A molecular genetic identification method for channel catfish and longfin catfish
A technology for longfin catfish and channel catfish, applied in the field of genetics, can solve problems such as unguaranteed quality, mixed channel catfish and longfin catfish, and no literature reports on microsatellite repetition regularity, etc., to achieve high and stable repetition rate good sex effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] 1. Primer design
[0023] Design a pair of specific PCR amplification primers, the primer sequence is: upstream primer SEQIDNO.1: 5'-ACGGTGTTCCTGTTACTGC-3', downstream primer SEQIDNO.2: 5'-CACCAGATGTTGCTATGC-3'.
[0024] 2. Sample collection
[0025] Thirty channel catfish and 30 longfin catfish were collected.
[0026] 3. Genomic DNA extraction
[0027] Take about 20 mg of caudal fin tissue from each fish, blot the surface moisture with filter paper, put it into a 1.5 ml centrifuge tube, and add 420 μL STE buffer (30 mmol / LTris-HCl, pH8.0, 200 mmol / LEDTA, 50 mmol / L NaCl). After mixing, add 80 μL of 10% SDS and 10 μL of 20 mg / mL proteinase K, digest at 56°C for 8-10 hours; add an equal volume of phenol: chloroform: isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1) to extract twice, and centrifuge at 12000r After 10 minutes, take the supernatant; add an equal volume of chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1) to extract once, centrifuge at 12000r for 10min, take the supernatant; add an equal volume...
Embodiment 2
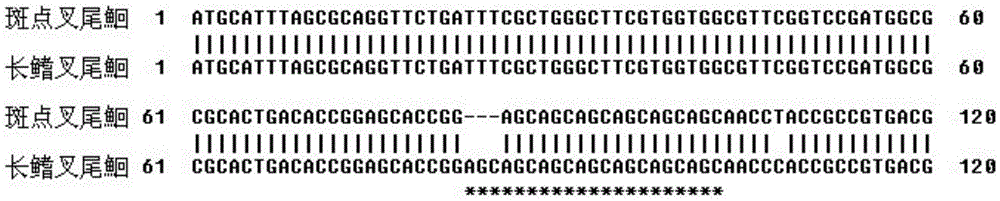
[0034] According to the method in Example 1, the sample was expanded to 100 individual channel catfish and longfin catfish, and the results still showed that the number of (AGC) microsatellite repeats of channel catfish from the 83rd site (MSTN-83) was six times, and the length The number of (AGC) microsatellite repeats from the 83rd locus (MSTN-83) in the fin catfish was seven.
[0035]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com