Method for quickly determining content of alpha-cellulose in dissolving pulp
A technology for rapid determination of cellulose content, applied in the measurement of color/spectral properties, etc., can solve the problems of no physical meaning and the limitations of a large number of original sample models, and achieve the effect of shortening the test time, simple technical means and simplifying the operation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Determination of α-cellulose content in eucalyptus and masson pine dissolving pulp
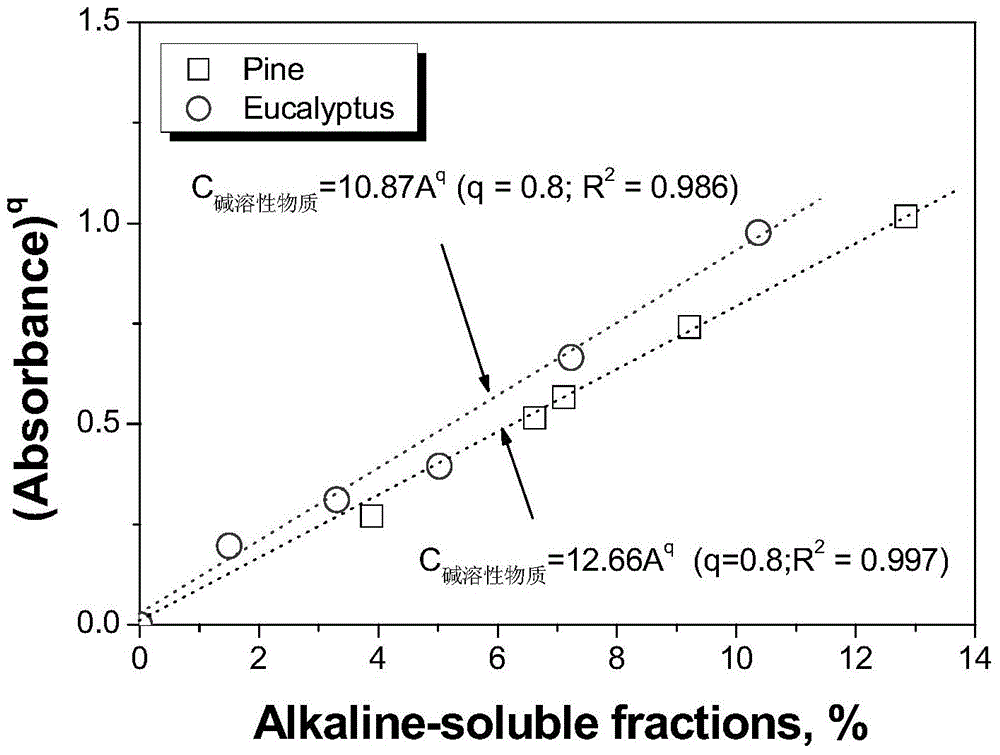
[0039] (1) Sample pretreatment: Accurately weigh a sample of eucalyptus or masson pine dissolving pulp equivalent to 2.50 g (accurate to 1 mg) of absolute dry weight in a beaker, and then add 25 mL of Sodium hydroxide solution, and then put the beaker in a constant temperature water bath, and use a flat glass rod to repeatedly immerse the sample for 2 to 3 minutes. Then add the remaining sodium hydroxide solution and stir it. Finally cover the beaker with a watch glass. It took 60 minutes from the first addition of sodium hydroxide to the end of the reaction. After the reaction was over, the beaker was taken out, and filtered with a washed and air-dried 30-mL 1G2 glass filter and a 250-mL suction filter flask, and the filtrate was collected in a glass bottle with a lid. The sample to be tested is dissolving pulp or pulp with negligible lignin content.
[0040] (2) Establish a standa...
Embodiment 2
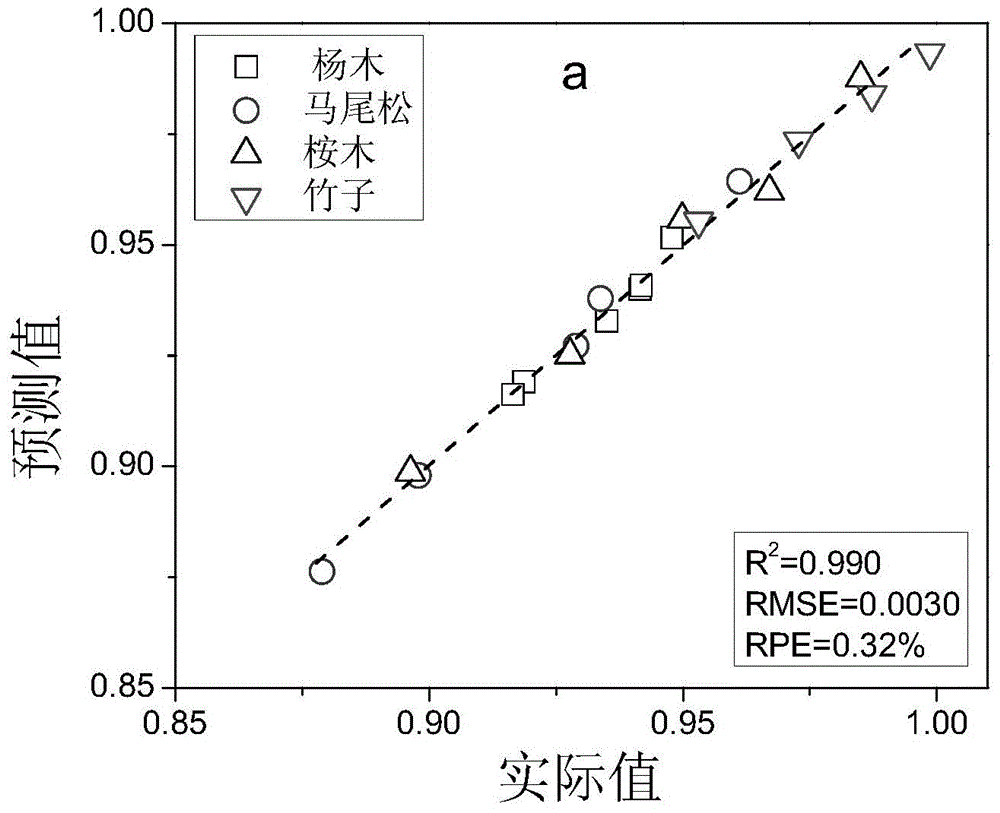
[0048] Determination of α-cellulose content in dissolving pulp of unknown species
[0049] (1) Sample pretreatment: Accurately weigh a sample of eucalyptus or masson pine dissolving pulp equivalent to 2.50 g (accurate to 1 mg) of absolute dry weight in a beaker, and then add 25 mL of Sodium hydroxide solution, and then put the beaker in a constant temperature water bath, and use a flat glass rod to repeatedly immerse the sample for 2 to 3 minutes. Then add the remaining sodium hydroxide solution and stir it. Finally cover the beaker with a watch glass. It took 60 minutes from the first addition of sodium hydroxide to the end of the reaction. After the reaction was over, the beaker was taken out, and filtered with a washed and air-dried 30-mL 1G2 glass filter and a 250-mL suction filter flask, and the filtrate was collected in a glass bottle with a lid. The sample to be tested is dissolving pulp or pulp with negligible lignin content.
[0050] (2) Establish a general model:...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com