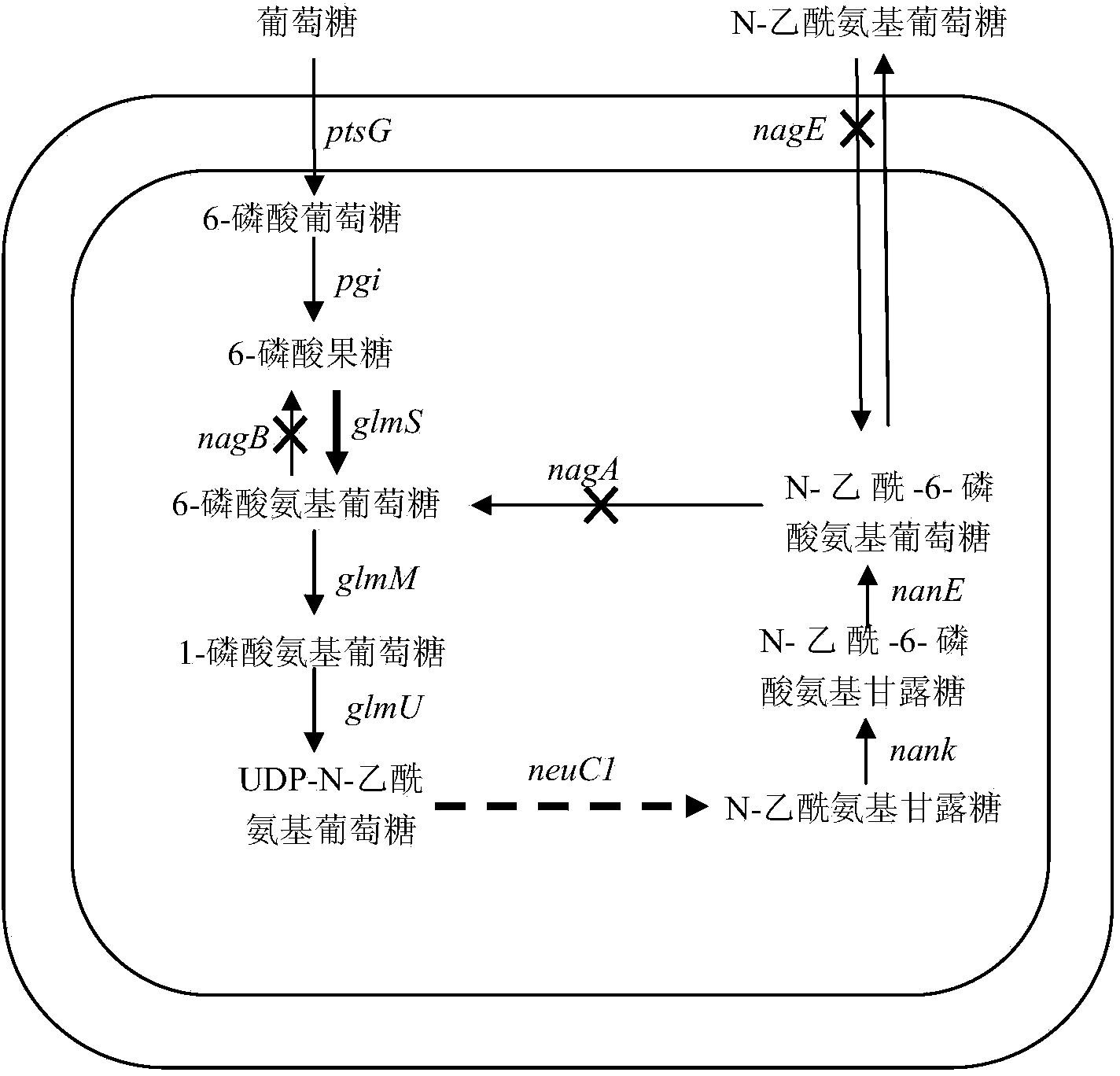
High-yield N-acetylglucosamine metabolic engineering bacterium, as well construction method and applications thereof
An acetamido and metabolic engineering technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of low yield, high cost, insufficient purity, etc., and achieve the effects of increasing yield, less accumulation of by-products, preventing backflow and consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] 1. Using the RED recombination method to inactivate the nagDCABE gene cluster in the strain, the specific steps are as follows:
[0033] 1. According to the sequence of Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (Invitrogen Company) genome (Genbank No.CP001509), design primers:
[0034] Upstream primer F-KO-nag:
[0035] ATCAGAGCCAACCACGTCCGCAGACGTGGTTGCTATTCAATTCCGGGGATCCGTCGACC (shown in SEQ ID NO.1)
[0036] Downstream primer R-KO-nag:
[0037]TGCGACGCTCAAGCGTCGCATCAGGCATAAAGCAGATTATGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTC (shown in SEQ ID NO.2)
[0038] Using primers F-KO-nag and R-KO-nag, plasmid pIJ773 as a template, and using commercial PCR reagents, the DNA fragments were amplified by PCR and purified for future use.
[0039] PCR reaction system: Tag enzyme 0.5 μl, 10×buffer 5 μl, template 1 μl, dNTP (2.5 mmol / L) 4 μl, primers (10 μ mol / L) 1.5 μl each, ddH2O3 6.5 μl;
[0040] PCR reaction process: 94°C for 5min, 94°C for 30s, 55°C for 45s, 72°C for 90s, 30 cycles, 72°C for 10min.
[0041] The o...
Embodiment 2
[0076] 1. The glmS and neuC1 genes were integrated into the chromosome of strain BL21(DE3) / Δnag for expression
[0077] 1. According to the sequence of plasmid pIJ778, design primer F-IJ778-KpnI:
[0078] CTAs GGTACC ATTCCGGGGATCCGTCGAC (shown in SEQ ID NO.9) R-IJ778-XhoI:
[0079] GAT CTCGAG TGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTC (shown in SEQ ID NO.10), using the plasmid pIJ778 as a template, PCR amplified to obtain a streptomycin-resistant DNA fragment;
[0080] 2. Purify the above-mentioned DNA fragment, digest it with KpnI and XhoI, and recover it for later use.
[0081] 3. Digest the plasmid vector pETDuet-glmS-neuC1 with KpnI and XhoI, purify it and connect it with the streptomycin-resistant DNA fragment purified in step 2, transform Escherichia coli DH5α, and obtain the integrated vector pETDuet-glmS-neuC-Str .
[0082] 4. Design the upstream primer F-ETDu-fucI:
[0083] ATGAAAAAAAATCAGCTTACCGAAAATTGGTATCCGCCCGTGCGTCCGGCGTAGAGGATC (shown in SEQ ID NO.11) and downstream primer R-E...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com