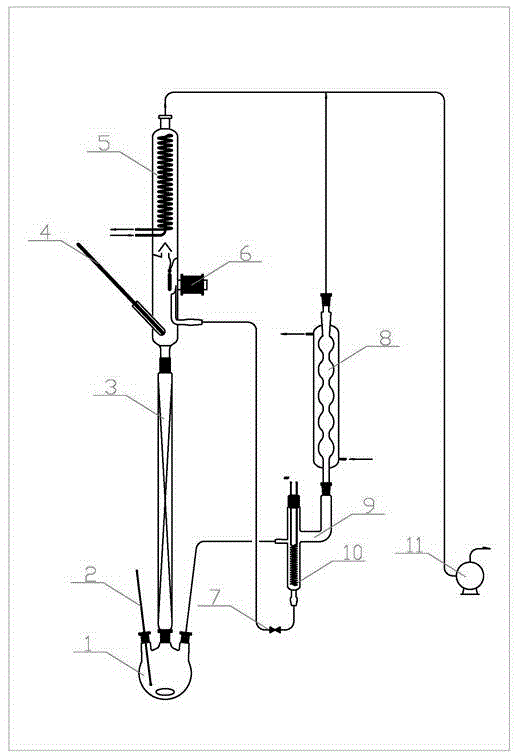
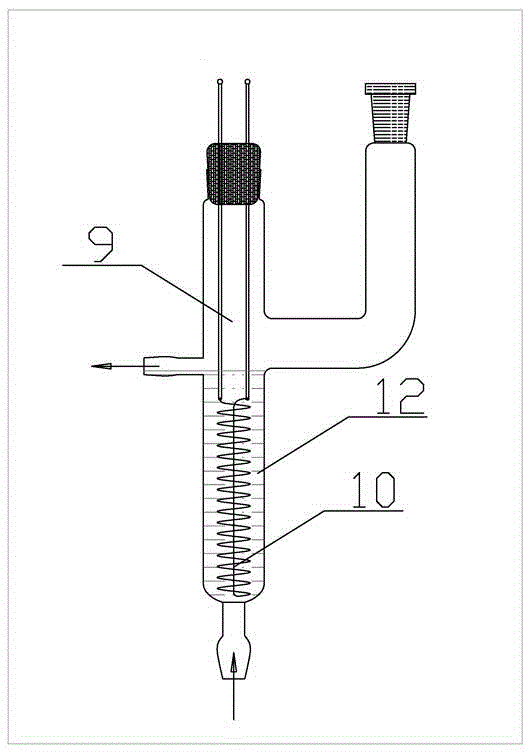
Method for preparing ocimene from thermo isomeric alpha-pinene in liquid phase
A technology for thermal isomerization and basilene, which is applied in the fields of isomerization to produce hydrocarbons, distillation purification/separation, etc., can solve the problems of poor basilene selectivity, high cost of instruments and equipment, harsh reaction conditions, etc., and achieves a small difference in boiling point. , The effect of low equipment cost and high selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Install the experimental setup, and then check the airtightness of the entire system. The air in the system was replaced with pure nitrogen. Inject 200ml of α-pinene into the reaction flask, add 0.80g of inhibitor BHT, and start magnetic stirring. Add pure α-pinene to the reaction chamber so that the cracking coil is submerged in the liquid, about 70ml. Turn on the vacuum pump to draw a vacuum, and turn on the condensate at the same time. After normalization, start heating the reaction flask with an oil bath. After the liquid boils, turn on the rectification tower to keep warm with voltage, and reflux for 1-2 hours. When the equilibrium is reached, the temperature at the top of the tower should be between 55-59°C. Adjust the ratio of the reflux flow rate to the production flow rate, that is, the reflux ratio is 1:1, so that α-pinene can be effectively separated. After the system runs smoothly (about 1-2h), the cracking reaction starts. The cracking voltage of the n...
Embodiment 2-5
[0031] The experimental operation method of Example 2-5 is the same as that of Example 1, except that the cracking voltage is different in Example 2-5, and the experimental results are shown in Table 2.
Embodiment 6-7
[0033] The experimental operation method of Embodiment 6-7 is the same as that of Embodiment 1, except that the liquid flow rate is different in Embodiment 6-7, and the experimental results are shown in Table 2.
[0034] Table 2 Experimental results of liquid phase cracking of α-pinene under different conditions.
[0035]
[0036] a. 1. α-pinene; 2. Dipentene; 3. Ocimene; 4. Allo-ocimene. The cycle time is 20h; Y represents the percentage content of each component in the cracked product (the peak of the corresponding peak in the gas chromatography Area); X represents the conversion rate of raw materials; S represents the selectivity of each component; b. Theoretical calculation value.
[0037] Examples 2-5 show that the thermal isomerization of α-pinene increases with the increase of reaction temperature, the conversion rate of α-pinene increases but the selectivity of ocimene decreases. From Examples 5-7, it can be concluded that with the increase of the liquid flow rate,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com