Colored rigid decorative member
一种装饰构件、有色的技术,应用在服饰、层压装置、运输和包装等方向,能够解决涂膜不能直接使用、耐损伤性低、外观性降低等问题,达到抑制损伤和磨耗、耐损伤性提高、提高耐损伤性的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
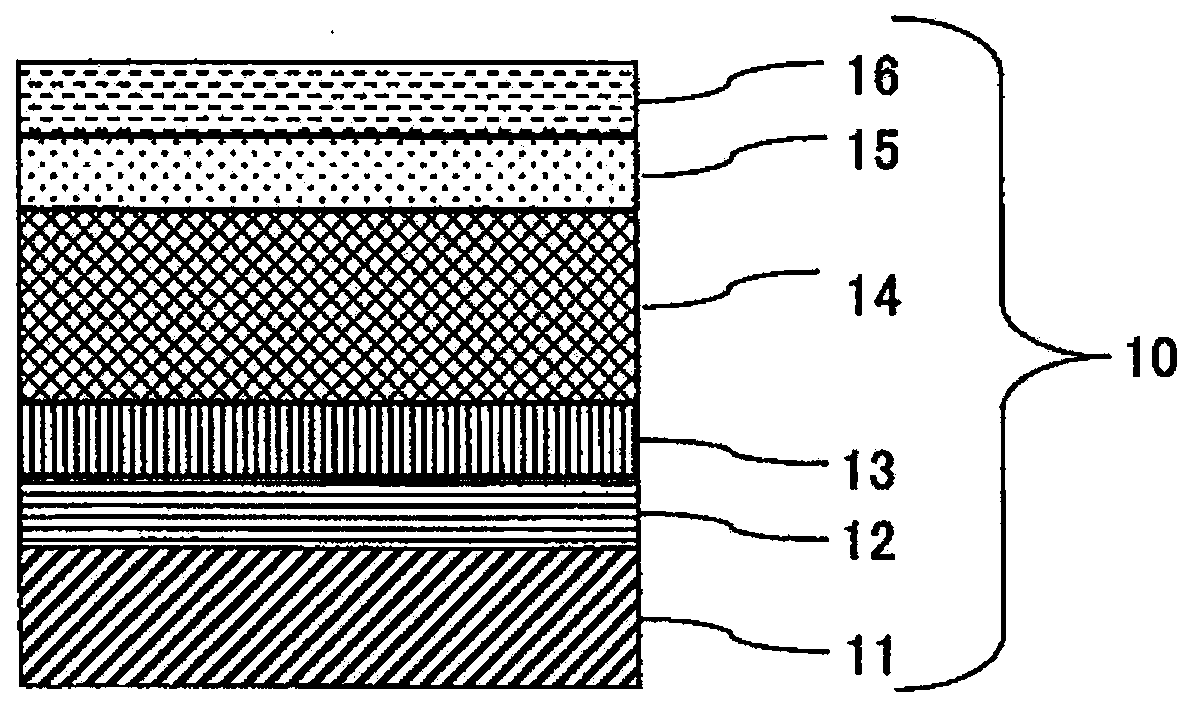
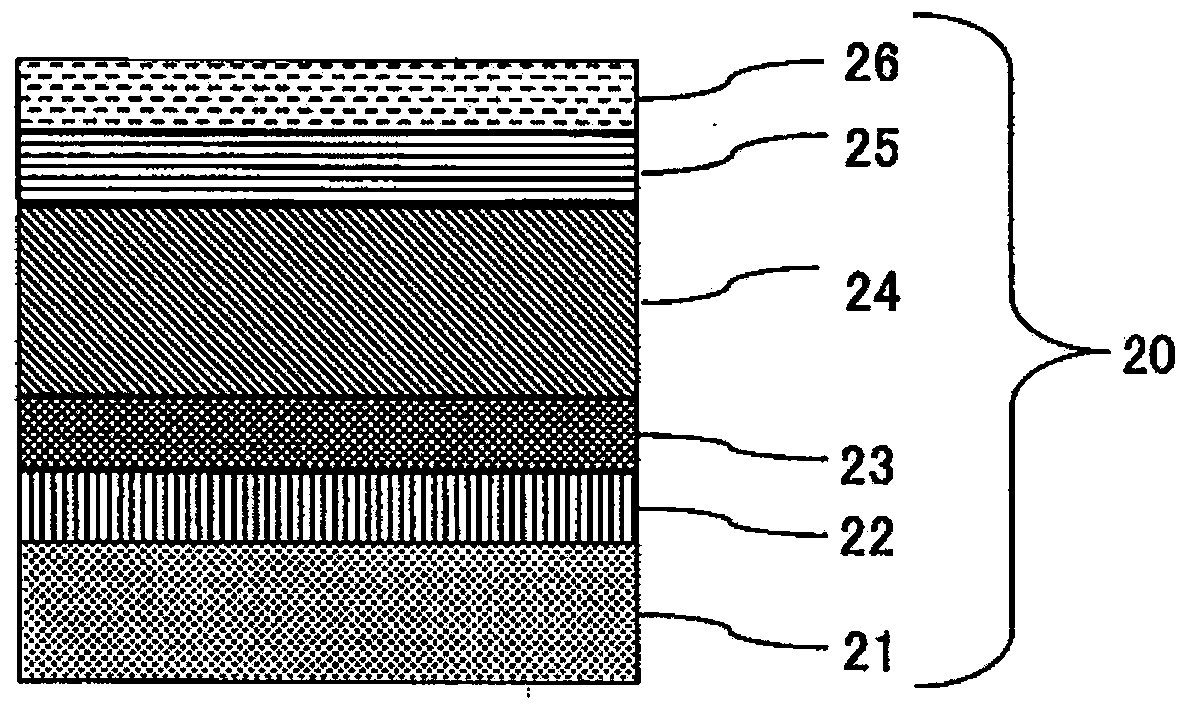
[0124] A sintered body of Mo45wt%, Nb55wt% and a metal Pt target were used as the sputtering target of Example 1. Such as figure 2As shown, a SUS316L material specified in JIS was used as the substrate 21, and an adhesion layer 22 made of a lower oxide of MoNb alloy was formed on the substrate 21 with a thickness of 0.1 μm by sputtering. Next, a gradient of methane was increased while introducing a trace amount of oxygen, thereby forming a gradient adhesive layer 23 of a 0.2 μm MoNb alloy oxycarbide film. After that, a 2.2 μm thin-film wear-resistant layer 24 composed of a MoNb alloy carbide film was formed. Furthermore, by reducing the gradient of methane, a color gradient layer 25 of 0.1 μm MoNb alloy carbide film was formed. After that, methane was stopped, and only argon gas was flowed in to form a 0.05 μm Pt film to fabricate the colored hard decorative member 20 .
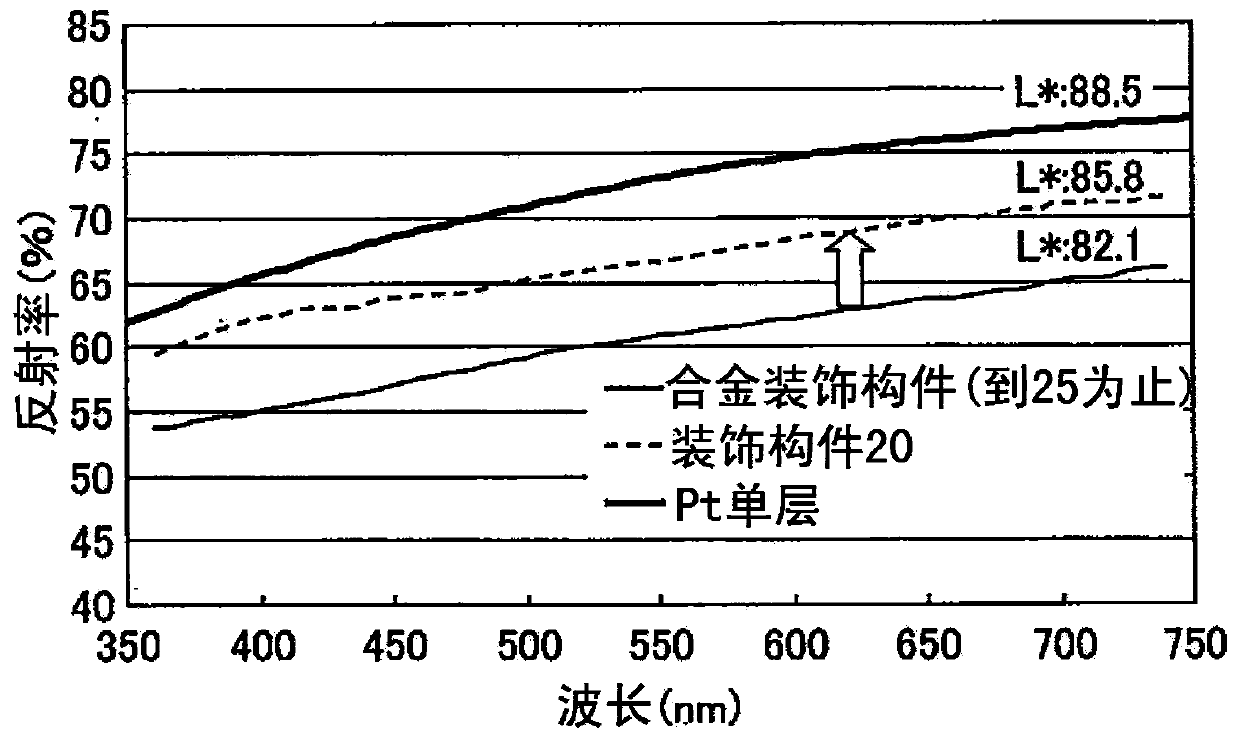
