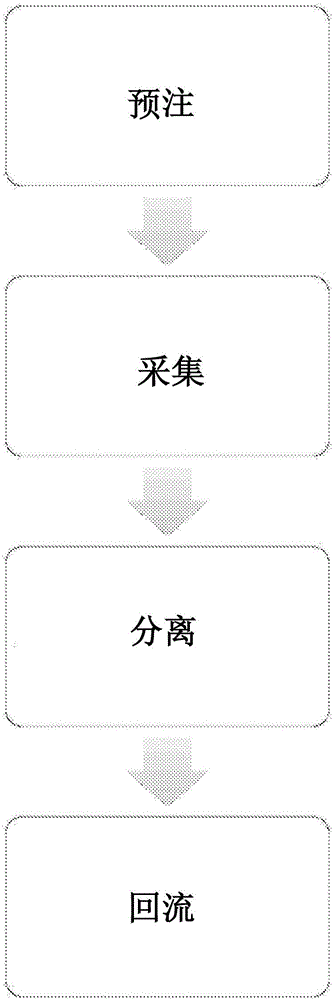
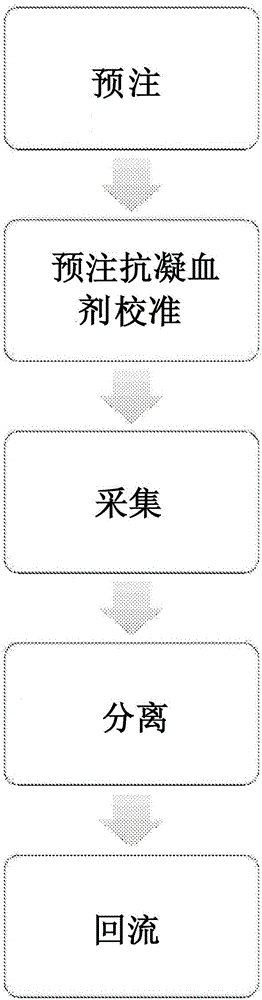
Priming anticoagulant line for blood extraction
An anticoagulant and anticoagulant technology, which can be used in blood circulation treatment, suction equipment, etc., and can solve the problem that the donor is not clinically significant.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
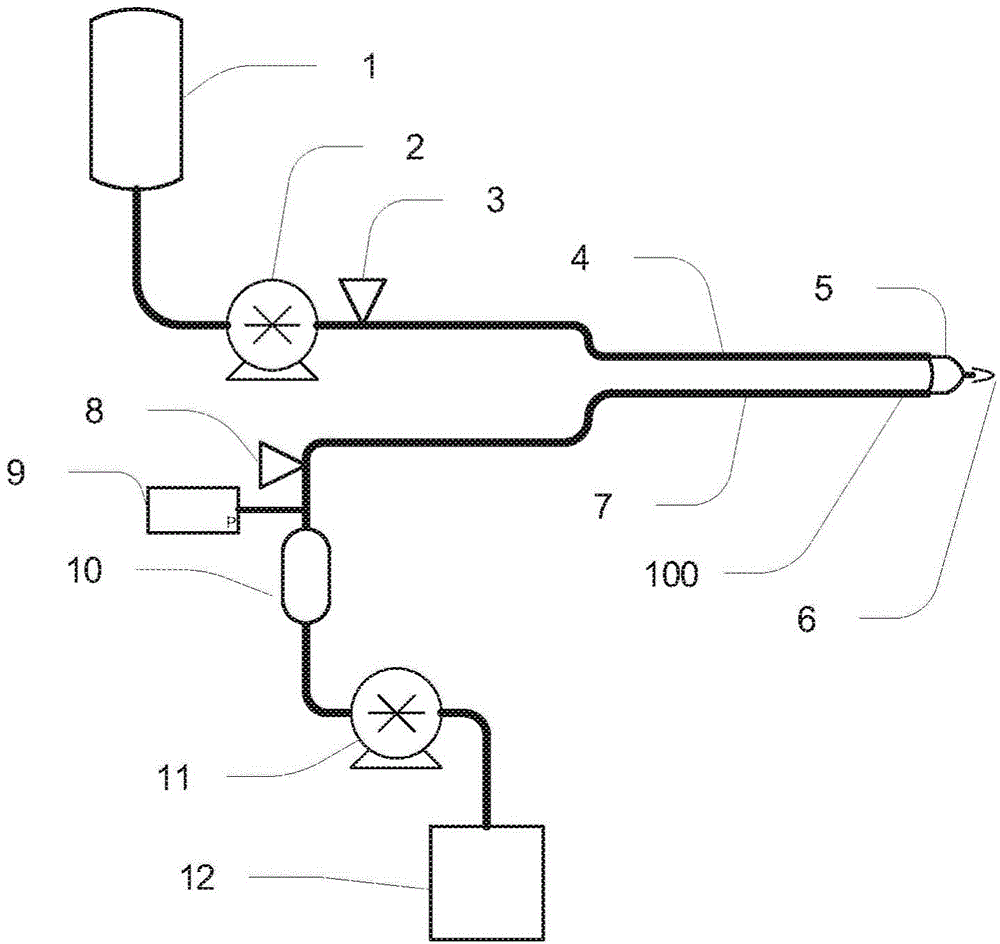
[0064] can be used for platelet-deficient plasma collection A plasma collection system (Haemonetics, Braintree, MA) demonstrates the non-limiting examples described herein. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration regulates the amount of blood collected from a donor used in blood component transfusions and is regulated in 21 C.F.R. §640.65. See Table 1. This regulation refers to the regulation (memorandum) from Kathryn C. Zoon, Director, FDA Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, Volume Limits for Automated Collection of Source Plasma (November 4, 1992); and see Compliance Policy Guide §252.110 Volume Limits for Automated Collection of Source Plasma (March, 6, 2000). The amount of anticoagulant (4% sodium citrate solution) added to whole blood was based on the ratio of anticoagulant to anticoagulated blood. The Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER) developed a nomogram that details the maximum volume of plasma that can be collected from a donor based on t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com