Three dimensional stereoscopic microscope
A stereoscopic and stereoscopic image pairing technology, applied in microscopes, stereoscopic systems, endoscopes, etc., can solve problems such as low contrast, difficult stereoscopic image fusion, and difficult observation of research objects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
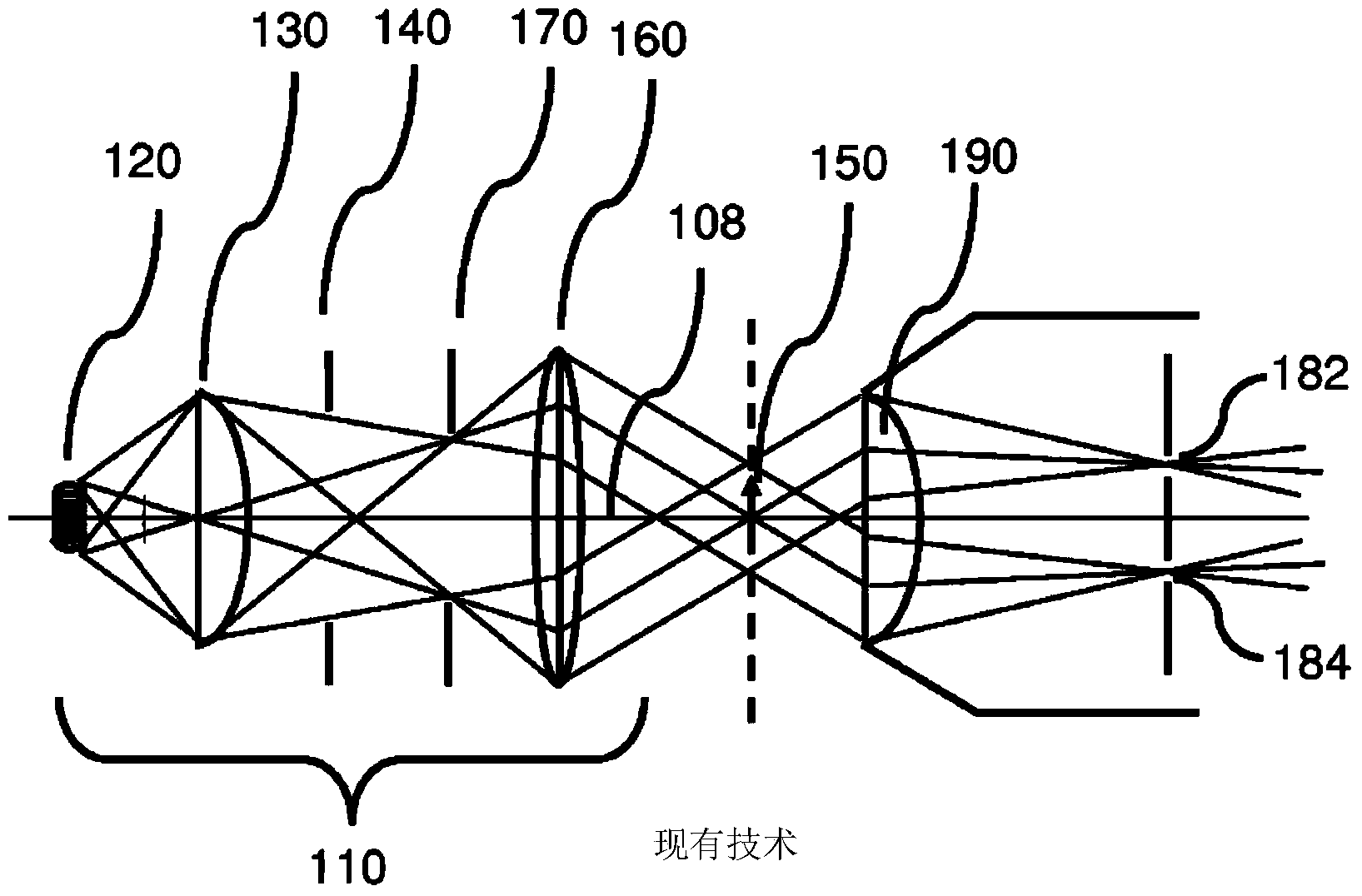
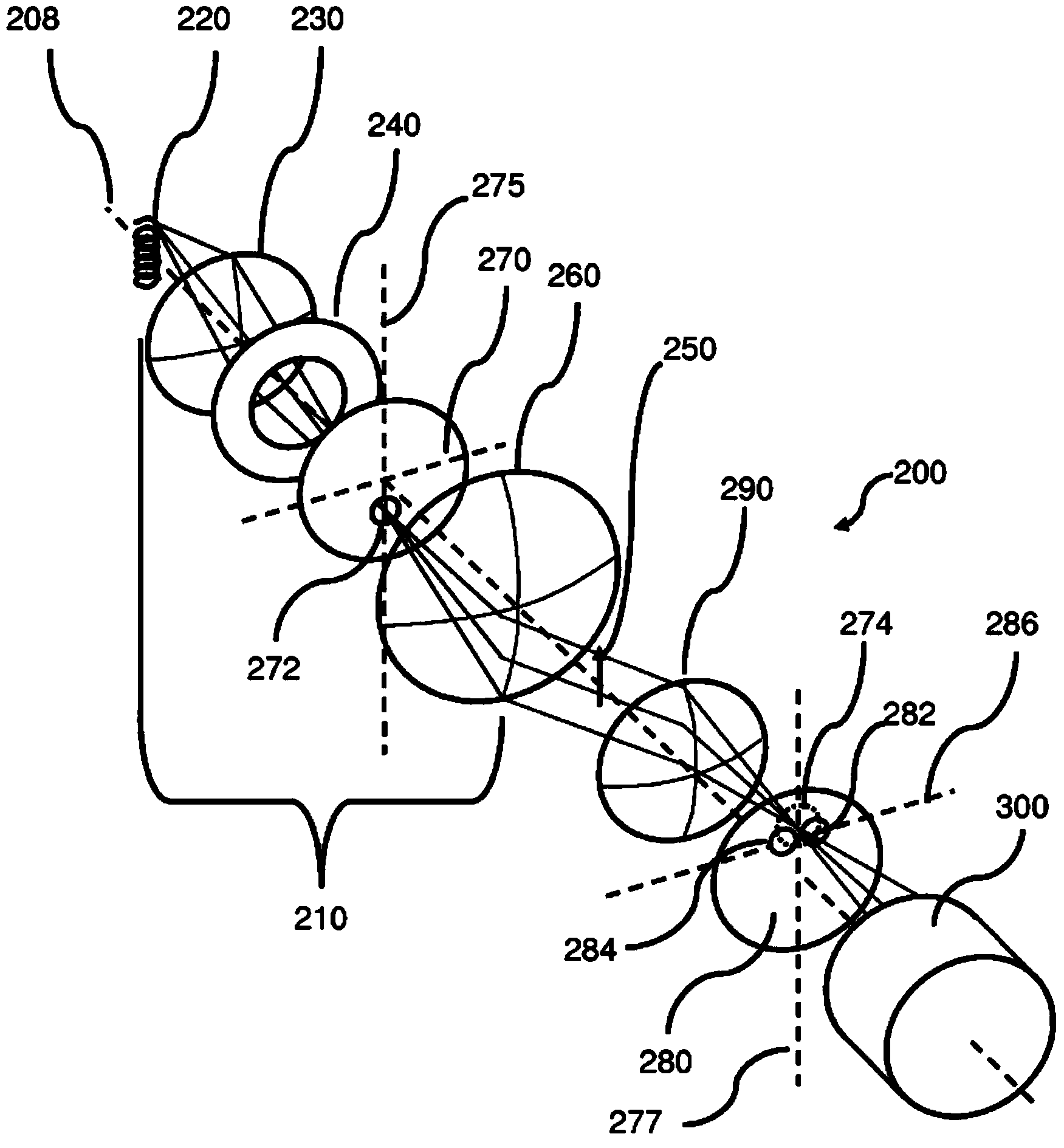
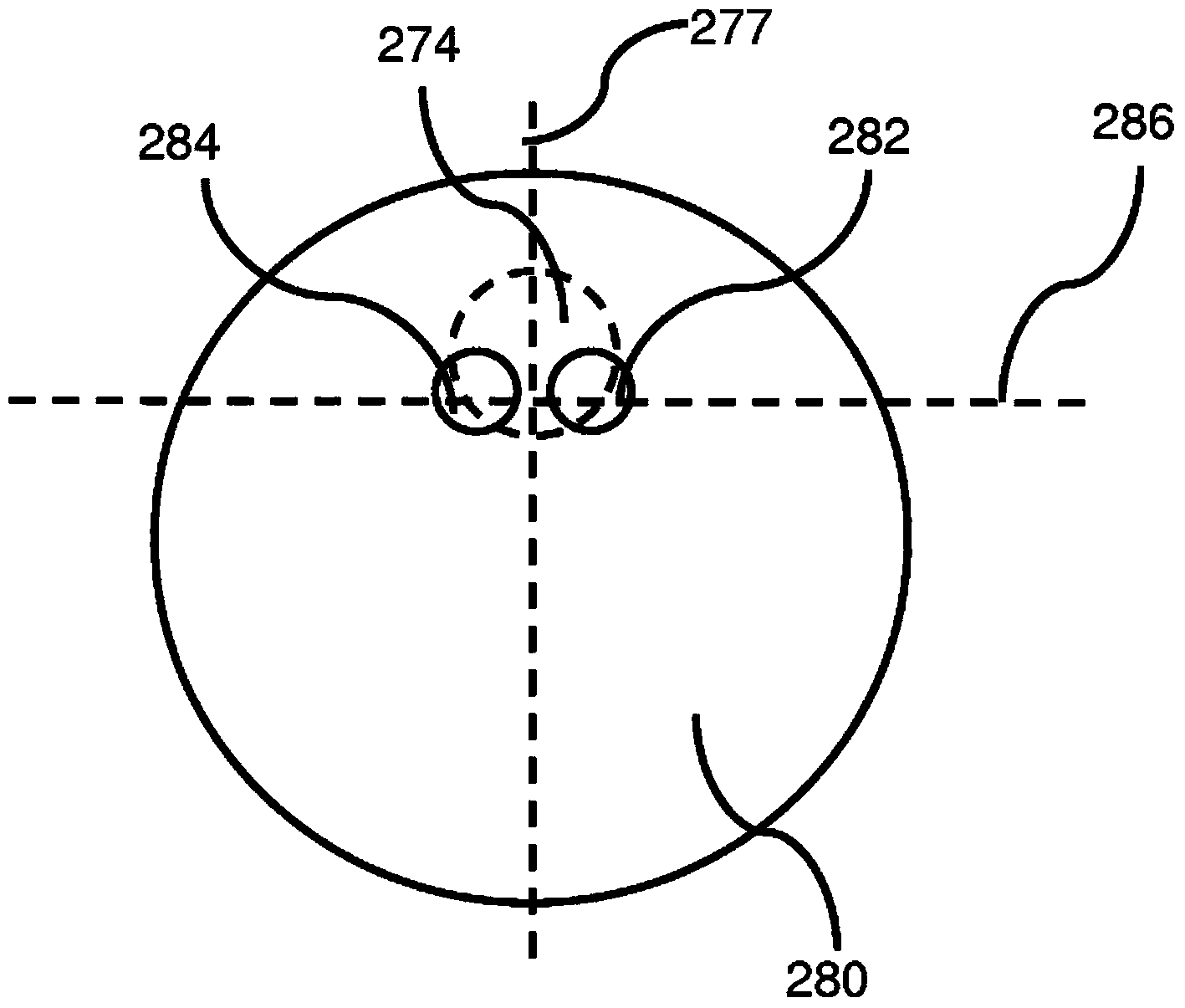
[0051]In a typical microscope, the intrusion of defects makes 3D depth perception very difficult indeed. Since the different surfaces of an object in this environment are often illuminated quite differently, the combination of the human eye and brain finds it very difficult to visually combine the left and right eye images to create a single 3D image. Instead, the image is simply rendered incongruously in one eye versus the other, which creates a great deal of viewing discomfort. This does not create a three-dimensional image in the human visual system, but two images that combine erratically and intermittently, creating visual fatigue. This effect is significantly exacerbated at the high numerical apertures of typical microscope objectives described above, since such lenses allow significantly greater perspective differences than typically occur in cameras and telescopic systems. This intermittent binding effect can potentially affect whatever three-dimensional view is avail...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com