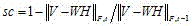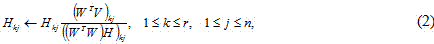Gene selection and cancer classification methods based on Monte Carlo and nonnegative matrix factorization
A factorization, non-negative matrix technology, applied in the field of stoichiometry, which can solve the problems of missing a lot of information and losing important information of the original gene data.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0014] The present invention will be described in detail below in combination with specific embodiments.
[0015] The non-negative matrix factorization method combines multivariate m x n data V decomposed into two non-negative W data and H data, namely:
[0016]
[0017] (1) In the formula, the rank of the matrix r is less than or equal to m with n The positive integer of is generally taken as a matrix V rank. H Take it as the basis matrix, then W is the coefficient matrix. The principle of multiplication is as follows:
[0018]
[0019]
[0020] When the above iterative process continues, the distance keeps decreasing, Represents the Frobenius norm (F-norm). The iterative process continues until certain convergence criteria are met, e.g., the distance There are only small changes before and after a certain iteration. After convergence is reached, the vectors in the basis matrix tend to be sparse. Important genes can be found through sparse basis m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com