Control device for a three-phase rotating machine
A technology for rotating machinery and control equipment, applied in torque ripple control, motor generator control, AC motor control, etc., can solve problems such as thermal characteristic deterioration, torque fluctuation, etc., to suppress the influence of current stress and reduce sound and/or vibration effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
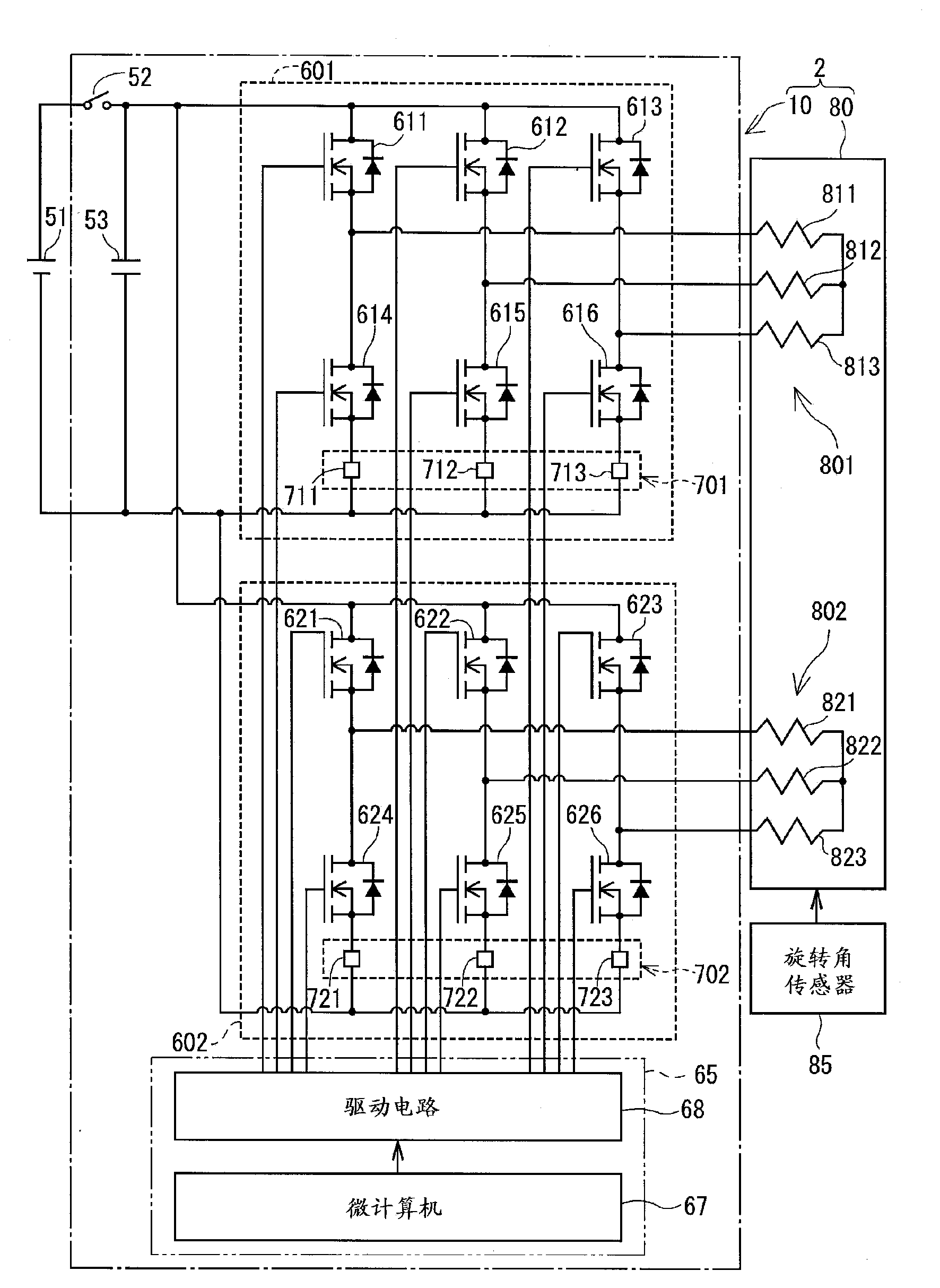
[0042] will refer to Figure 1-16 A first embodiment of the present disclosure is described.
