Micro-electromechanical reflector and method for manufacturing micro-electromechanical reflector
A reflector and micro-electromechanical technology, which is applied in the manufacture of micro-structure devices, processes for producing decorative surface effects, micro-structure technology, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in deriving heat from the substrate, restrictions on the freedom of movement of electrodes or micro-mirrors, etc. , to achieve a stable conductive connection surface and improve the effect of precision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
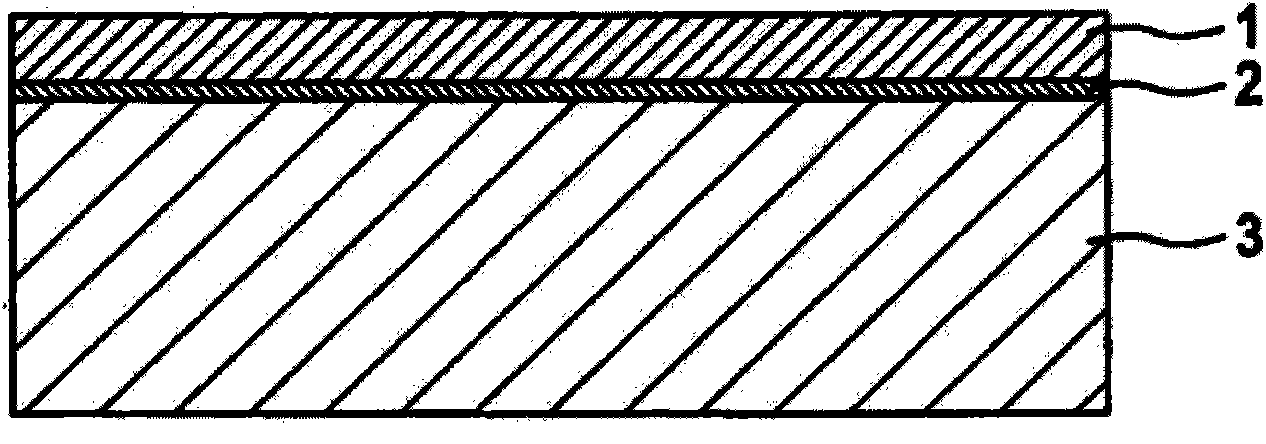
[0047] figure 1 A schematic diagram of a first intermediate product in the manufacture of a microelectromechanical reflector is shown in cross-section. In this case, the electrode substrate 3 can be provided with an oxide layer 2 which is applied to the surface of the electrode substrate 3 . A monocrystalline silicon layer 1 can then be applied on the oxide layer 2 . In one embodiment variant, the monocrystalline silicon layer 1 can be the first functional layer on a silicon-on-insulator wafer ("silicon an insulator: SOI wafer") as electrode substrate 3 .
