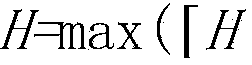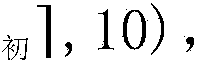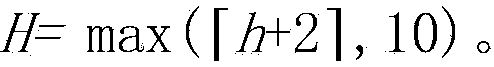Method for calculating height of venting riser of natural gas transmission pipeline
A technology for venting risers and calculation methods, which is applied in calculations, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., and can solve problems such as difficulty in obtaining safe, accurate and reasonable heights of venting risers, no calculation process, and inability to meet actual application requirements, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0120] For a pipeline to transport natural gas, its valve chamber in the first-level area needs to be designed and constructed to vent a riser, and the specific height of the riser is calculated.
[0121] S011. The diameter of the trunk line pipe to which the venting riser belongs is 1026mm (1.026m), and the operating pressure is 5Mpa (5×10 6 Pa), the distance between valve chambers is 32km (3.2×10 4 m), the natural gas compression factor is 0.87, the operating temperature is 20℃ (293K), and the maximum emptying time is 8h (2.88×10 4 s). The area where the venting riser is located is grade one, there is no building within 10m, and the local average wind speed at a height of 20m u ∞ =8.94m / s;
[0122] S012. Calculate the relevant parameters required to calculate the natural gas venting standpipe according to the basic data;
[0123] Among them, the mass flow rate of natural gas venting:
[0124] m q = 2 π D 2 ( P ZRT ) · L T v = 2 π · ...
Embodiment 2
[0147] Calculate the specific height of the valve chamber venting riser of the gas pipeline in Example 1, which is located in the second, third, and fourth level areas.
[0148] S021. The diameter of the trunk line pipe to which the venting riser belongs is 1026mm (1.026m), and the operating pressure is 5Mpa (5×10 6 Pa), the distance between valve chambers is 32km (3.2×10 4 m), the natural gas compression factor is 0.87, the operating temperature is 20℃ (293K), and the maximum emptying time is 8h (2.88×10 4 s). The area where the venting riser is located is grade one, there is no building within 10m, and the local average wind speed at a height of 20m u ∞ =8.94m / s;
[0149] S022. Calculate the relevant parameters required to calculate the natural gas venting standpipe according to the basic data;
[0150] Among them, the mass flow rate of natural gas venting:
[0151] m q = 2 π D 2 ( P ZRT ) · L T v = 2 π · 1.0 26 2 ( 5...
Embodiment 3
[0175] Calculate that the gas pipeline described in Example 1 shortens the maximum emptying time by 6h (2.16×10 4 s) After venting the height of the riser in the valve chamber of the first level area.
[0176] S031. The trunk line pipe diameter to which the venting riser belongs is 1026mm (1.026m), and the operating pressure is 5Mpa (5×10 6 Pa), the distance between valve chambers is 32km (3.2×10 4 m), the natural gas compression factor is 0.87, the operating temperature is 20℃ (293K), and the maximum emptying time is 8h (2.88×10 4 s). The area where the venting riser is located is grade one, there is no building within 10m, and the local average wind speed at a height of 20m u ∞ =8.94m / s;
[0177] S035. Calculate the relevant parameters required to calculate the natural gas venting standpipe according to the basic data;
[0178] Mass flow rate of natural gas venting:
[0179] m q = 2 π D 2 ( P ZRT ) · L T v = 2 π · 1.0 26 2 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com