[0125] image 3 It is to compare the colored rigid decorative member 20 obtained in this Example 1 wi...
Embodiment 2
[0130] A sintered body with Mo30wt% and Ta70wt% and a metal Ti target were used as sputtering targets in Example 2. Such as Figure 8 As shown, a SUS316L material specified in JIS was used as the base material 31, and a 0.1 μm adhesion layer 32 composed of a lower oxide of MoTa alloy was formed on the base material 31 by sputtering. Next, a gradient of methane was increased while introducing a trace amount of oxygen, thereby forming a gradient adhesive layer 33 of a 0.2 μm MoTa alloy oxycarbide film. After that, a 2.0 μm thin-film wear-resistant layer 34 composed of a MoTa alloy carbide film was formed. Thereafter, by reducing the methane gradient, a color gradient layer 35 of 0.1 μm MoTa alloy carbide film was formed. Thereafter, the sputtering of the MoTa alloy was stopped, and the Ti target was discharged while introducing argon gas and nitrogen gas to form a 0.2 μm TiN film 36 to produce the colored hard decorative member 30 . The appearance color expressed by the Lab c...
Embodiment 3
[0134] A sintered body of Mo60wt%, Nb30wt%, Cr10wt%, and metal Ti and metal Si targets were used as sputtering targets in Example 3. Such as Figure 11 As shown, a SUS316L material specified in JIS was used as the base material 41 , and a 0.1 μm adhesion layer 42 composed of a lower oxide of MoNbCr alloy was formed on the base material 41 by a sputtering method. Next, a gradient of methane was increased while introducing a trace amount of oxygen, thereby forming a gradient adhesive layer 43 of a 0.2 μm MoNbCr alloy oxycarbide film. After that, a 2.2 μm thin-film wear-resistant layer 44 composed of a MoNbCr alloy carbide film was formed. Thereafter, by reducing the methane gradient, a color gradient layer 45 of 0.1 μm MoNbCr alloy carbide film was formed. Thereafter, the sputtering of the MoNbCr alloy was stopped, and the Ti target was discharged while introducing argon gas to form a 0.05 μm Ti film 46 , and then the sputtering of the Ti target was stopped, and a 0.1 μm Si fi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| coating thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| coating thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| coating thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com