Low-temperature over-summering preservation and cultivation method of brassica napus L microspore culture embryoid
A technology for microspore culture and Brassica napus, which is applied in horticultural methods, botanical equipment and methods, horticulture, etc., can solve problems such as the difficulty of oversummering seedlings, and achieve the effects of low cost, simple method, and improved efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
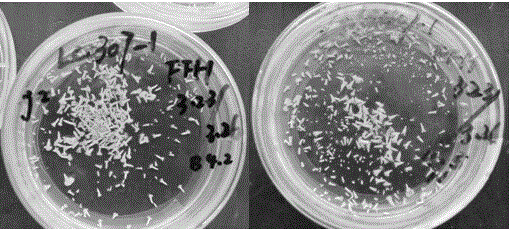
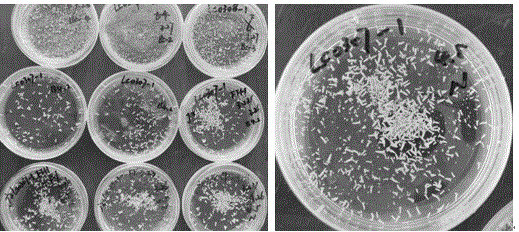
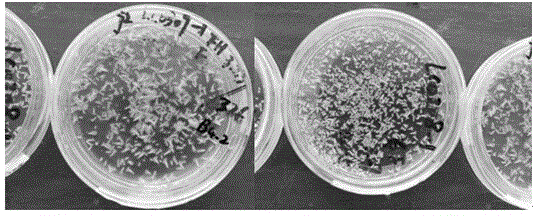
[0020] Embodiment 1 of the present invention: a low-temperature over-summer preservation culture method for culturing embryoid bodies of Brassica napus microspores. After culturing free microspores in NLN-13 medium for 26 days, an embryoid body with an embryo age of 26 days was obtained. The obtained embryoid bodies were placed in new NLN-13 medium, and the pH of the new NLN-13 medium was reduced to 5.5. The embryoid bodies were placed in a glass petri dish with a diameter of 6 cm, and each dish was stored for 150~ 200 embryoid bodies; then they will be stored in a refrigerator at 3°C. After 60 days of storage, they need to be taken out of the refrigerator at 3°C and transferred to an incubator at 8°C for 24 hours, and then replaced with new NLN-13 (PH 5.5) liquid culture medium; replace it and put it back in the incubator at 8°C for 24 hours, then store it in the refrigerator at 3°C for 120 days; during this period, replace the NLN-10 medium every 60 days, The method is t...
Embodiment 2
[0021] Embodiment 2 of the present invention: Brassica napus microspore culture embryoid body low-temperature over-summer preservation culture method, after the free microspores are cultured in NLN-13 medium for 25 days, the embryoid body with an embryo age of 25 days is obtained, The obtained embryoid bodies were placed in new NLN-13 medium, and the pH of the new NLN-13 medium was reduced to 5.5. The embryoid bodies were placed in a glass petri dish with a diameter of 6 cm, and each dish was stored for 150~ 200 embryoid bodies; and then stored in a refrigerator at 3°C for 60 days.
Embodiment 3
[0022] Embodiment 3 of the present invention: a low-temperature over-summer preservation culture method for culturing embryoid bodies of Brassica napus microspores, after culturing free microspores in NLN-13 medium for 28 days, to obtain embryoid bodies with an embryo age of 28 days, The obtained embryoid bodies were placed in new NLN-13 medium, and the pH of the new NLN-13 medium was reduced to 5.5. The embryoid bodies were placed in a glass petri dish with a diameter of 6 cm, and each dish was stored for 150~ 200 embryoid bodies; then they will be stored in a refrigerator at 3°C. After 60 days of storage, they need to be taken out of the refrigerator at 3°C and transferred to an incubator at 8°C for 24 hours, and then replaced with new NLN-13 (PH 5.5) liquid culture medium; replace it and put it back in the incubator at 8°C for 24 hours, and then store it in the refrigerator at 3°C for 90 days; The method is the same as above, and the pH of the NLN-10 medium is 5.5.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com