Static equivalence method of external network in interconnected power grid
An external network, static equivalent technology, applied in the direction of AC network circuits, electrical components, circuit devices, etc., can solve the problems of not being good enough, relatively large errors, etc., and achieve good static security analysis, high static equivalent accuracy, and maximum security The effect of error and relative error improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
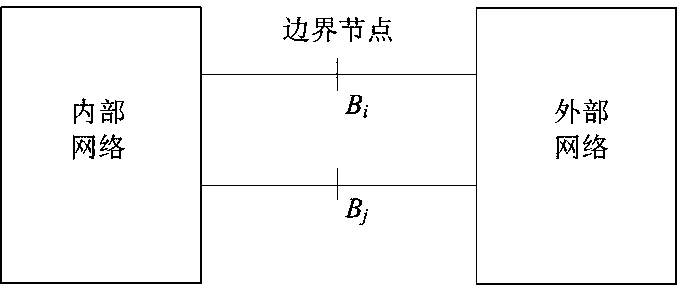
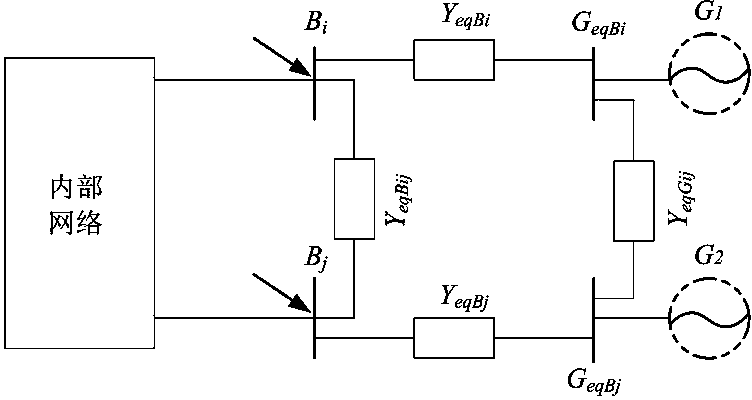
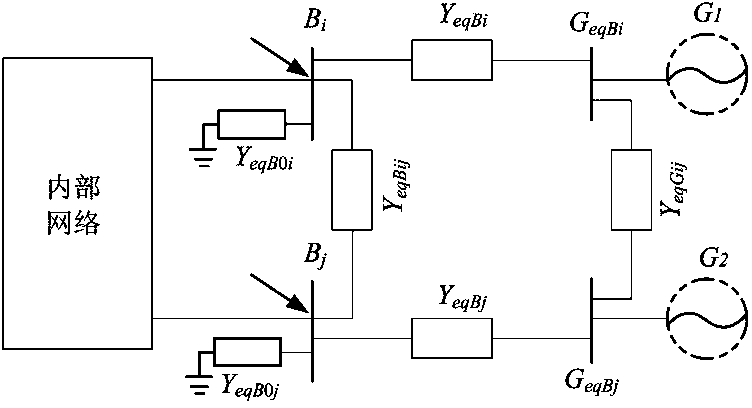
[0021] A static equivalence method for an external network in an interconnected grid, the method has the following steps:
[0022] (1) Obtain the basic information of the interconnected grid before the static equivalent of the external network. These basic information are: impedance parameters and susceptance parameters to the ground of all lines in the interconnected grid, impedance parameters, admittance parameters to the ground and transformation ratio parameters of the transformer , the ground admittance parameters of all nodes; the voltage of non-generator nodes on the internal network and the boundary; the injection current of the non-generator nodes on the internal network and the boundary; Node voltage; according to the obtained impedance parameters and ground susceptance parameters of all lines in the interconnected grid, transformer impedance parameters, ground admittance parameters and transformation ratio parameters, and ground admittance parameters of all nodes, th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com