Human body behavior identification method adopting non-supervision multiple-view feature selection
A feature selection and recognition method technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, instruments, computer components, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to give full play to the advantages of multi-view features and less research, so as to improve the recognition accuracy and anti-noise interference ability Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
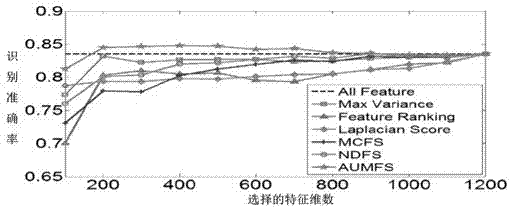
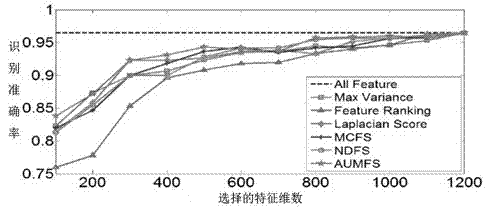
[0053] The public human behavior dataset KTH is used to test the human behavior recognition ability of this method. The KTH dataset contains a total of 600 human action videos divided into 6 different motion types. figure 1 Shows some KTH behavior video data samples, figure 2 and image 3 It shows the comparison between this method (denoted as AUMFS) and other existing methods (Max Vairance, Laplacian Score, Feature Ranking, Multi-Cluster Feature Selection (MCFS) and Nonnegative Discriminative Feature Selection (NDFS)) comparison method recognition performance with the feature selection dimension change comparison results, Figure 4 is the sensitivity of different parameters of the method performance under the KTH data set, Figure 5 The method iteration convergence curve is shown. Below in conjunction with the concrete technical scheme described above illustrate the steps that this example implements, as follows:
[0054] 1) First, 80% of the KTH data set is used as a p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com