A Method of Controlled Caving for Hard Roof of Coal Seam
A technology of hard roof and roof, used in earth-moving drilling, surface mining, underground mining, etc., can solve problems such as poor controllability, pollution, and in-situ stress effects, and achieve the effect of easy operation and good controllability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
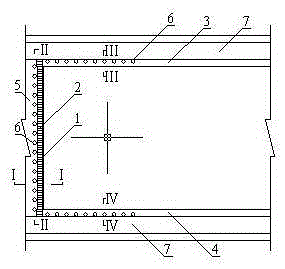
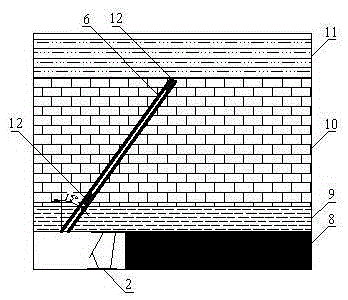
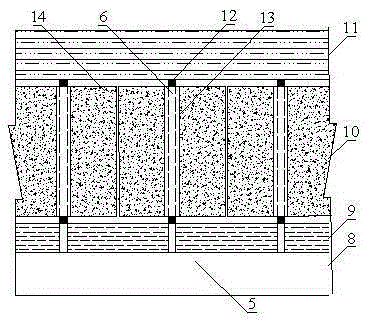
[0031] Such as figure 1 , 2, 3, 4, and 5, a method for controlling the caving of a single hard rock roof in a coal seam, in a near-horizontal coal seam 8 (thickness 3m), direct roof 9 (mudstone with a thickness of 2m), old roof 10 (thickness 10m In the limestone), after the construction of the cut hole 5 and before the mining of the coal wall 1 of the working face, on the roof rock layer behind the hydraulic support 2, a row of inclined working face coal wall 1 is constructed along the direction perpendicular to the advancing direction of the working face. Drill hole 6. The distance between adjacent boreholes is 5m, the angle between the direction of the borehole axis and the vertical direction of the roof is 15°, and the depth of the borehole is 12.5m. interface (see figure 2 ); after the construction of all the boreholes 6 in the open cut hole 5 is completed, and before the mining of the working face, implement hydraulic cutting 13 to all the boreholes 6 (refer to imag...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Such as Figure 6 , 7 , 8, 9, and 10, a method for controlling the caving of the composite hard rock roof of the coal seam, in a near-horizontal coal seam 8 (thickness 3m), direct roof 9 (mudstone thickness 2m), old top fine sandstone 15 (thickness 4m), Laoding mudstone layer 16 (thickness 1m), and Laoding limestone layer 17 (thickness 5m), after the construction of cut hole 5 and before the coal wall 1 of the working face has been mined, the hydraulic support 2. On the roof rock layer at the rear, a row of boreholes 6 inclined to the coal wall 1 of the working face are constructed along the direction perpendicular to the advancing direction of the working face. The distance between adjacent drilling holes is 5m, the angle between the direction of the drilling axis and the vertical direction of the roof is 15°, and the drilling depth is 12.5m. Layer 16 and Laoding limestone layer 17 reach the interface between the overlying rock layer 11 and Laoding limestone layer 17...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Such as figure 1 , 2 , 3, 4, and 5, a method for controlling the caving of a single hard rock roof in a coal seam, in a near-horizontal coal seam 8 (thickness 3m), direct roof 9 (mudstone with a thickness of 2m), old roof 10 (thickness 5m In the limestone), the distance between adjacent boreholes is 20m, the angle between the direction of the borehole axis and the vertical direction of the roof is 45°, and the depth of the borehole is 10m.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com