Method and device for counting insoluble particles
A particle counting and solubility technology, applied in measurement devices, particle and sedimentation analysis, particle size analysis, etc., which can solve the problem of high requirements on the number and speed of MCU104 ports, large power consumption of circuit PCB area, and unfavorable device miniaturization and intelligence. and other problems, to achieve the effect of improving detection accuracy and sensitivity, simplifying circuit design, reliability and anti-interference guarantee
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
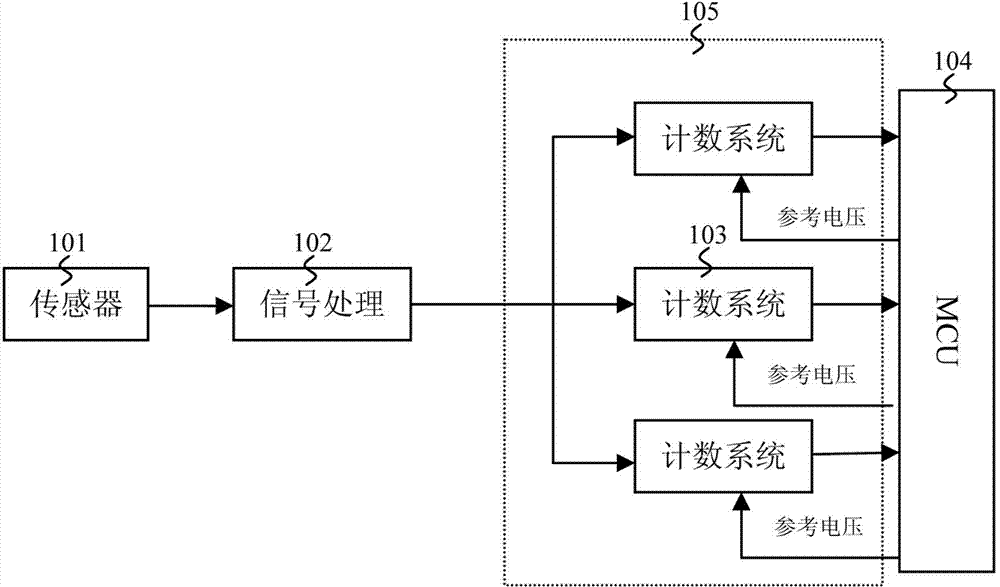
[0032] Embodiment one: see attached Figure 4 shown. A device for counting insoluble particles, which includes a sensor 401, a signal processing circuit 402 connected to the output end of the sensor 401, a signal isolation circuit 403 connected to the output end of the signal processing circuit 402, and an output end of the signal isolation circuit 403 The connected ADC sampling circuit 404 and the MCU signal discrimination and counting circuit 405 connected to the output end of the ADC sampling circuit 404 .
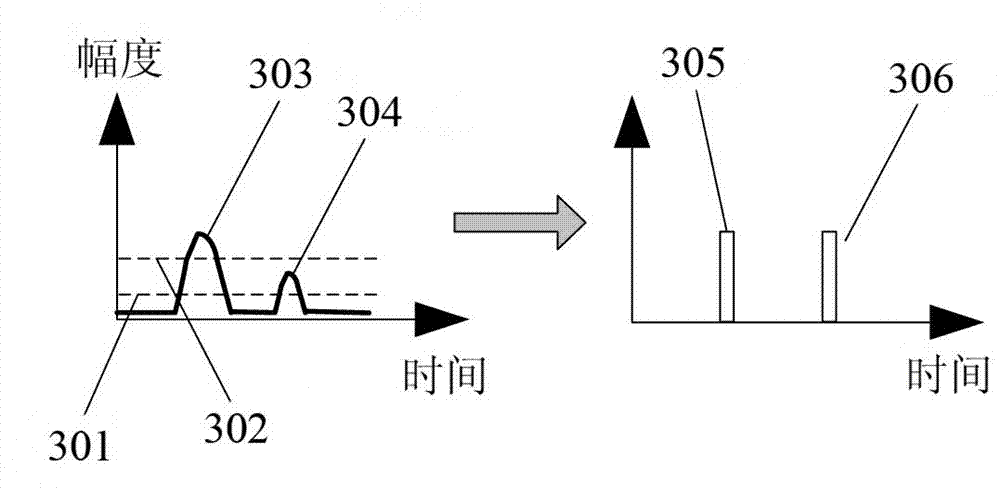
[0033] Sensor 401 as attached Figure 5 As shown in , it works based on the photoresist principle, and is composed of a semiconductor laser 501, an optical lens group, a sample pool and a photodiode 505. The magnitude is converted into a corresponding weak current signal.
[0034] Suppose the length of the detection area of the sample cell of the sensor 401 is L, the radius of the insoluble particles is R, and the moving velocity of the insoluble particles is V, th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com