Heavy metal in-situ control and vegetation improvement method of lead-zinc smelting waste slag
A heavy metal and waste slag technology, applied in the restoration of polluted soil, etc., can solve problems such as heavy metal pollution, achieve the effects of increasing water holding capacity, increasing the mineral nutrient content of the stockyard medium and soil microbial activity, and improving the planting conditions of the stockyard
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
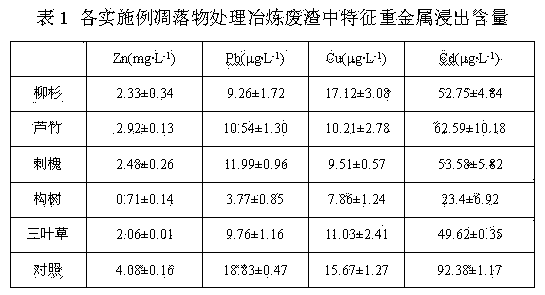
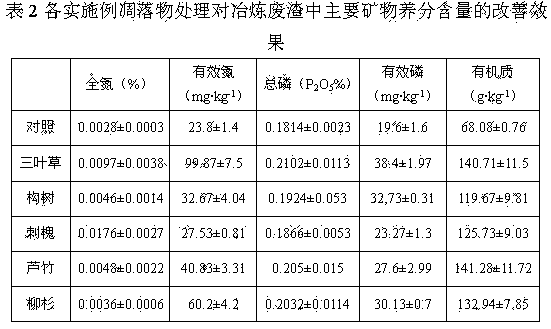
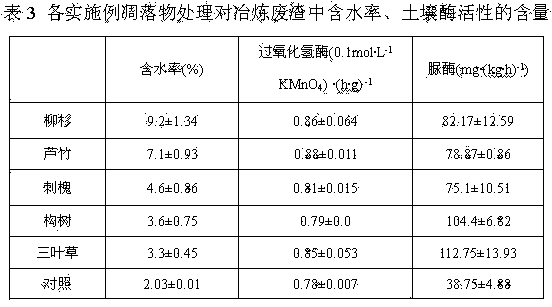
[0012] Embodiment 1 of the present invention: heavy metal in-situ control and plant growth improvement method of lead-zinc smelting waste residue, collect litter such as dead branches and fallen leaves of cedar cedar in spring and summer, cut and break to below 2cm; weigh 500 g of lead-zinc The smelting waste residue was placed in a nutrient bowl, and the litter of the pioneer plant Cryptomeria cedar (Cedaraceae Cryptomeria, a coniferous evergreen tree) to be planted in large quantities in the lead-zinc slag field was placed in a covering thickness of 2 cm, and then the covering The litter was mixed with 5cm of the surface of the storage yard; at the same time, the lead-zinc smelting residue group without added plant litter was used as a blank (control), sprayed with clean water, mixed evenly, covered with non-woven fabric, and then degraded naturally for 3 months, and selected to remove undegraded litter The material part shall be sieved according to the requirements of the fo...
Embodiment 2
[0014] Embodiment 2 of the present invention: heavy metal in-situ control and vegetation improvement method of lead-zinc smelting waste slag, collecting litter such as the litter of Arundos reed in autumn and winter, shearing and crushing to below 2cm; other is the same as embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0015] Embodiment 3 of the present invention: heavy metal in-situ control and vegetation improvement method of lead-zinc smelting waste slag, collecting litter such as black locust leaves in autumn and winter, shearing and crushing to less than 2 cm; others are the same as embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com