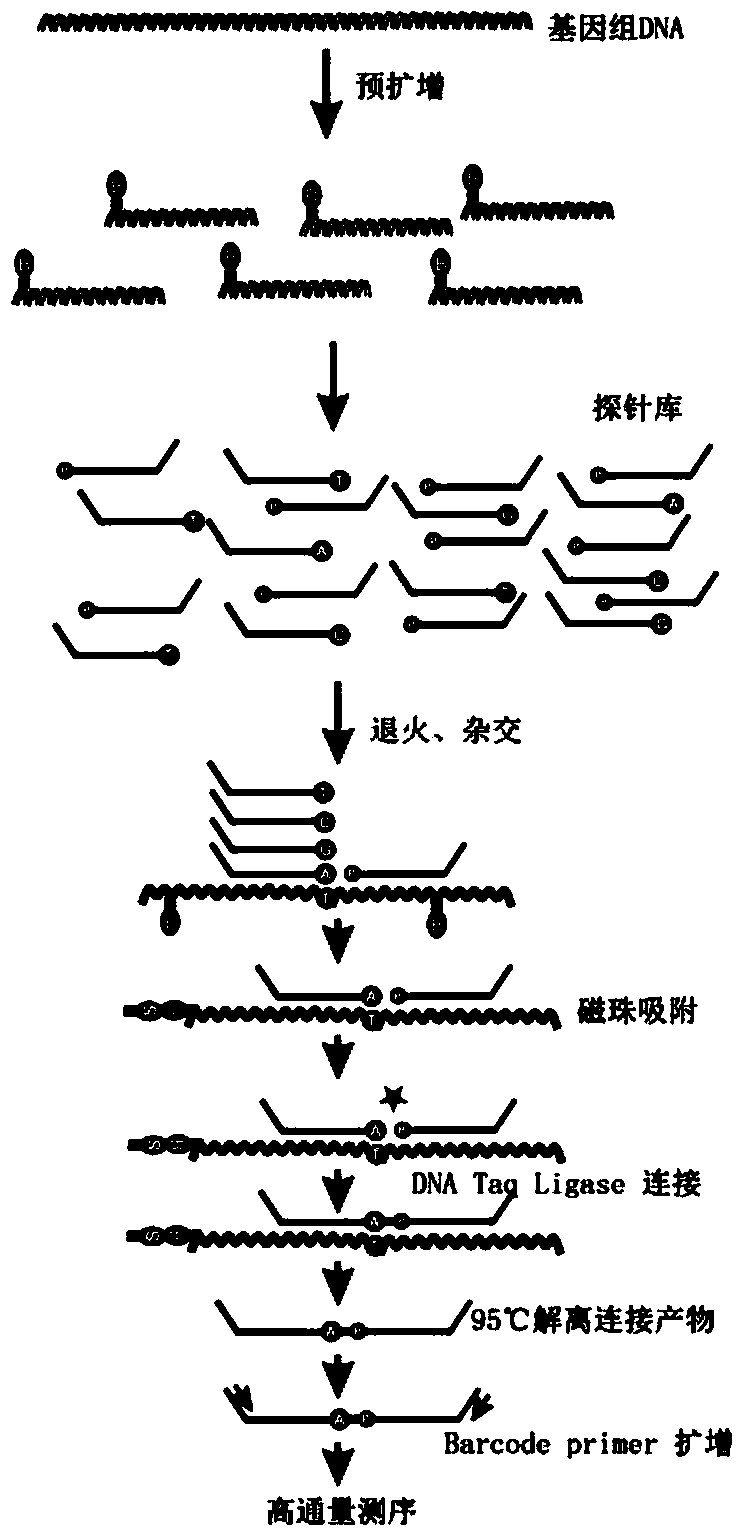
SNP (single-nucleotide polymorphism) detection method based on high-flux sequencing
A technology for sequencing and detecting probes, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbiological measurement/inspection, etc. It can solve the problems of nucleic acid sample sequencing with unfavorable concentration, library construction quality, hybridization efficiency, waste of sequencing space, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
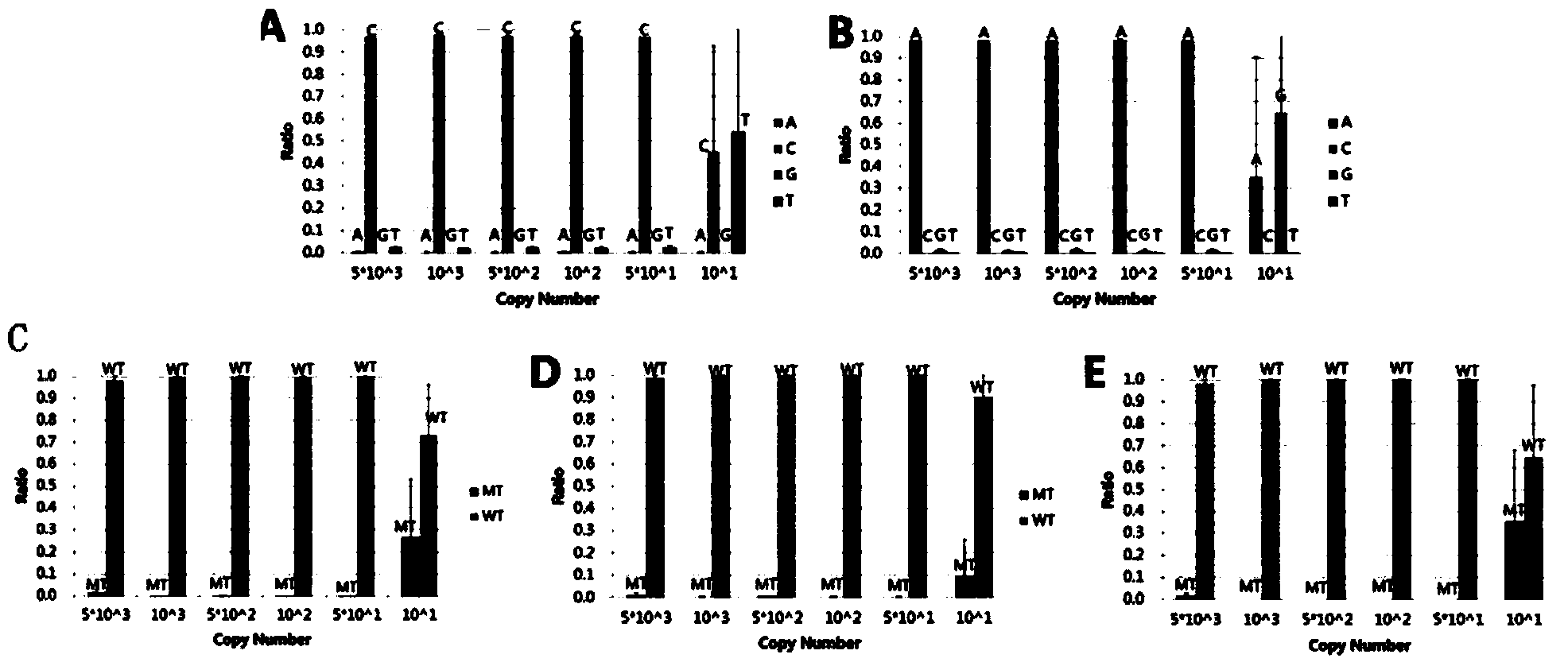
[0106] Example 1. SNP detection based on high-throughput sequencing technology mixed plasmid samples of 5 deafness-related mutation sites
[0107] This example detects all deafness sites. All the plasmids related to deafness sites were constructed by Boao Biological Group Co., Ltd. All plasmids have been sequenced to verify that their sequences are correct. The relevant plasmid sequence information is shown in Table 1. The mutation types include SNP mutation or Deletion / Insertion Mutations:
[0108] Table 1 shows the sequence information of plasmids related to deafness sites
[0109]
[0110] Note: WT means this site is wild type, del means deletion mutation, > means SNP mutation.
[0111] Plasmid pGEMT-299WT was obtained by using primers XPMS0299F / XPMS0299R to amplify the fragment 299WT containing 235, 176, and 299 sites using human genomic DNA as a template, and then cloned into pGEMT-easy vector.
[0112] The 235, 176, and 299 positions in the fragment 299WT sequence w...
