Kit for quantitatively detecting EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) gene mutation and application thereof
A kit and gene technology, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as insufficient determination of weakly positive patients with mutations, inability to give the proportion of EGFR gene mutations, inability to detect blood samples, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
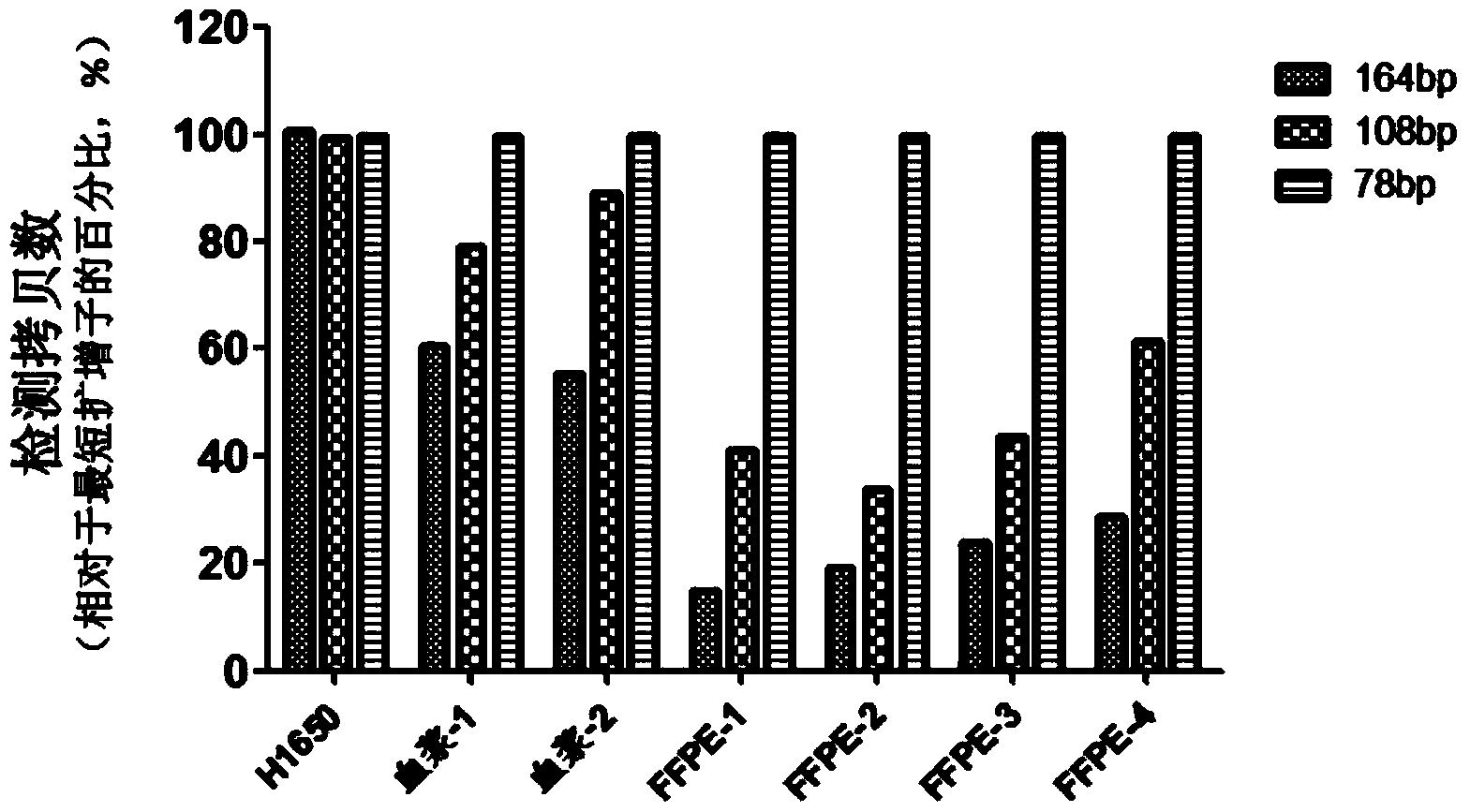
[0072] Embodiment 1, the selection of amplified fragment length
[0073] Formaldehyde-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tumor tissue samples are often used as the first choice for research because they are easier to store for a long time. In addition, studies have shown that the DNA content in plasma of tumor patients is significantly higher than that of blood samples from normal healthy people, and plasma, serum, etc. are easier to obtain in clinical practice and less traumatic to patients, so blood samples are also an ideal source of clinical samples . However, studies have shown that genomic DNA extracted from FFPE samples and plasma samples is fragmented, most of which are less than 200bp. Fragmented DNA brings certain difficulties to subsequent PCR-based detection.
