Optical fiber micrometric displacement sensor based on Mach-Zehnder interference and manufacturing method of optical micrometric displacement sensor
A technology of a micro-displacement sensor and a manufacturing method, which is applied to instruments, optical devices, coupling of optical waveguides, etc., can solve the problems of high manufacturing cost, low sensitivity, complicated manufacturing procedures, etc., and achieves convenient operation, low cost, and simple process. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
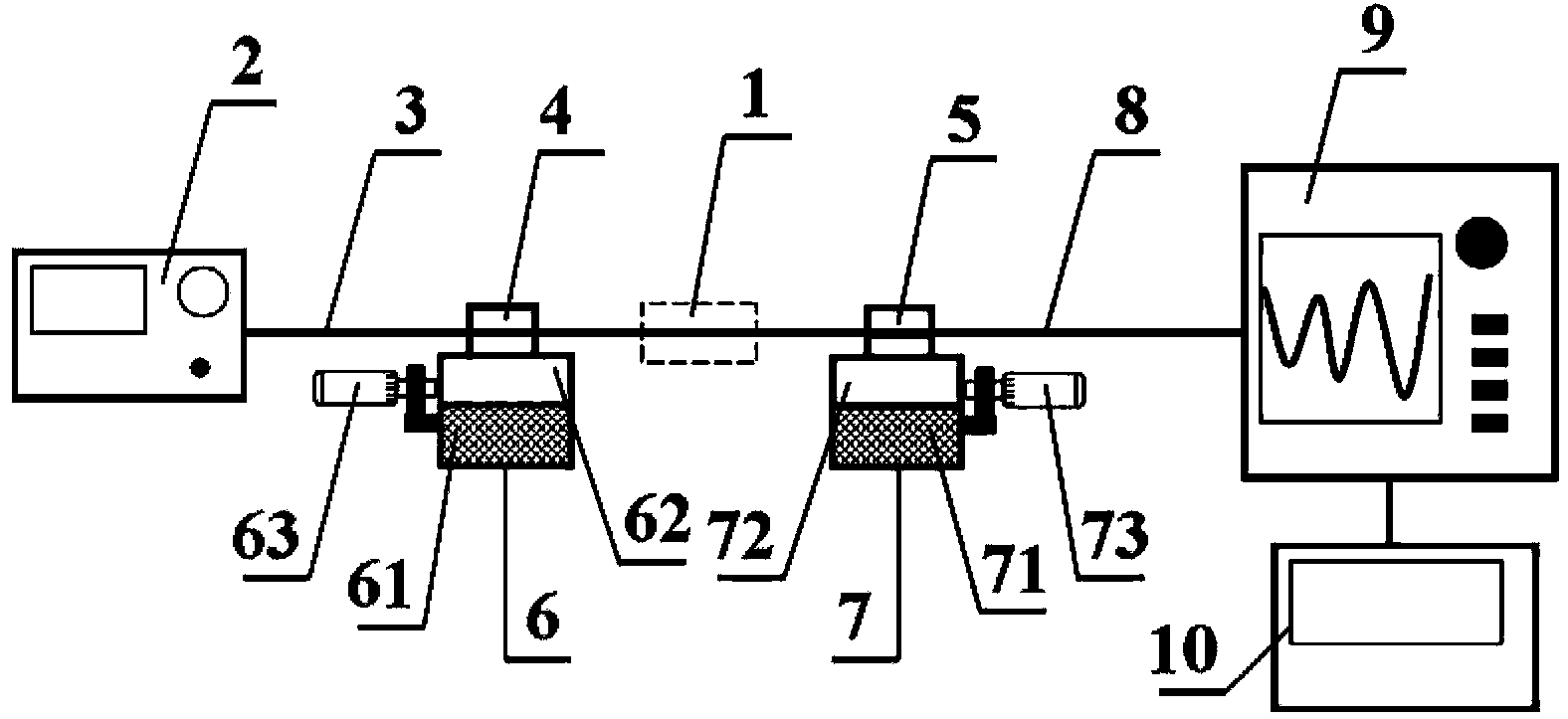
[0026] Embodiment one: a kind of optical fiber micro-displacement sensor based on Mach-Zehnder interference, such as figure 1As shown, it is composed of an input single-mode fiber 11, a first microbend structure fiber 12, a conduction single-mode fiber 13, a second microbend structure fiber 14 and an output single-mode fiber 15, and light passes through the core of the input single-mode fiber 11 Transmitted into the first microbend structure fiber 12, the light is divided into two parts in the first microbend structure fiber 12, a part of the light remains in the core of the first microbend structure fiber 12 to propagate in the core fundamental mode, and the other part of the light Enter the cladding of the first microbend structure fiber 12 to propagate in the cladding mode, and the light propagated in the core fundamental mode output by the first microbend structure fiber 12 is transmitted to the second microbend through the core of the conductive single-mode fiber 13 In th...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Embodiment 2: The method for preparing the optical fiber micro-displacement sensor in this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1, only the structural parameters of the optical fiber micro-displacement sensor are different, namely: the length L of the conductive single-mode optical fiber 13 C =2.5mm; the vertical distance L between the planes where the two ends of the first microbending structure optical fiber 12 are located b1 =745 μm, the vertical distance L between the planes where the two ends of the second microbend structure optical fiber 14 are located b2 =762 μm; the radial offset L of the first microbend optical fiber 12 d1 =100 μm, the radial offset L of the second microbend structure optical fiber 14 d2 =110μm.
Embodiment 3
[0038] Embodiment 3: The manufacturing method of preparing the optical fiber micro-displacement sensor in this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1, only the structural parameters of the optical fiber micro-displacement sensor are different, that is: the length L of the conductive single-mode optical fiber C =11.5mm; the vertical distance L between the planes where the two ends of the first microbending structure optical fiber 12 are located b1 =743 μm, the vertical distance L between the planes where the two ends of the second microbending structure optical fiber 14 are located b2 =752 μm; the radial offset L of the first microbend optical fiber 12 d1 =102 μm, the radial offset L of the second microbend fiber 14 d2 =105 μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com