Preparation method of hydrogenated rosin glyceride
A technology of rosin glyceride and hydrogenated rosin, which is applied in the field of deep processing of rosin, can solve the problems of increasing production cost, prolonging the process, and low product purity, and achieves the effects of reducing the generation of esterification reaction by-products, reducing production costs, and high purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
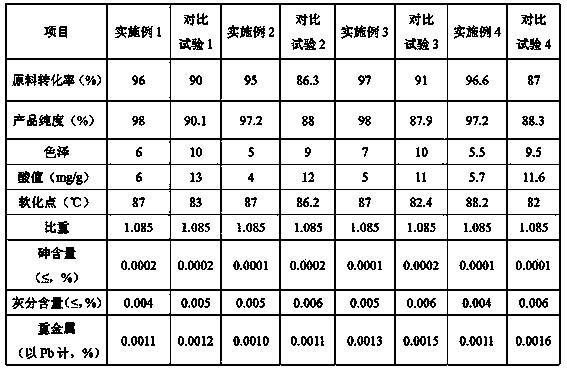
[0018] 100 grams of rosin and 0.05 grams of palladium-carbon catalyst were added to the hydrogenation reaction kettle successively, and then hydrogen was introduced. The hydrogen pressure in the kettle was controlled to be 3 MPa, and the reaction temperature was controlled to 220 ° C. The reaction was performed for 6 hours, and the palladium-carbon catalyst was filtered and removed to obtain 100 grams of hydrogenated rosin; then add 9.1 grams of glycerol and 0.03 grams of zinc oxide to 100 grams of hydrogenated rosin, control the reaction temperature to 280° C., and react for 4 hours to obtain hydrogenated rosin glyceride.
[0019] Comparative test 1: 100 grams of rosin was heated and dissolved, then 9.8 grams of glycerol and 0.03 grams of zinc oxide were added, the reaction temperature was controlled to 280°C, and the esterification reaction was carried out for 4 hours to obtain rosin glyceride.
Embodiment 2
[0021] 500 grams of rosin and 0.4 grams of palladium-carbon catalyst were successively added to the hydrogenation reaction kettle, and then hydrogen was introduced. The hydrogen pressure in the kettle was controlled to be 4 MPa, and the reaction temperature was controlled to 260 ° C. After 4.5 hours of reaction, the palladium-carbon catalyst was filtered and removed to obtain 500 grams of hydrogenated rosin; then add 68 grams of glycerol and 0.25 grams of zinc oxide to 500 grams of hydrogenated rosin, control the reaction temperature to 275° C., and react for 3 hours to obtain hydrogenated rosin glyceride.
[0022] Comparative test 2: 500 grams of rosin was heated to dissolve, then 68 grams of glycerol and 0.25 grams of zinc oxide were added, the reaction temperature was controlled to 275°C, and the esterification reaction was carried out for 3 hours to obtain rosin glyceride.
Embodiment 3
[0024] 1000 grams of rosin and 0.8 grams of palladium-carbon catalyst were successively added to the hydrogenation reaction kettle, and then hydrogen was introduced. The hydrogen pressure in the kettle was controlled to be 4.5 MPa, and the reaction temperature was controlled to 230 ° C. The reaction time was 4.5 hours, and the palladium-carbon catalyst was removed by filtration. , to obtain 1000 grams of hydrogenated rosin; then add 106 grams of glycerol and 0.7 grams of zinc oxide to the hydrogenated rosin, control the reaction temperature to 275 ° C, and react for 3 hours to obtain hydrogenated rosin glyceride.
[0025] Comparative test 3: 1000 grams of rosin was heated and dissolved, then 106 grams of glycerol and 0.7 grams of zinc oxide were added, the reaction temperature was controlled to 275°C, and the esterification reaction was carried out for 3 hours to obtain rosin glycerol ester.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com