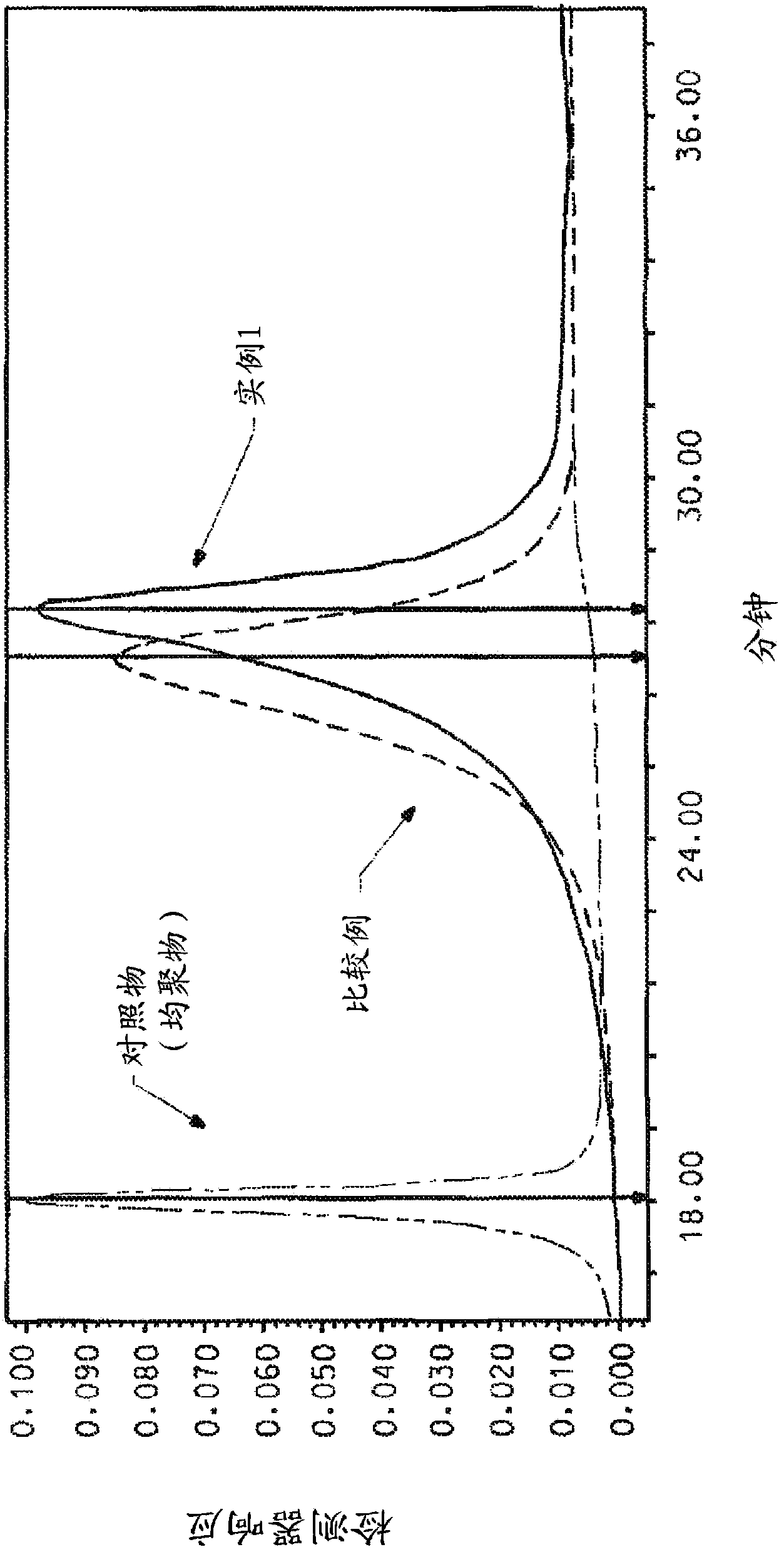
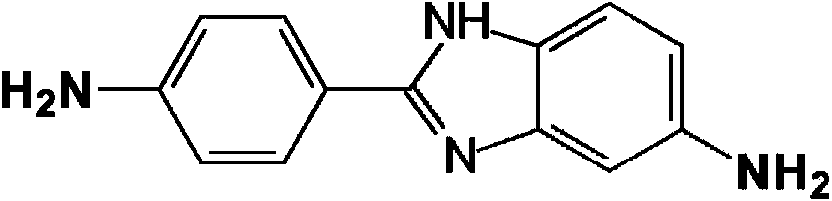
Aramid copolymer
A technology of polymer and p-phenylenediamine, which is applied in the field of preparing aromatic polyamide polymers, and can solve problems such as control of the position of monomer components without
Active Publication Date: 2014-04-30
DUPONT SAFETY & CONSTR INC
View PDF12 Cites 0 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
[0005] Therefore, by conventional polymerization method, in NMP / CaCl 2 DAPBI / PPD copolymers made in solvent systems tend not to have control over the position of the monomer components
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
example
example 1
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
The invention concerns polymer powder comprising 2-(4-amino phenyl)-5 (6) amino phenyl benzimidazole (DAPBI), paraphenylene diamine, and terephthaloyl dichloride, capable of being dissolved in a solvent system comprising (i) N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) or dimethylacetamide (DMAC) and (ii) an inorganic salt; wherein said polymer is capable of being redissolved in said solvent system after said polymer has been removed from said solvent system.
Description
technical field [0001] This patent application relates to a process for the preparation of aromatic polyamide polymers derived from 5(6)-amino-2-(p-aminophenyl)benzimidazole (DAPBI), p-phenylenediamine (PPD) and terephthaloyl dichloride (TCl), capable of forming fibers with excellent physical properties. Background technique [0002] Derived from 5(6)-amino-2-(p-aminophenyl)benzimidazole (DAPBI), p-phenylenediamine (PPD) and terephthaloyl dichloride (TCl or T, also commonly known as p-phenylene Diformyl chloride) fibers are known in the art. Such copolymers are Russian-made high-strength fibers (for example under the trade name and )Foundation. See Russian Patent Application 2,045,586. [0003] The two amines on DAPBI differ greatly in terms of reactivity and positional factors. The amine shown on the right side of the structure below (azole amine) is an order of magnitude more reactive than the amine on the left side of the structure (benzylamine). [0004] [0...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More Patent Type & Authority Applications(China)
IPC IPC(8): C08G69/32C08G73/18
CPCC08K3/16C08K5/3415C08G73/18C08K5/20C08G69/32C08G69/265C08L77/10C08L79/04
Inventor K-S.李
Owner DUPONT SAFETY & CONSTR INC
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com