Miniature anti-explosion protection element and manufacturing method thereof
A protection component and miniature technology, which is applied in electrical components, fuse manufacturing, emergency protection devices, etc., can solve the problems of low breaking capacity and poor anti-surge capacity, etc., to improve breaking capacity, improve anti-surge capacity, and improve breaking Characteristics and Effects of Surge Resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
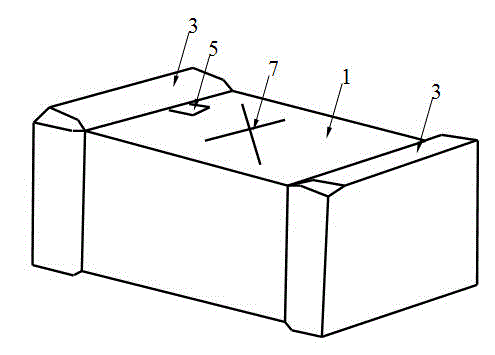
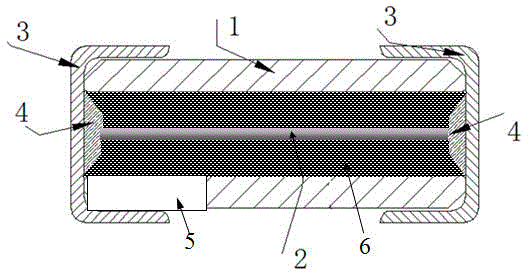
[0050] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, an explosion-proof miniature protection element of the present invention includes an insulating shell 1 , a metal melt 2 , an end electrode 3 , solder 4 , a notch 5 , an arc-extinguishing material 6 and a character mark 7 . In this example, the size of the explosion-proof miniature protection element is 6.1mm*2.5mm*2.5mm (length*width*height). Two ends of the insulating case 1 are respectively fixed with an end electrode 3 , and the fixing method is that the end electrode 3 is wrapped on the end of the insulating case 1 . The metal melt 2 is suspended in the interior of the insulating shell 1, preferably at the center of the insulating shell 1, and the two ends of the metal melt 2 are respectively fixed on the end electrodes 3 on both ends of the insulating shell 1 by solder 4 , and form an electrical connection with the terminal electrode 3 . The arc extinguishing material 6 is fully filled between the insulating casing 1 and...
Embodiment 2
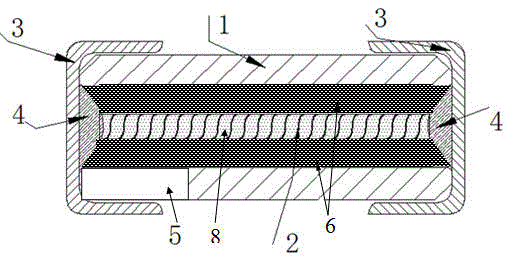
[0053] Such as image 3 As shown, the difference between Embodiment 2 and Embodiment 1 of an explosion-proof miniature protection element of the present invention is that the metal melt 2 is a wire material, and the metal melt 2 is first wound on a glass fiber wire 8 to form a winding Wire structure, and then the winding wire is suspended through the interior of the insulating shell 1, and the two ends of the winding wire are respectively fixed on the two end electrodes 3 provided on the insulating shell 1 by solder 4 to form an electrical connection. The metal melt 2 can also be a metal sheet. The parts of embodiment 2 that are the same as those of embodiment 1 will not be described in detail here.
Embodiment 3
[0055] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the difference between Embodiment 3 and Embodiment 1 of an explosion-proof miniature protection element of the present invention is that a notch 5 is respectively provided at the two ends of the same side of the insulating shell 1, and the size of the notch 5 is 1.8 mm*0.3mm (length*width), that is, the length of the notch 5 accounts for 29.5% of the length of the insulating shell 1, the width of the notch 5 accounts for 12% of the width of the side where the notch 5 is located, and the length of the exposed terminal electrode 3 is 0.4mm. That is, it accounts for 6.6% of the length of the insulating case 1 . The parts of embodiment 3 that are the same as those of embodiment 1 will not be described in detail here.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com