Non-destructive readout ferroelectric memory and manufacturing method and operation method thereof
A non-destructive read-out, ferroelectric memory technology, applied in the preparation of ferroelectric memory, in the field of ferroelectric memory, can solve the problems of reduced device reliability, low storage density, and reduced ferroelectric capacitor C ratio, and achieves a beneficial effect. Small size, simple preparation, low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0057] The following introduces some of the possible embodiments of the present invention, which are intended to provide a basic understanding of the present invention, but are not intended to identify key or decisive elements of the present invention or limit the scope of protection.
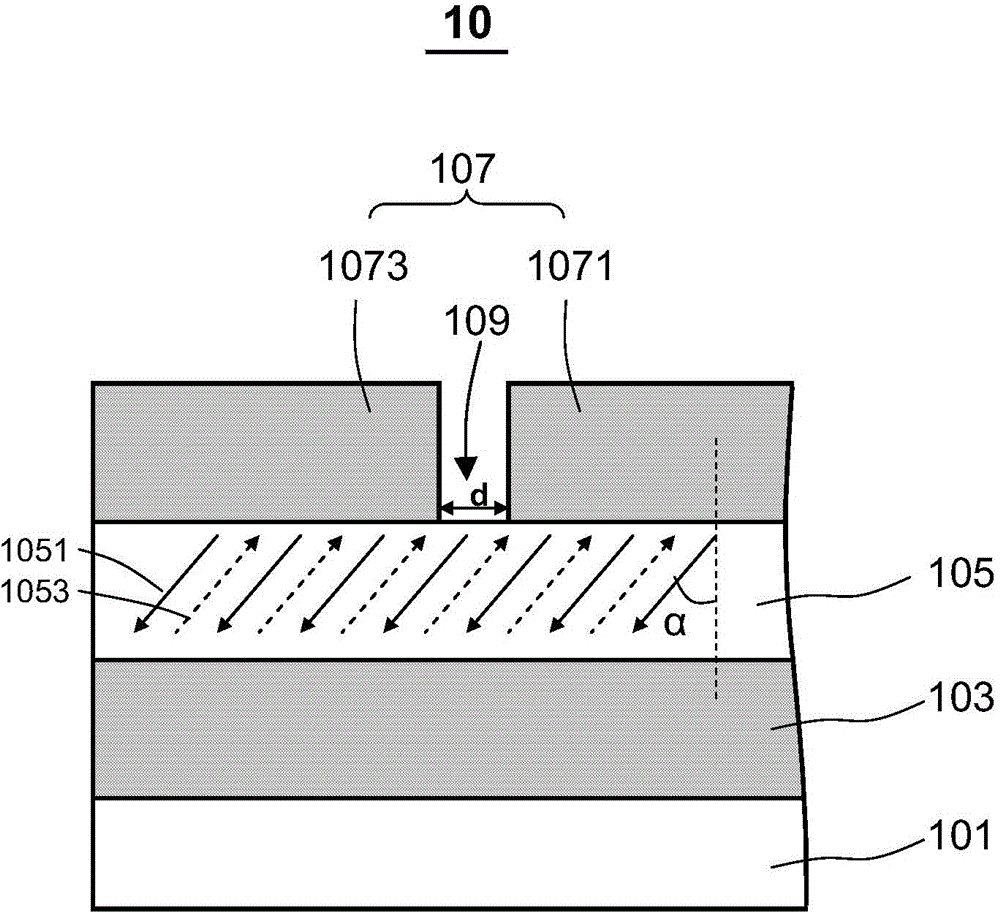
[0058] In the drawings, for the sake of clarity, the thicknesses of layers and regions are exaggerated, and the dimensional proportional relationship among the various parts in the illustration does not reflect the actual dimensional proportional relationship.
[0059] In the following embodiments, for clarity of description, the domain direction or polarization direction is exemplarily given, but it should be understood that the domain direction or polarization direction of the ferroelectric memory is not limited to the embodiment shown in the figure. out direction.
[0060] figure 1 Shown is a schematic cross-sectional structure diagram of a non-destructive readout ferroelectric memory accor...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com