[0074] Taking the detection of exon No. 4 of the EGFR gene as an example, in order to investigate the influence of DNA fragmentation extracted from FFPE samples and plasma samples, the inventors designed 3 se...
Embodiment 2
[0088] Embodiment 2, the selection of amplification primer length
[0089] In this embodiment, the detection of the L858R mutation of the EGFR gene is taken as an example, and the mutant plasmid T-L858R and the wild plasmid T-exon20-21 are used as templates.
[0090] In the amplification detection primers involved in the method, the inventors designed detection sites on the front primers, so the front primers are the key to distinguish mutant and wild-type genes. The present inventors designed amplification detection pre-primers of different lengths, and designed the last base of the pre-primers at the base mutation site of L858R to investigate the ability of pre-primers of different lengths to distinguish mutant genes from wild-type genes. Taking the detection of the L858R mutation of the EGFR gene as an example, the front primer sequences of different lengths are shown in Table 8, the back primer used is R858, and the probe used is P858. respectively for 1.0×10 5 The copie...
Embodiment 3
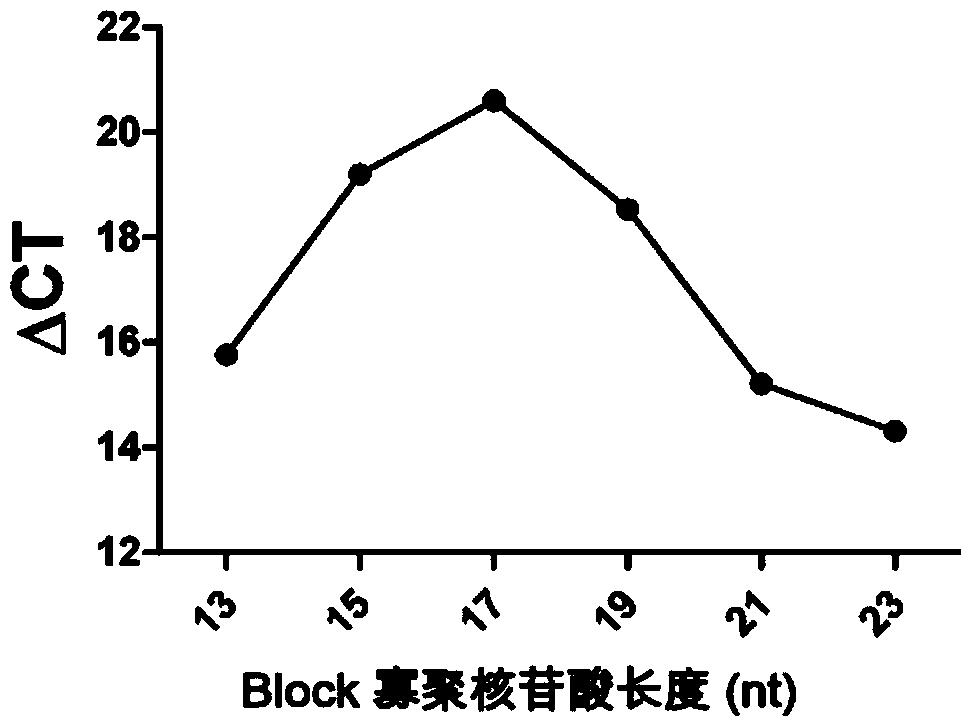
[0097] Embodiment 3, the effect of competitive Block oligonucleotide
[0098] Templates used in this example: mutant plasmids: T-T790M, T-L858R; wild-type plasmids: T-exon20-21.
[0099] The primers used in this example are F-858-5 and R-858 for L858R, the probe is P-858; the primers F-790 and R-790 for T790M, and the probe P-790.
[0100] For the L858R and T790M mutation sites of the EGFR gene, the inventors designed competitive Block oligonucleotides B-858-1 and B-790-1 (Table 3), respectively. Block oligonucleotides and wild-type The gene is completely complementary and partially complementary to the mutant gene. In the presence of the wild-type gene, the Block oligonucleotide can block the wild-type gene and prevent the amplification of the wild-type gene from causing false positives, thus improving the specificity of detection. sex. Select the mutant plasmid and the wild-type plasmid for comparison, and perform PCR amplification detection, in which the competitive Block...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com