A Genome-Wide SNP Locus Analysis Method Combining Random Forest and Relief‑F
A random forest and whole genome technology, applied in the field of data processing, can solve the problems of difficult identification of rare SNP loci and unsatisfactory effect of single locus identification, and achieve the effect of reducing dimension
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0037] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. It should be noted that this embodiment is based on the technical solution and provides detailed implementation steps and specific operation methods, but the present invention is not limited to this embodiment.
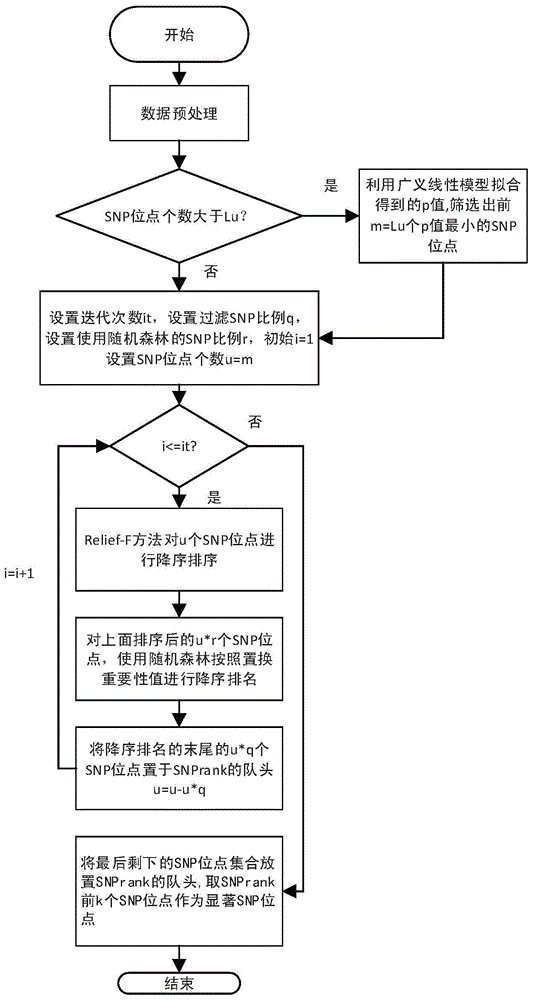
[0038] refer to figure 1 , the specific implementation steps of the present invention are as follows.
[0039] Step 1, preprocessing the SNP data:
[0040] If the sample data is in the base pair form of AA, encode each SNP site into the number of the smallest allele; if the smallest allele is a, then according to the number of occurrences of the smallest allele , and the genotypes AA, Aa, and aa are coded as 0, 1, and 2, respectively. Remove the SNP sites whose minimum allele frequency is less than the set value. The set value was set at 0.05. The purpose of removing the SNP sites whose minimum allele frequency is less than the set value is to filter out the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com