A bimaterial hollow cannula for isolation of primary airway epithelial cells
An epithelial cell and dual-material technology, applied in the field of medical instruments, can solve the problems of loss of cilia directional swing in vivo physiological function, expensive respiratory epithelial cells, and difficult clamping of reentrant arterial clips. The effect of strong repeatability and easy promotion and application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1. The making of two-material bushing
[0029] (1) Take a GA-1073 silicone tube with 45-degree inclined ends and flat ends at both ends, with an inner diameter of 0.6mm and an outer diameter of 0.8mm;
[0030] (2) Take 25mm Teflon hollow tube with 20mm and both ends are flat ends, inner diameter 0.8mm, outer diameter 1.0mm,
[0031] (3) Apply 10 microliters of Wenjin Chaoneng 380 silicone glue to the flat end of the GA-1073 silicone tube, insert it into the Teflon hollow tube, insert 5mm and fix it for 15 seconds to obtain the dual-material sleeve.
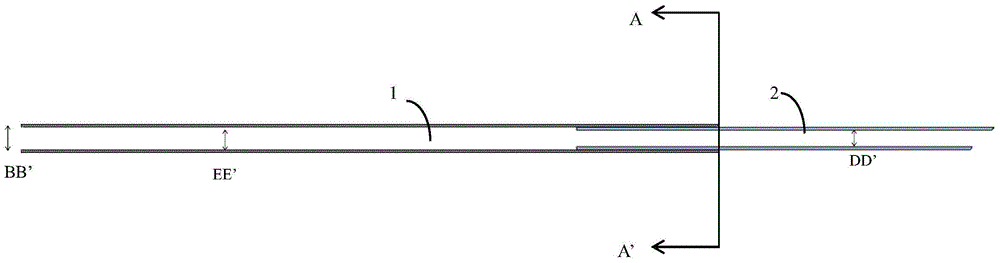
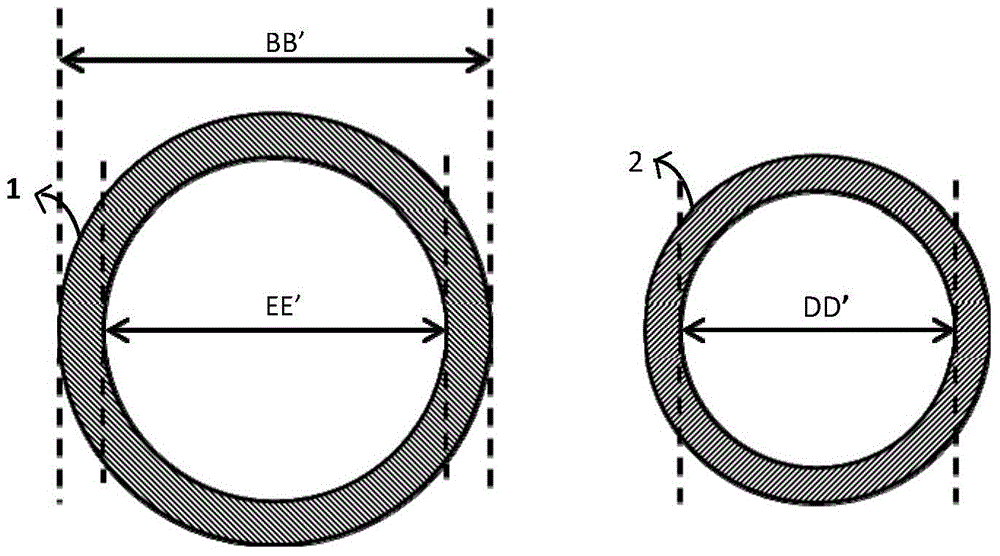
[0032] figure 1 Shown is a perspective view of the dual-material hollow sleeve of the present invention (taking the special dual-material hollow sleeve for mice as an example), wherein
[0033] 1 is Teflon hollow tube, length: 25mm
[0034] 2 is GA-1073 silicone tube, length: 20mm
[0035] BB' is Teflon hollow tube outer diameter: 1.0mm
[0036] CC' is a GA-1073 silicone tube inserted into a Teflon hollow tu...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2. Isolation of mouse trachea
[0040] (1) BALB / c mice were sacrificed by neck dislocation, their heads were tilted up, and their chest and abdomen were soaked in alcohol for 30 seconds for disinfection, taking care to protect the oral cavity and nasal passages from alcohol stimulation. Fix it on the operating table, cut the skin along the linea alba under aseptic conditions, expose the abdominal aorta, incise and let the blood flow out, the purpose is to avoid mixing too many red blood cells when separating the respiratory epithelial cells;
[0041] (2) Bluntly dissect the trachea, expose the trachea, and fully dissociate it;
[0042] (3) Wear the double-strand No. 1 surgical thread 100mm, cut a small gap 5mm below the cricoid cartilage of the trachea, insert the 45-degree oblique end of the dual-material sleeve GA-1073 silicone tube, insert half of the trachea to a depth of about 5mm, and use No. 1 surgical thread Tie a tight knot on the outside of the trache...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3. Digestion of Tracheal Tissue and Removal of Red Blood Cells
[0046] (1) Inject a little 0.05% pronase pre-cooled at 4°C into the trachea fixed at the tip of the cannula through the dual-material cannula, and wash the inner wall of the trachea to remove the washed PBS;
[0047] (2) Fill the entire trachea with 0.05% pronase, so that the trachea expands slightly like a balloon, and clamp the part of the Teflon hollow tube folded in half with a 30mm arterial clamp to seal the entire trachea-cannula combination;
[0048] (3) Fix and infiltrate the entire trachea in MEM added with penicillin, and digest for 8 hours;
[0049] (4) Cut off the lower trachea, collect the digestive juice, and use a 1ml syringe to draw PBS to flush the trachea;
[0050] (5) Collect about 1.5ml of washing liquid (collecting liquid + PBS washing trachea liquid), transfer it to an EP tube after merging, and centrifuge at 500X g for 4 minutes to remove the supernatant;
[0051] (6) Add 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com