Human-derived bacteria that induce proliferation or accumulation of regulatory t cells
A regulatory, bacterial technology applied in the field of human-derived bacteria that induce the proliferation or accumulation of regulatory T cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0159] The bacterial composition can also be administered to individuals also receiving antibiotic treatment. The present inventors have demonstrated that antibiotics against Gram-positive bacteria such as vancomycin and metronidazole can effectively eliminate or greatly reduce bacterial species belonging to the class Clostridia from the gastrointestinal tract of mammals and subsequently reduce the regulatory T Cellular level (Example 5, Figure 30). Without wishing to be bound by theory, the critical role of bacteria belonging to the Clostridia class in the preservation of immune tolerance strongly suggests that their absence or reduced levels may play a critical role in autoimmune diseases characterized by insufficient immune tolerance . Thus, individuals undergoing a course of antibiotics against Gram-positive bacteria (for example, individuals who are being infected by therapeutic pathogens such as Clostridium difficile and Giardia) who have undergone a deletion of bacteri...
Embodiment 1
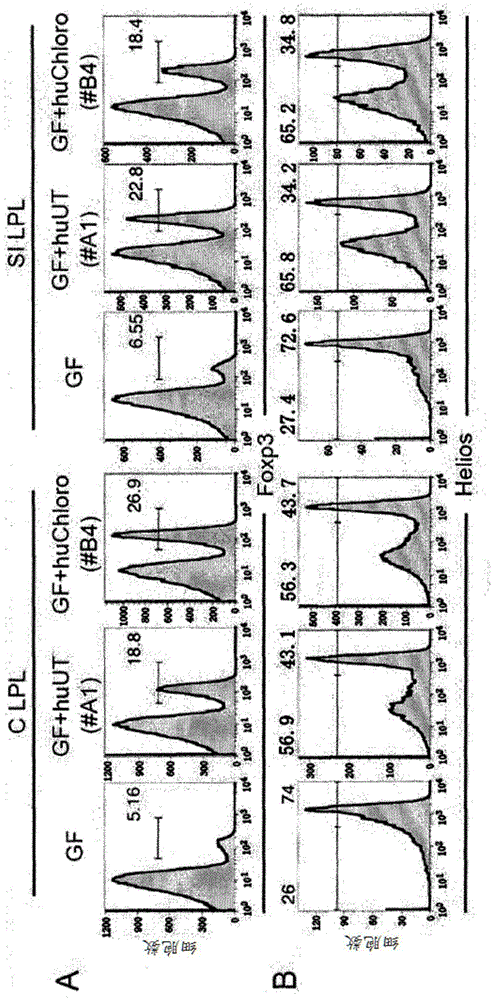
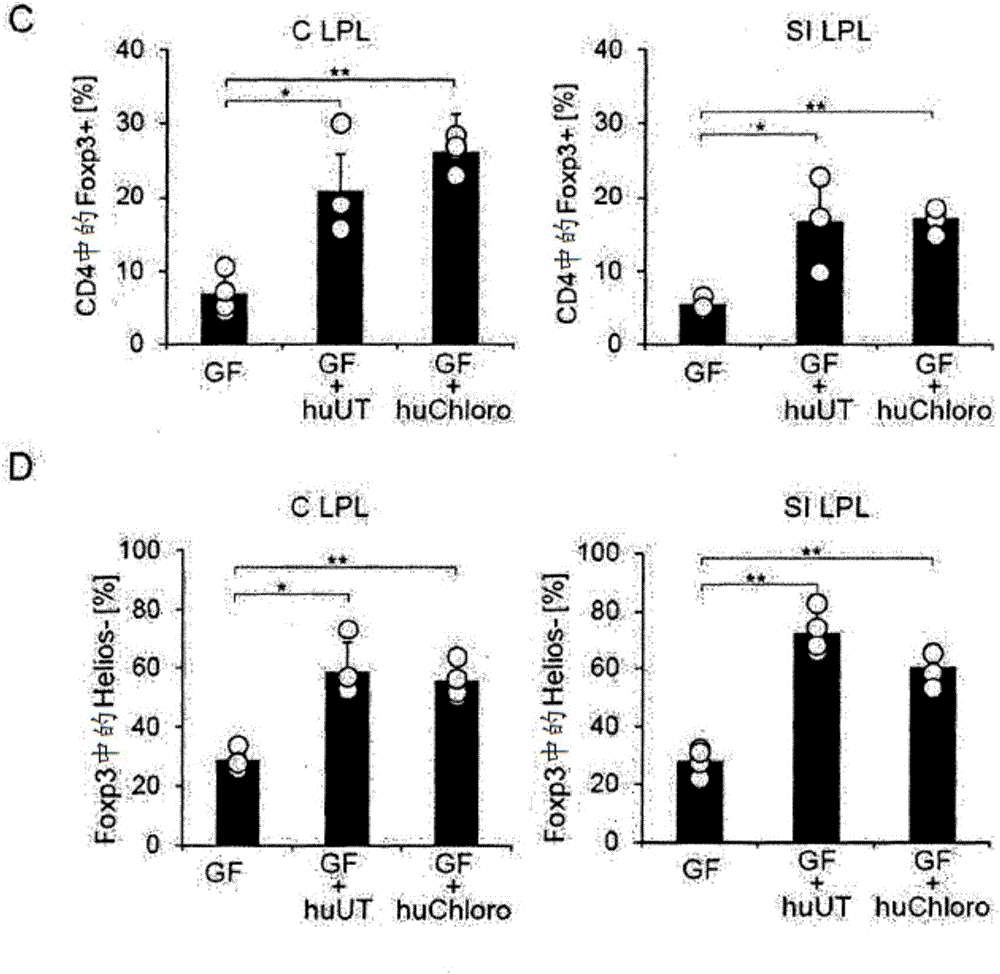
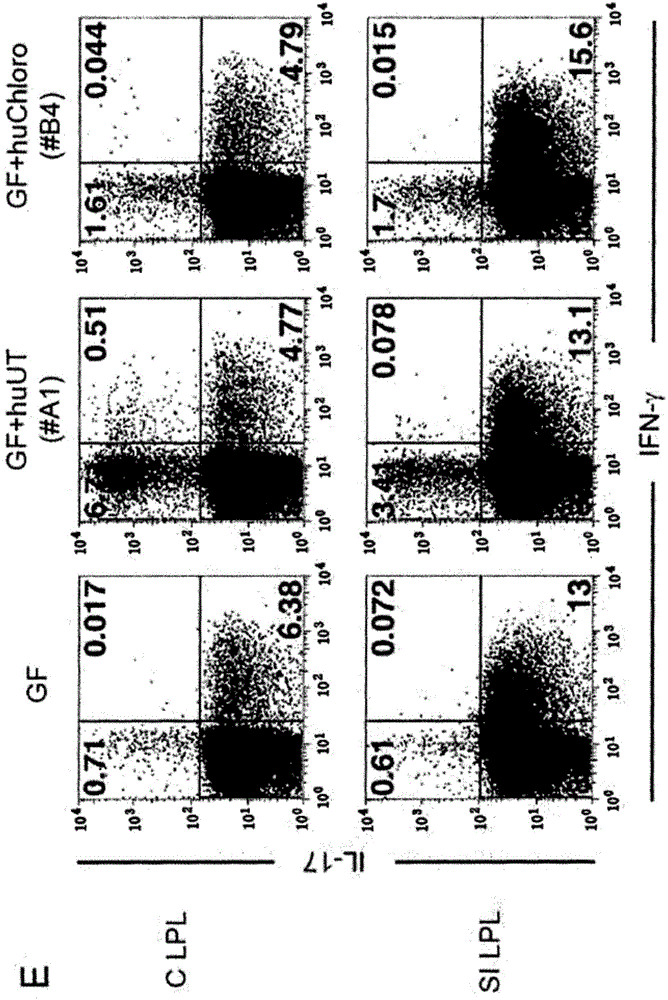
[0236] Example 1: First, it was investigated whether the accumulation of regulatory T cells (Treg cells) in the lamina propria of the colon was dependent on commensal bacteria. Specifically, lymphocytes were isolated from the peripheral lymph nodes (pLN) of Balb / c mice fed in the absence of specific pathogenic bacteria (SPF) or