Microwave stare correlated imaging device capable of performing random frequency hopping based on different code speeds
A technology of correlative imaging and microwave staring, which is applied in the directions of measurement devices, radio wave measurement systems, radio wave reflection/re-radiation, etc., can solve the problems of angular resolution limitation, limited application, long revisit period, etc., and achieve high resolution , the effect of reducing redundancy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] The technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be clearly and completely described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments are only some of the embodiments of the present invention, not all of them. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without making creative efforts belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
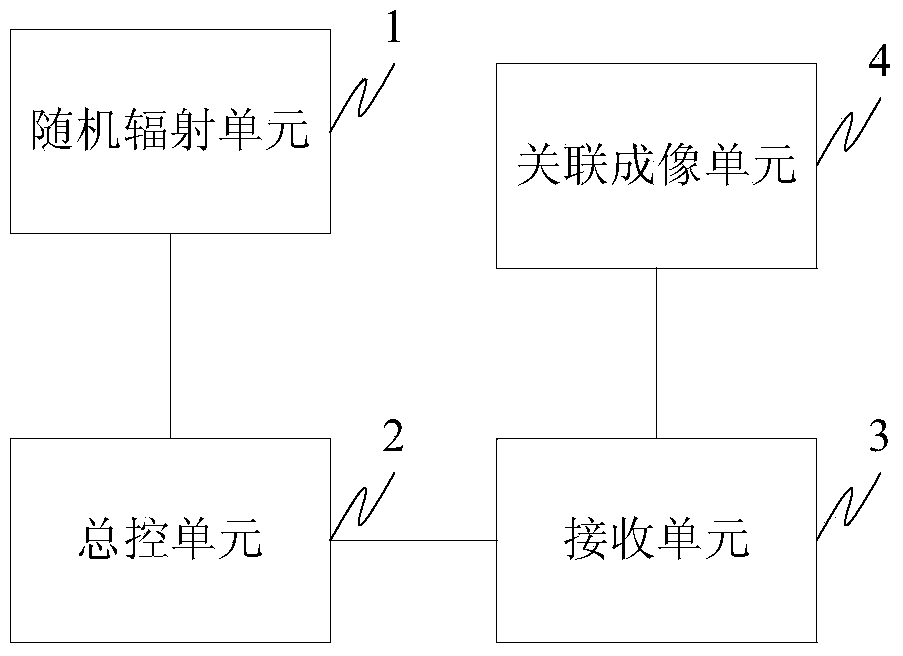
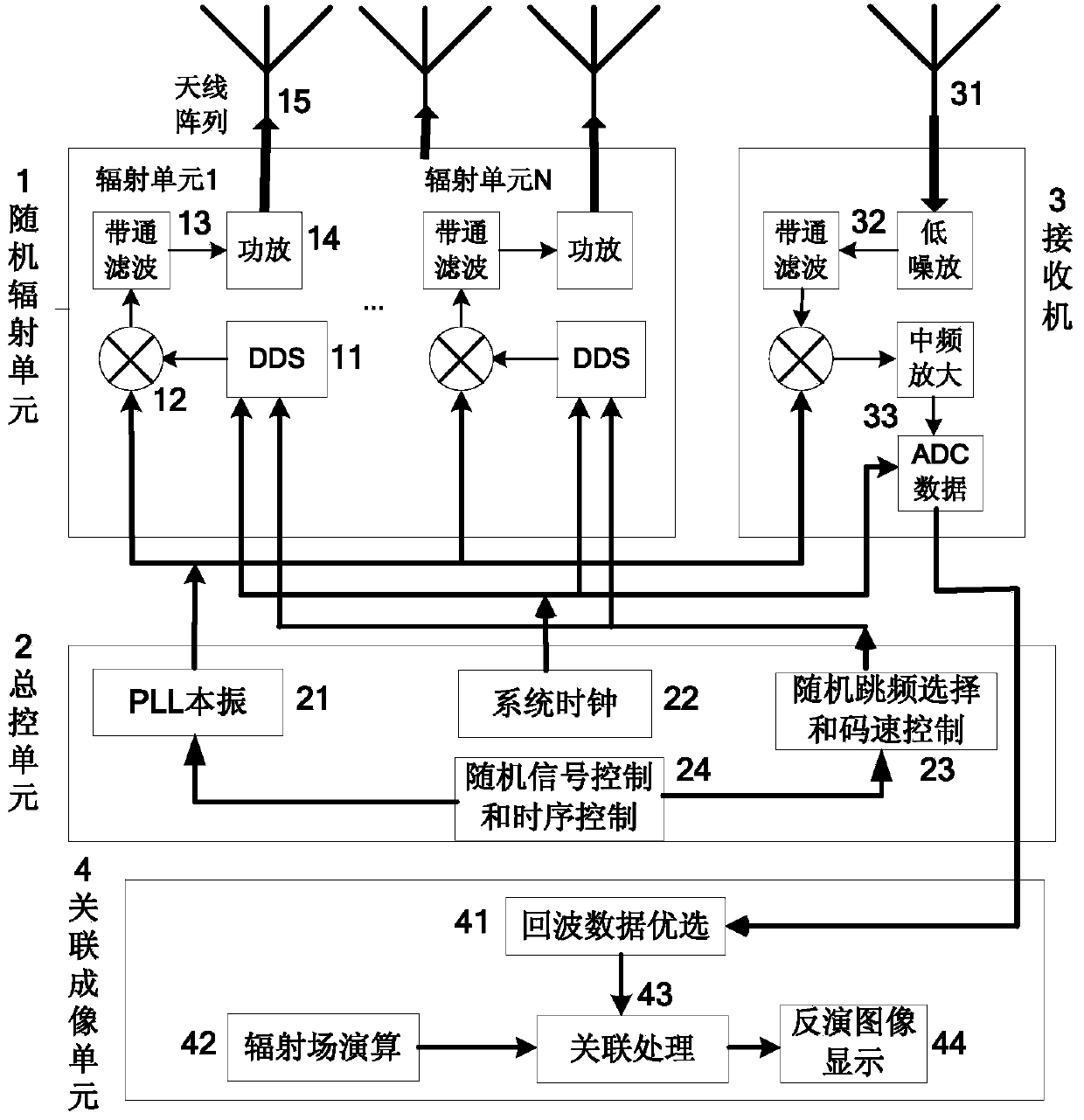
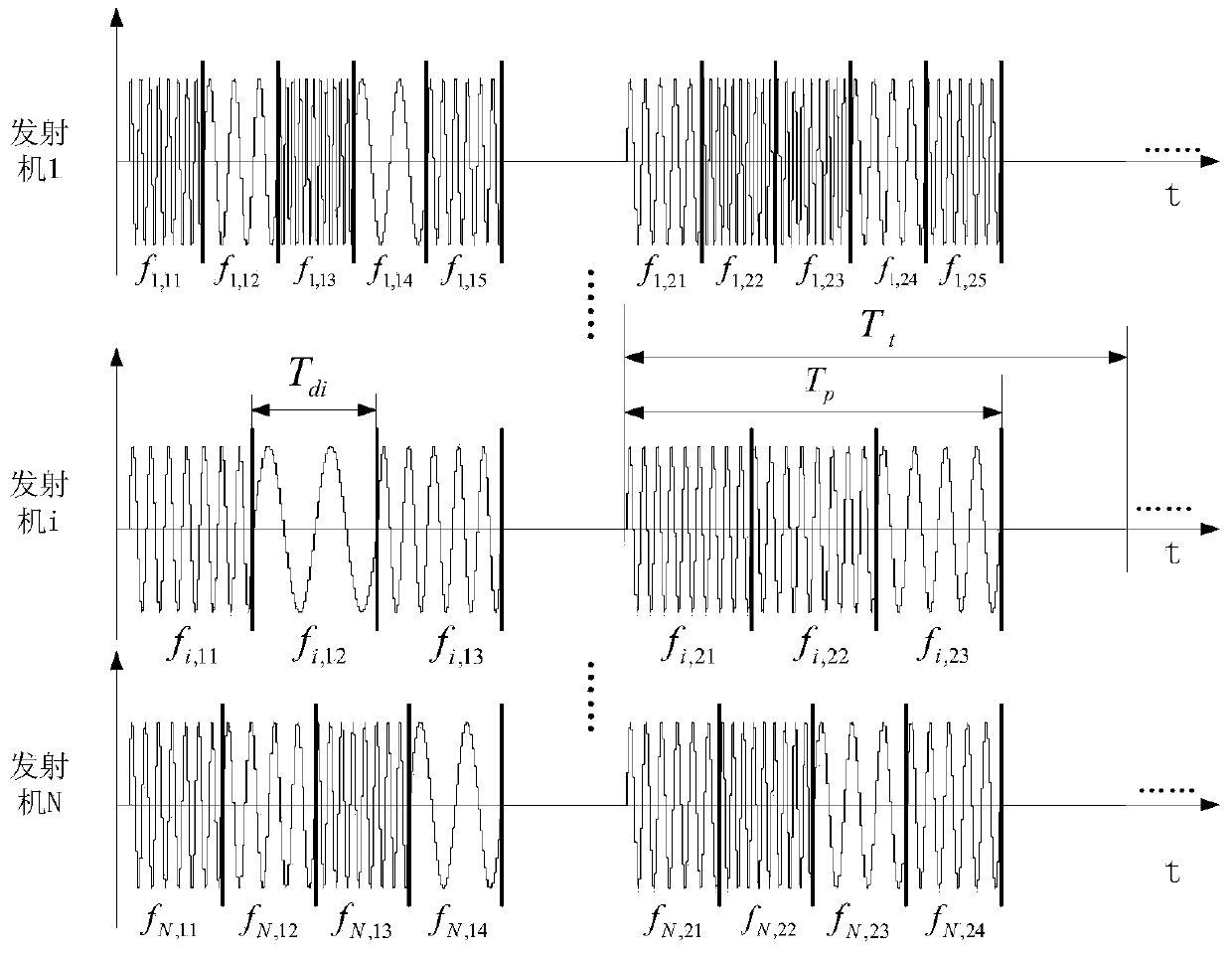
[0024] The first prerequisite for realizing high-resolution microwave staring correlative imaging is to form an ideal space-time two-dimensional random microwave radiation field in the target area. There are non-correlation features between the radiation fields at the position, and non-correlation features between the radiation fields in the target area at different times. In engineering, under the conditions of limited array size, limited bandwidt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com