Real-time three-dimensional reconstruction key frame determination method based on position and orientation changes
A real-time three-dimensional, pose change technology, applied in the field of robot and UAV visual autonomous navigation, can solve the problems of not considering the quality of key frame image and positioning quality, not considering the change of camera field of view, wasting system running time, etc., to achieve calculation The effect of low cost, high stability, and low error rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0040] Describe the present invention below in conjunction with specific embodiment:
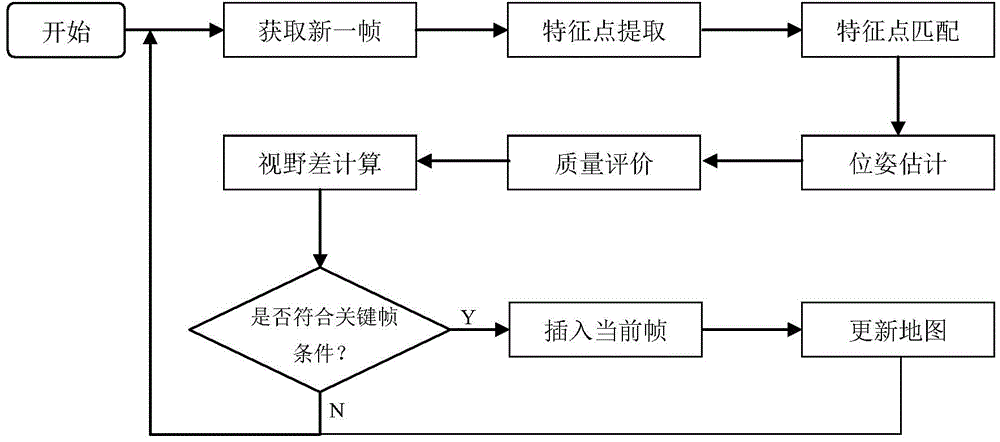
[0041] For the images captured by the camera in real time, the following four steps are required to determine whether it is selected as a key frame. The first step is originally included in the navigation application. The first two steps provide judgment data for the next two steps, and finally determine the current frame. Whether the frame is a keyframe.
[0042] The first step: current frame positioning. For robot autonomous navigation, only a small number of key frames are required for map creation, while the frequency of positioning is relatively high. For the image frame currently acquired by the camera, the current camera in the map can be obtained by matching the feature points with the existing map. pose information. The obtained pose information can be used for navigation on the one hand, and can also be used as the selection and judgment conditions of key frames. In this process...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com