Combination optimization self-adaptive frequency domain blind equalization method and system
An adaptive equalization and combination optimization technology, applied in baseband system components, shaping networks in transmitters/receivers, etc., can solve problems such as inability to obtain blind equalization performance, high computational complexity, and impact on blind equalization system performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0052] The technical solutions provided by the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with specific examples. It should be understood that the following specific embodiments are only used to illustrate the present invention and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention.
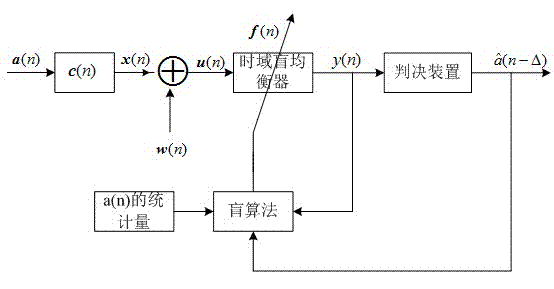
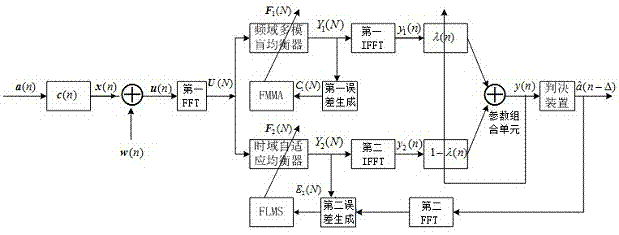
[0053] figure 2 Schematic diagram of adaptive frequency-domain blind equalization method (hereinafter referred to as COAFBEA method) for combinatorial optimization. The method involves two different types of frequency-domain equalizers, one is a frequency-domain multi-mode blind equalizer, which works in a blind equalization mode; the other is a frequency-domain adaptive equalizer, which works in a DD mode. When the system works in the frequency domain blind equalization mode, the intersymbol interference is eliminated at the initial stage of equalization or when the channel changes suddenly; when a sufficiently low steady-state mean square error is obtained in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com