A resistance gene and its encoded protein for degrading the herbicide glyphosate
A glyphosate and anti-glyphosate technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as undiscovered glyphosate degradation genes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
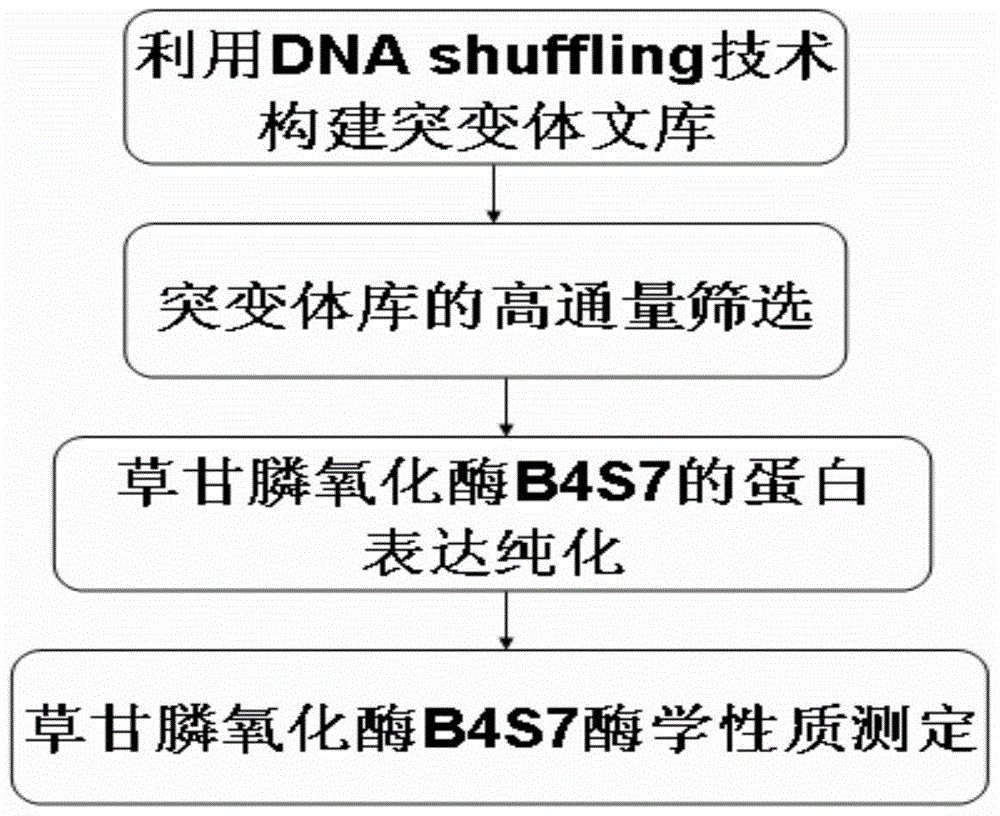
[0027] Example 1 Construction of mutant library using DNA shuffling technology
[0028] The present invention uses the mutants B3S1, B3S4, B3S6 and B3S7 from Bacillus cereus glycine oxidase (BceGO) as templates (Zhan et al.2013), referring to the DNA shuffling method reported by Stemmer and using ultrasonication to process DNA fragments, DNA shuffling (Stemmer 1994; Miller et al.2002), recombination of beneficial mutation sites to achieve further improvement of glycine oxidase from Bacillus cereus, so as to obtain glyphosate oxidase with better glyphosate degradation activity , lay a solid foundation for the application of glyphosate-resistant crops, and reduce the residual amount of glyphosate in plants, so that plants can reduce the threat to human health through the food chain while removing glyphosate's growth inhibition.