from the colon or small intestine (SI) lamina propria of the mice. CD4 and Foxp3 were stained by antibodies. Then, CD4 was analyzed by flow cytometry + Foxp3 in lymphocytes + cell ratio. The results showed that Foxp3 + Treg cells are present at high frequency in the lamina propria of the gastrointestinal tract of mice maintained in a specific pathogen free (SPF) environment, especially the lamina propria of the colon. In addition, it was also found that Foxp3 in the colon lamina propria + The number of Treg cells gradually increased until three months after birth, while Foxp3 in peripheral lymph nodes + The number of Treg cells remains essentially...
Embodiment 2
[0238] Example 2: Next, it was investigated whether the temporal accumulation of Treg cells in the colon found in Example 1 is related to the colonization of the intestinal commensal microbiota. Specifically, the small intestine, colon, and peripheral lymph nodes isolated from mice (8 weeks old: Balb / c mice, IQI mice, and C57BL / 6 mice) fed in a germ-free (GF) or SPF environment were analyzed. CD4 expression and Foxp3 expression in lymphocytes. Similar results were obtained in three or more independent experiments.
[0239] In addition, lamina propria lymphocytes were collected from SPF mice and GF mice (Balb / c mice or C57BL / 6 mice). CD4 and Foxp3 were stained with antibodies. Then, lamina propria lymphocytes were analyzed by FACS.
[0240] In addition, lymphocytes were isolated from colonic lamina propria, small intestinal lamina propria (SI), Peyer's patches (PP) and mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN) of mice administered antibiotics orally with water for eight weeks (SPF C57BL / ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com