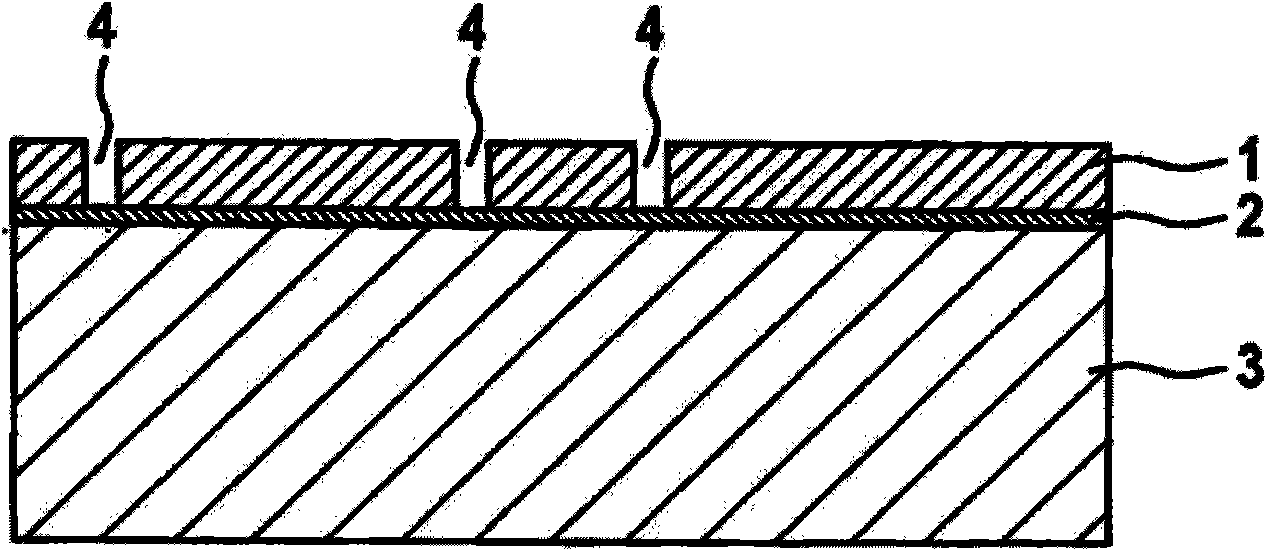
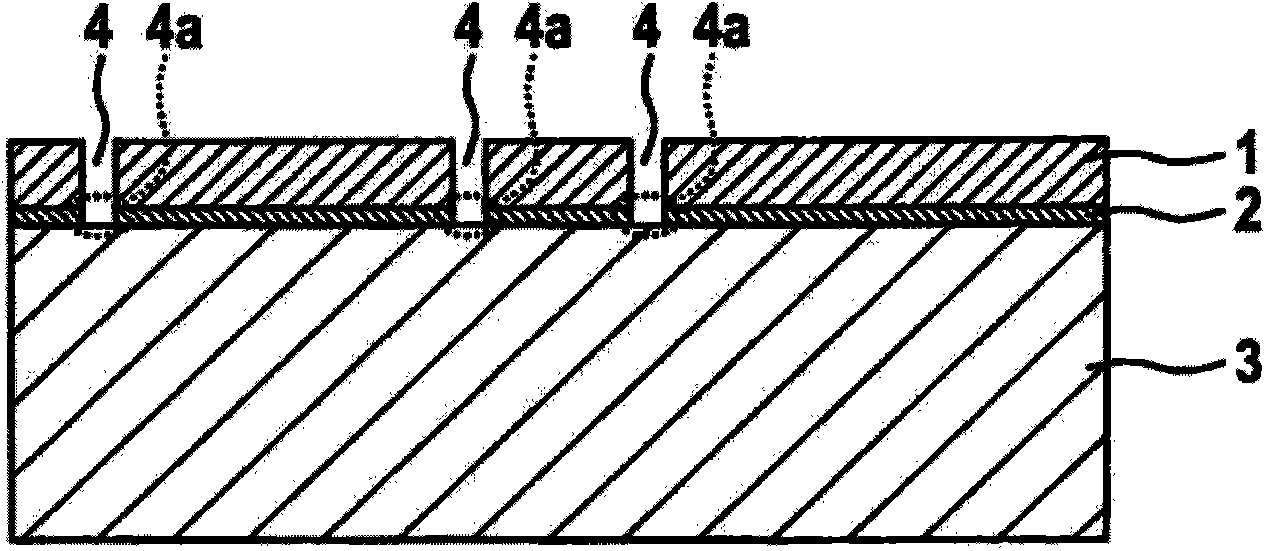
[0048] Such as figure 2 As shown, a via (Vias ("vertical interconnect access (vertical interconnect channel)") or a trench 4 can be provided in the monocrystalline silicon layer 1, which extends down to the oxide layer 2. As image 3 As shown, the oxide layer 2 is etched in the region of the via bottom or trench bottom 4 a, likewise up to the electrode substrate 3 .
[0049] Figure 4 Schematic showing one intermediat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com