[0029] The specific steps are as follows:
[0030] (1) Amplification of the template gene
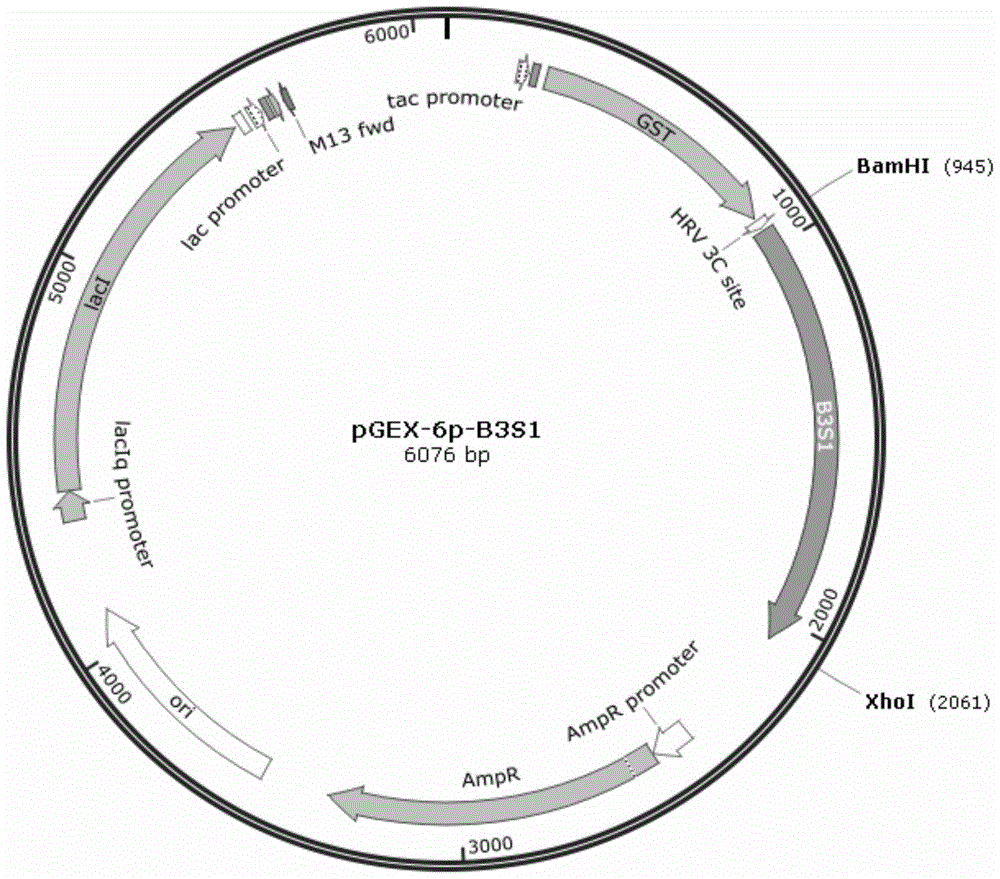
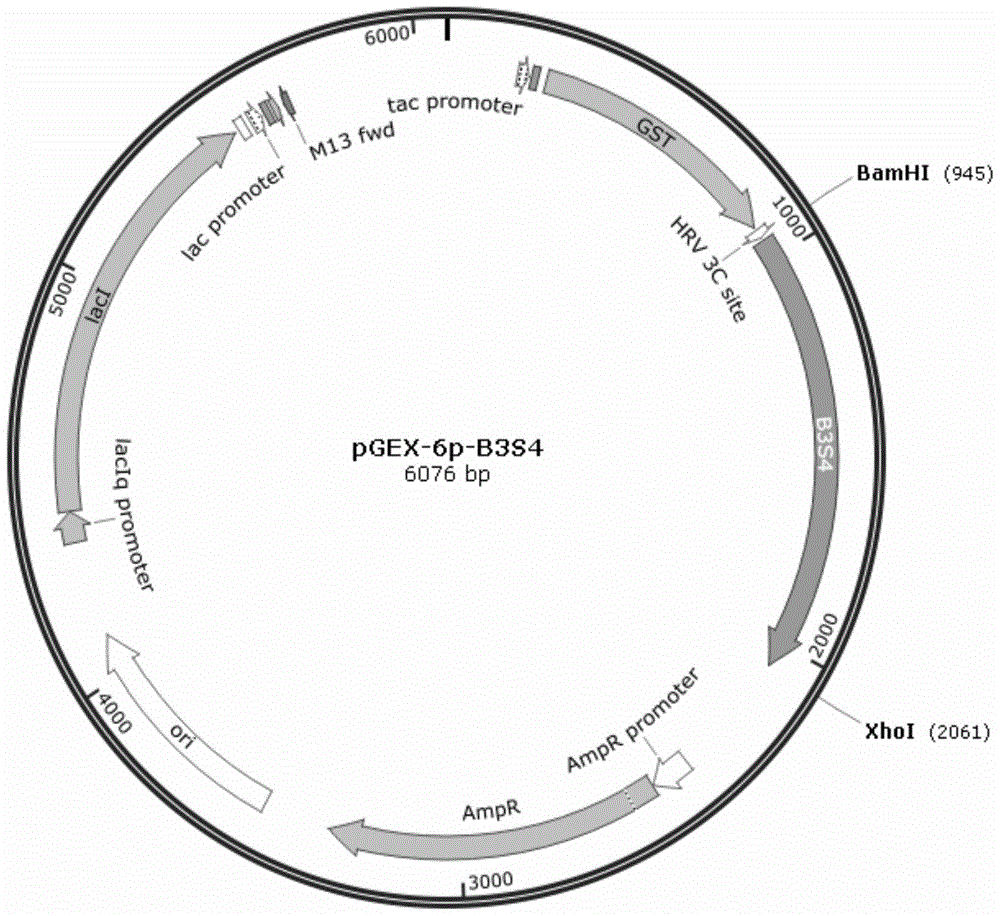
[0031] Extract pGEX-6p-B3S1 ( figure 2 ), pGEX-6p-B3S4 ...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2 Screening of mutants with high glyphosate oxidation activity (high-throughput screening based on 96-well plate)
[0056] This method refers to the screening method reported by (Zhan et al.2013). Inoculate the control bacteria (Escherichia coli DH5α containing the recombinant plasmid pGEX-6p-B3S1) and the clones in the mutant library into 96 deep wells containing 600 μL of liquid LB medium (adding ampicillin to a concentration of 100 μg / ml) At the same time, the bacteria in each well were backed up on the ampicillin-resistant plate. Seal the 96-deep-well plate, shake and culture at 200 rpm at 37°C for 16 hours, add 200 μL of LB liquid medium containing ampicillin (100 μg / ml), IPTG (final concentration 0.1 mM) and T7 phage (Tarahovsky et al.1994) to each well , 28 ℃ 200rpm shaking culture for 6h to induce protein expression and be lysed by phage to release. Pipette 159 μL of crude enzyme solution (lysed supernatant, containing target protein) into a 96-microwe...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Example 3 Protein expression and purification of mutant B4S7
[0058] The recombinant plasmid pGEX-6p-B4S7 ( Figure 7 ) mixed with E.coli BL21(DE3) competent cells, transformed by electric shock, spread on an ampicillin-resistant plate (ampicillin concentration 100 μg / mL), and cultured overnight at 37°C until a single colony visible to the naked eye grew out. Pick a single clone and inoculate it into 20 mL liquid LB medium (containing 100 μg / mL ampicillin), and culture overnight at 37°C with shaking at 200 rpm. Transfer 1% of the bacterial solution to 2L of fresh liquid LB medium (containing 100 μg / mL ampicillin), shake culture at 200 rpm at 37 °C until the OD600 is 0.6, add the inducer IPTG with a final concentration of 0.1 mM, and induce at 160 rpm at 22 °C Cultured for 12h to express the protein. The cells were collected by centrifugation, washed twice with 50 mM sodium pyrophosphate buffer (pH 7.0), and then resuspended in 40 mL of pre-cooled 50 mM sodium pyropho...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| catalytic efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com