Space-time two-dimensional clutter spectrum estimation method based on iterative weighted minimum variance
A minimum variance and iterative weighting technique, applied in the radar field, can solve problems such as loss of system degrees of freedom and insufficient accuracy of space-time two-dimensional clutter spectrum estimation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
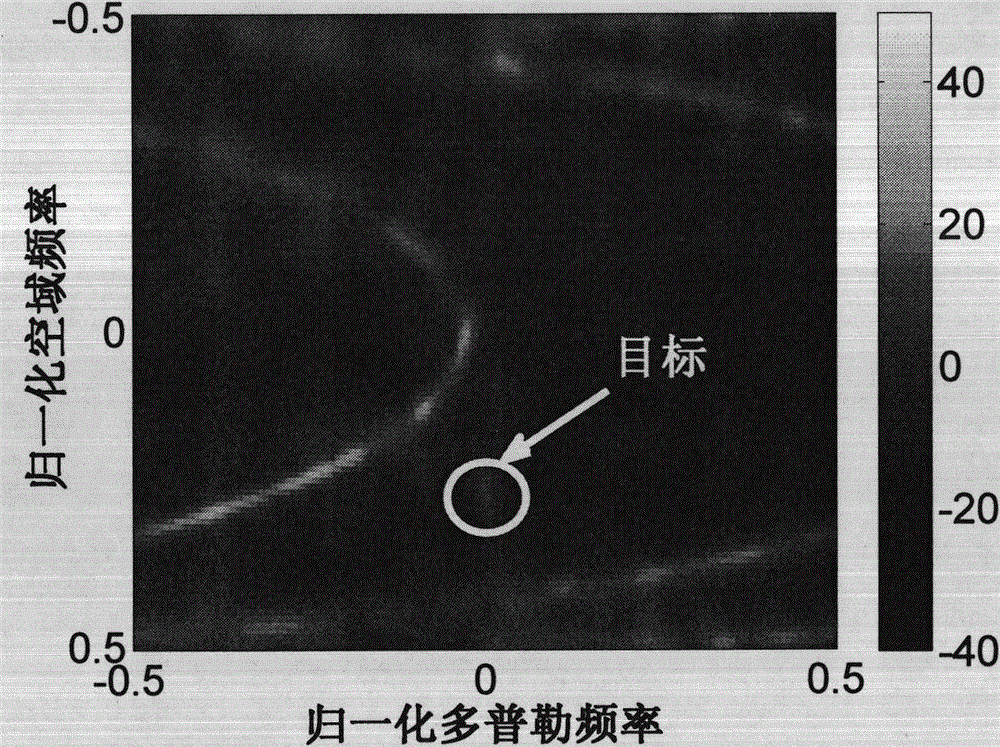
[0038] The invention is a space-time two-dimensional clutter spectrum estimation method based on iterative weighted minimum variance, which can be used for estimating the space-time two-dimensional clutter spectrum in the non-uniform environment of airborne radar. In this example, the radar works in down-looking mode, the radar transmits signals in the L-band, the wavelength is 0.2m, the range sampling frequency used by the radar is 1MHz, the pulse repetition frequency is 400Hz, the radius of curvature of the earth is 6378km, and the height of the carrier aircraft is 8km. The carrier speed is 80m / s, the number of pulses is 22, the number of antenna receiving channels is 11, the array element spacing is 0.5 times the wavelength, the angle α between the antenna axis and the carrier speed direction is -90°, the main beam pointing and The included angle ψ of the antenna axis is 60°, and the elevation angle of the main beam is 0°. The noise-to-noise ratio is 40dB, and the signal-...
Embodiment 2
[0063] The space-time two-dimensional clutter spectrum estimation method based on iterative weighted minimum variance is the same as that in Embodiment 1. The performance of the space-time two-dimensional clutter spectrum estimation method of the present invention will be further described through simulation experiments below.
[0064] 1. Simulation parameters
[0065] In this experiment, the range sampling frequency f used by the radar is s 1MHz, wavelength λ is 0.2m, pulse repetition frequency f r is 400Hz, the radius of curvature of the earth R is 6378km, the altitude H of the carrier aircraft is 8km, the velocity V of the carrier aircraft is 80m / s, the number of pulses P is 22, the number of antenna receiving channels is 11, and the distance between the array elements is 0.5 times the wavelength, satisfying d / λ≤0.5, there will be no grating lobes in the antenna pattern, the CNR is 40dB, the angle α between the antenna axis and the aircraft speed direction is -90°, and the...
Embodiment 3
[0069] The space-time two-dimensional clutter spectrum estimation method based on the iterative weighted minimum variance is the same as that in Embodiment 1, and the simulation conditions are the same as in Embodiment 2.
[0070] In order to further illustrate the advantages of the present invention, Figure 4 The one-dimensional power spectrum comparison curves of the present invention and the traditional IAA method at the spatial frequency of the target are given. from Figure 4 It can be seen from the figure that the estimation result of the traditional IAA spectrum estimation method to the clutter ridge is relatively poor, and the clutter ridge is obviously broadened, while the clutter spectrum estimated by the present invention is very narrow, and the estimation result of the present invention to the clutter ridge is obviously better than traditional method.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com