Embodiment 2
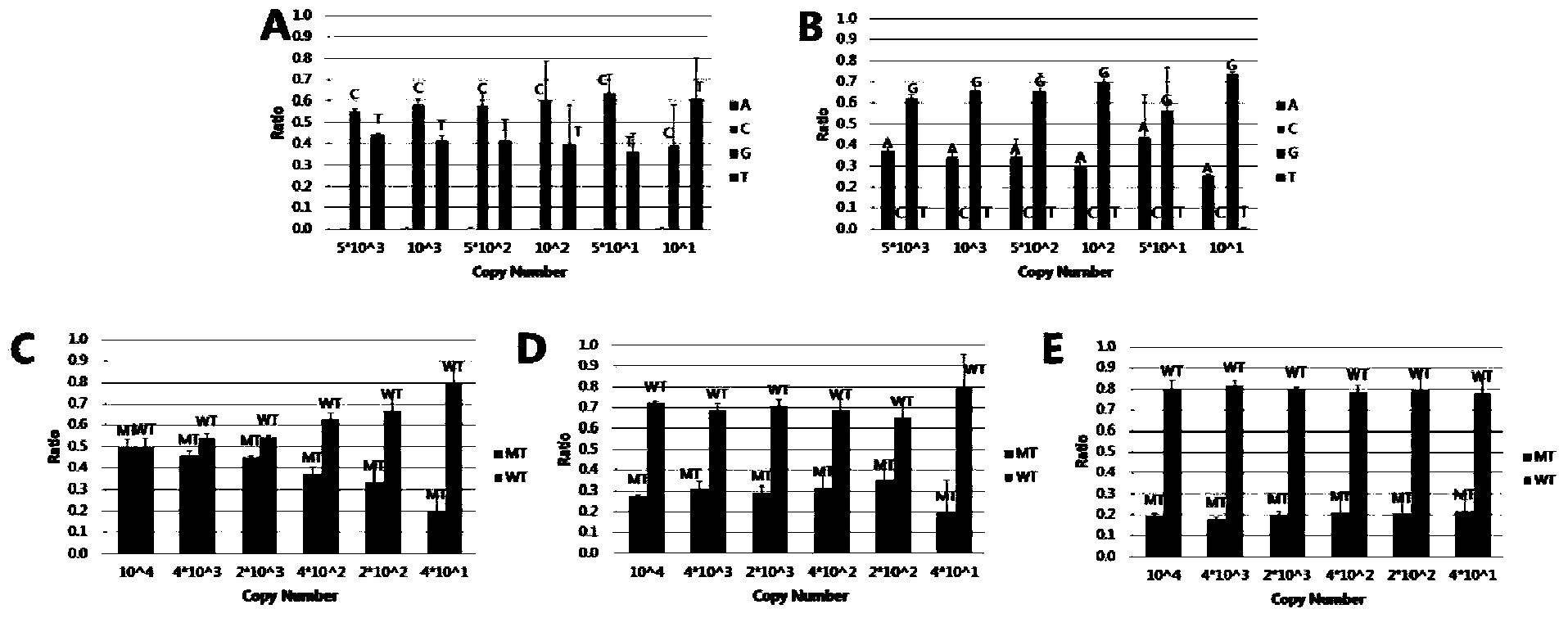
[0183] Embodiment 2, SNP detection human genome DNA sample based on high-throughput sequencing technology
[0184] 1. Design of probes and preamplification primers
[0185] 1. Preparation of samples to be tested
[0186] Blood genomic DNA of deaf patients (235 purified mutant genomic DNA has been verified) and normal human blood genomic DNA (wild-type genomic DNA), each sample is set to repeat 3 times, and the concentration of nucleic acid used is 10n g / uL.
[0187] 2. Design of probes and preamplification primers
[0188] 1) Probe design
[0189] The design principle is the same as in Example 1, and the probes are as follows in Table 5:
[0190] Table 5 is the probe
[0191]
[0192] 2), the design of pre-amplification primers
[0193] The design principles are the same as in Example 1, and the primers are GJB234F1 / GJB234R1-B.
[0194] Two, preamplification: same as embodiment 1;
[0195] Three, hybridization: same as embodiment 1;
[0196] Four, connection: same...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com