A quantitative detection method for living bacteria based on fish technology
A quantitative detection method and live bacteria technology, applied in the field of microbial detection, can solve the problems of heavy workload, time-consuming, inability to apply culture method detection, etc., and achieve a strong universal effect
Active Publication Date: 2016-10-26
FUZHOU UNIV
View PDF0 Cites 1 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
[0002] The culture method is currently the most widely used specific detection method for active microorganisms, but the culture method has obvious disadvantages: on the one hand, the method takes a long time, the workload is heavy, and the detection results have a large lag; on the other hand, for feces Bacteria that are not cultivable or in a viable non-culturable state (Viable but Non-culturable, VBNC) in the sample cannot be detected by culture methods
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment Construction
[0030] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with specific examples, but the present invention is not limited thereto.
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
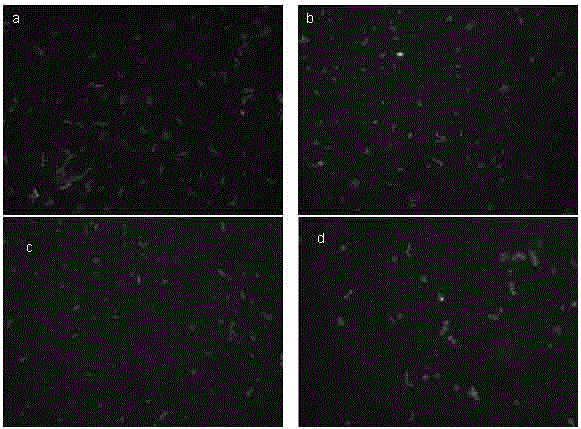
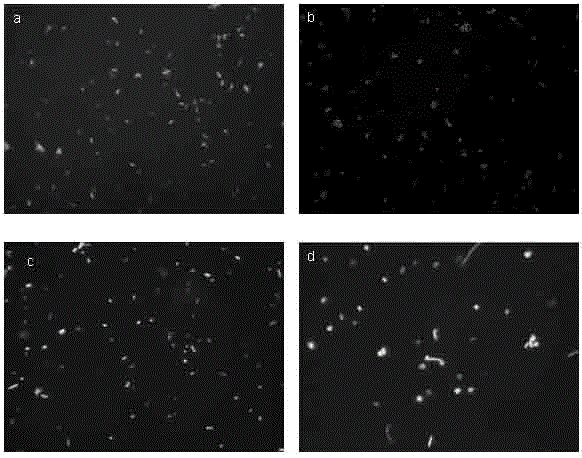
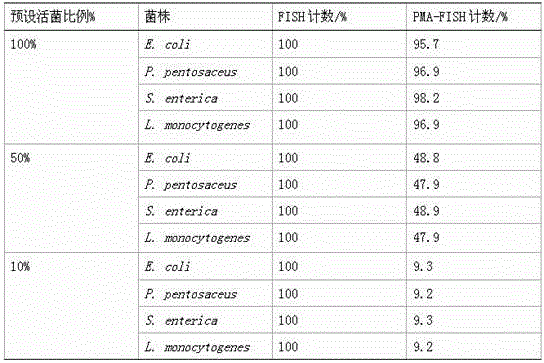
The invention belongs to the field of microorganism detection and relates to a method for quantitative detection of living bacteria based on FISH technology. Before the implementation of the conventional fluorescence in situ hybridization method, the method adds the pretreatment step of PMA nucleic acid dye; during the PMA treatment process, the nucleic acid in the dead bacteria cells is covalently combined with PMA, and it emits orange under the blue light excitation of the fluorescence microscope Fluorescence, so that it can be known that the bacteria with orange fluorescence are dead bacteria in the original system, and the rRNA in the living bacteria cells is combined with the fluorescent probe in the hybridization step, and the fluorescent probe emits green fluorescence under the blue light excitation of the fluorescence microscope, so that the green fluorescence can be known Bacteria are living bacteria in the original system. The invention realizes the effective distinction of dead and alive bacteria in the sample system by improving the fluorescence in situ hybridization technology, that is, adding the step of PMA dye treatment, and constructs a set of methods that can quickly quantify the active bacteria in the sample. This method has strong universality for bacterial quantification.
Description
technical field [0001] The invention belongs to the field of microorganism detection and relates to a method for quantitative detection of living bacteria based on FISH technology. Background technique [0002] The culture method is currently the most widely used specific detection method for active microorganisms, but the culture method has obvious disadvantages: on the one hand, the method takes a long time, the workload is heavy, and the detection results have a large lag; on the other hand, for feces Bacteria that are not culturable or in a viable non-culturable state (Viable but Non-culturable, VBNC) in the sample cannot be detected by culture methods. [0003] Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) technology uses fluorescently labeled specific nucleic acid probes to hybridize with corresponding target DNA molecules or RNA molecules in cells, and observes fluorescent signals under a fluorescent microscope or confocal laser scanner to determine the specific probes th...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More Patent Type & Authority Patents(China)
IPC IPC(8): C12Q1/68C12Q1/06
CPCC12Q1/6841C12Q1/689C12Q2563/107C12Q2543/10
Inventor 倪莉陈智超刘志彬张雯
Owner FUZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com