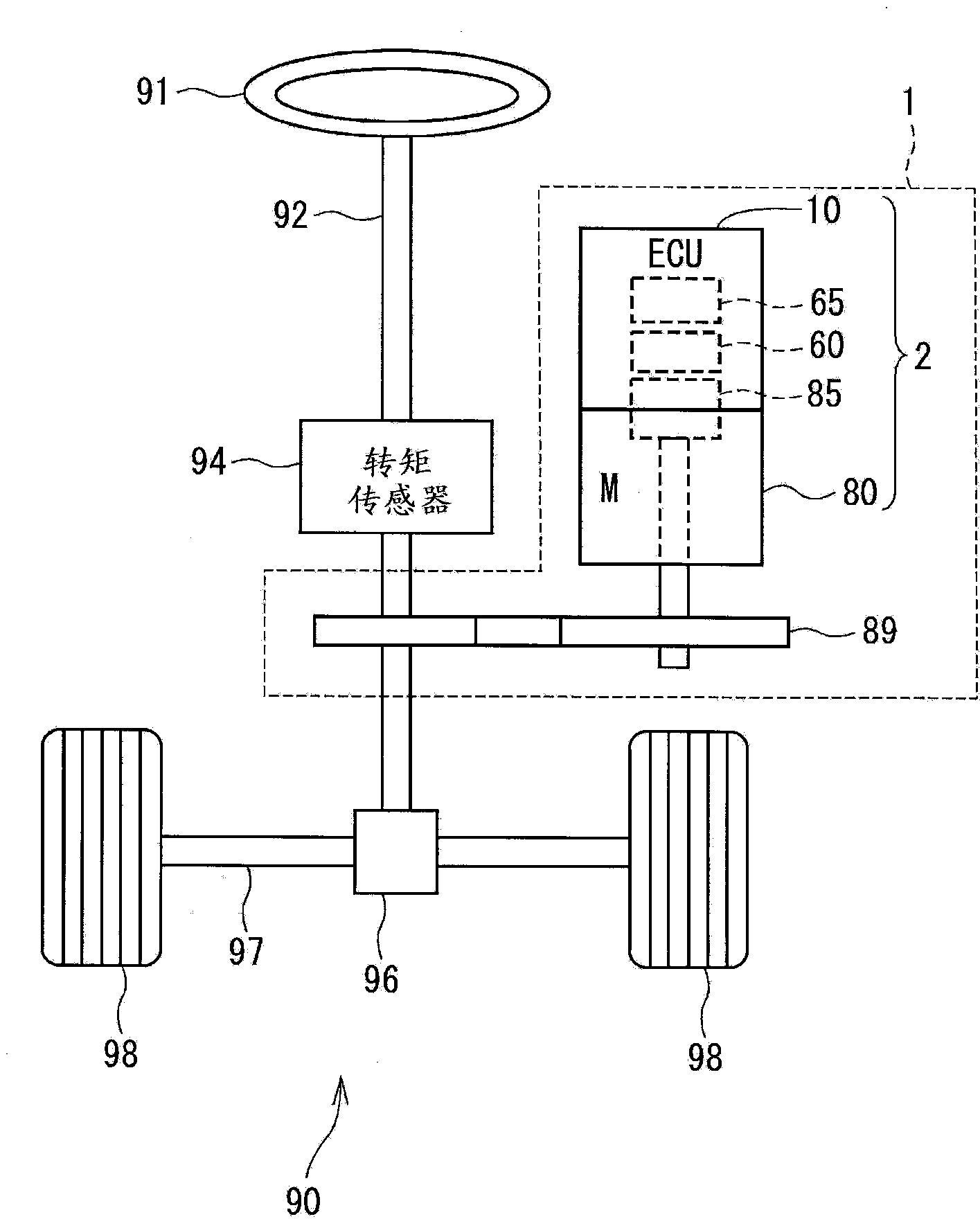
[0043] [Structure of control equipment for three-phase rotating machinery]
[0044] figure 2 The entire structure of a steering system 90 including the electric power steering apparatus 1 is shown. A steered wheel 91 is secured to the top of a steering shaft 92, which is provided with a torque sensor 94 which senses the steering torque of the shaft. The bottom of the steering shaft 92 has a pinion 96 that meshes with a rack 97 . A pair of wheels 98 are rotatably connected to both ends of the rack gear 97 via tie rods or the like. Pinion 96 converts rotational motion of steering shaft 92 into linear motion of rack gear 97 . The steering device 1 steers the pair of wheels 98 by an angle according to the linear displacement of the rack 97 .
[0045] The steering device 1 includes an actuator 2 and a reduction gear 89 . The actuator 2 rotates the rotary shaft. The gear 89 reduce...
no. 2 example
[0190] exist Figure 17 In the second embodiment shown in , the difference / sum gain ratio α is a constant value αL in the low frequency range ZL where the reference frequency fr is lower than the threshold value frt, and is a constant value αL in the high frequency range where the reference frequency fr is equal to or higher than the threshold value frt In ZH, the ratio α varies with the reference frequency fr. The reference frequency threshold frt is equivalent to the frequency at which the stress component of the induced voltage of the motor 80 is equal to or greater than a predetermined value in the high frequency range ZH.
[0191] In the low frequency range ZL where the motor 80 rotates at a relatively low speed, the stress component of the induced voltage is on an order that it does not cause a problem. It is therefore desirable to fix the difference / sum gain ratio α at an optimum value that limits overcurrent in one of the first and second units if the other fails.
...
no. 3 example
[0194] exist Figure 18 In the third embodiment shown, in the low frequency range ZL where the reference frequency fr is lower than the threshold value frt, the difference / sum gain ratio α is a constant value αL, and in the high frequency range where the reference frequency fr is equal to or higher than the threshold value frt In ZH, the difference / sum gain ratio α is a constant value αH smaller than the value αL.
[0195] The ECU 10 uniformly uses the difference / sum gain ratio αH suitable for the actually assumed highest frequency fr over the entire high frequency range ZH where the motor 80 rotates at a relatively high speed and the influence of the stress component must be suppressed. Therefore, the relationship between the reference frequency fr and the difference / sum gain ratio α is shown in two stages. This makes setup simpler than alpha.
[0196] In a modification (not shown) of the third embodiment, the high-frequency range ZH in which the reference frequency fr is e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com