Sensing element with unevenly distributed multiple magnetic sheet locations and magnetic flux inside casing
A technology of evenly distributed, sensing elements, applied in the direction of transmission of sensing components, vehicle components, transportation and packaging using electric/magnetic devices, which can solve problems such as different sensing parameters, large differences in sensing parameters, and distortion of power demand models.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
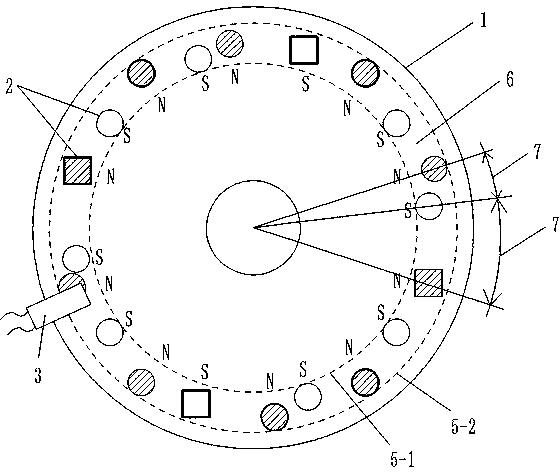
[0074] Embodiment 1, a sensor element in which the position of multiple magnetic sheets and the magnetic flux are unevenly distributed in the shell of a Hall output multiple signal model
[0075] Such as figure 1 , 3 , with the concave surfaces of an annular groove rotating disk 1 and an annular groove fixing disk 40 facing each other, the size of the annular groove rotating disk 1 and the annular groove fixing disk 40 just makes the annular groove fixing disk 40 fit in In the annular groove of the annular groove rotating disk 1, two disks are synthesized into a fitting inner hollow shell that can rotate relatively, and the concave surfaces of the two disks are sandwiched into a hollow ring 41; the annular groove rotating disk at the position of the hollow ring 41 1 is pasted and fixed with 20 permanent magnet sheets 2. On the surface of the annular groove rotating disk 1 with the permanent magnet sheet 2 and the surface of the permanent magnet sheet 2, a clamping magnetic ...
Embodiment 2
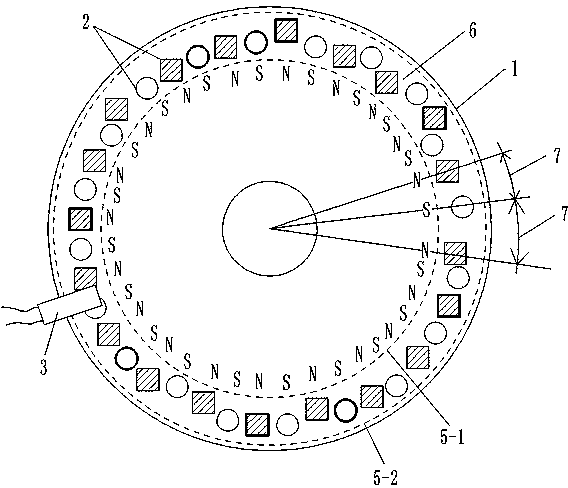
[0088] Embodiment 2, Sensing element with non-uniform distribution of multi-magnetic sheet positions and magnetic flux in a high-density housing
[0089] Such as figure 2 , 3 , the diameter of the circular groove rotating disk 1 in the hollow ring 41 is 10.0 centimeters, and 40 permanent magnet sheets 2 are established on the annular groove rotating disk 1, and the diameters of the 40 permanent magnet sheets 2 are respectively 0.6 centimeters, and the permanent magnet sheets 2 The thickness is 0.2mm, the magnetic flux is 146---279(B·H)max / KJ·m -3 Different selection values within the range, and the magnetic fluxes of adjacent permanent magnets 2 are not equal. Hall 3 keeps a distance of 0.2 cm from each permanent magnet 2 in the rotating state, so that when each rotating permanent magnet 2 passes through Hall 3, Hall 3 can generate a corresponding rectangular wave electric signal output. The structures of other rotating discs 1, permanent magnets 2, and Hall 3 are the sa...
Embodiment 3
[0090] Embodiment 3, using a plurality of Halls to select any one of the signal models in the casing of the multi-magnetic sheet position and the sensor element with uneven distribution of magnetic flux
[0091] Such as figure 1 , 4 , The structure of the rotating disc 1, the permanent magnet sheet 2, and the Hall 3 is the same as that of the embodiment 1. The few differences are as follows:
[0092] The thickness of the permanent magnet sheet 2 is 0.5 mm.
[0093] Hall hole and Hall: The annular groove fixed disk 40 has six Hall holes 11 , and the six Hall holes 11 are different from the center of the circle where the circular trajectory lines of the permanent magnet pieces 2 are located. That is, the semi-longitude lengths from each Hall hole 11 to the center of the circle where the circular locus line is located are unequal, but each Hall hole 11 is at the inner circular locus line 5-1 of the annular groove rotating disk 1 and the outer circular locus line 5-1. Corresp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com