Centralized resource management method based on genetic algorithm
A genetic algorithm and resource management technology, applied in the field of wireless communication, can solve problems such as limiting system performance, not considering user business needs, and not meeting the status quo of mobile communication services
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
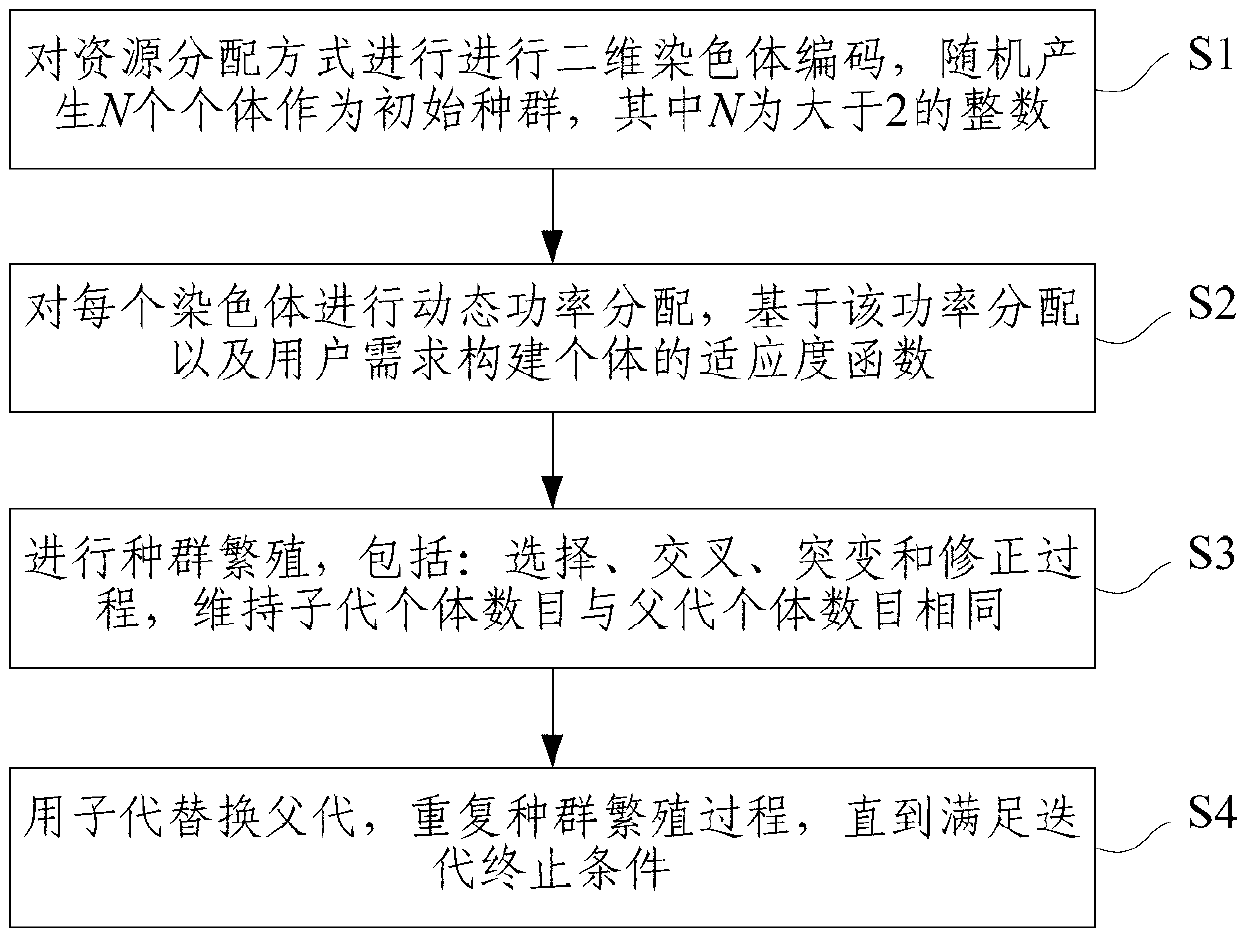
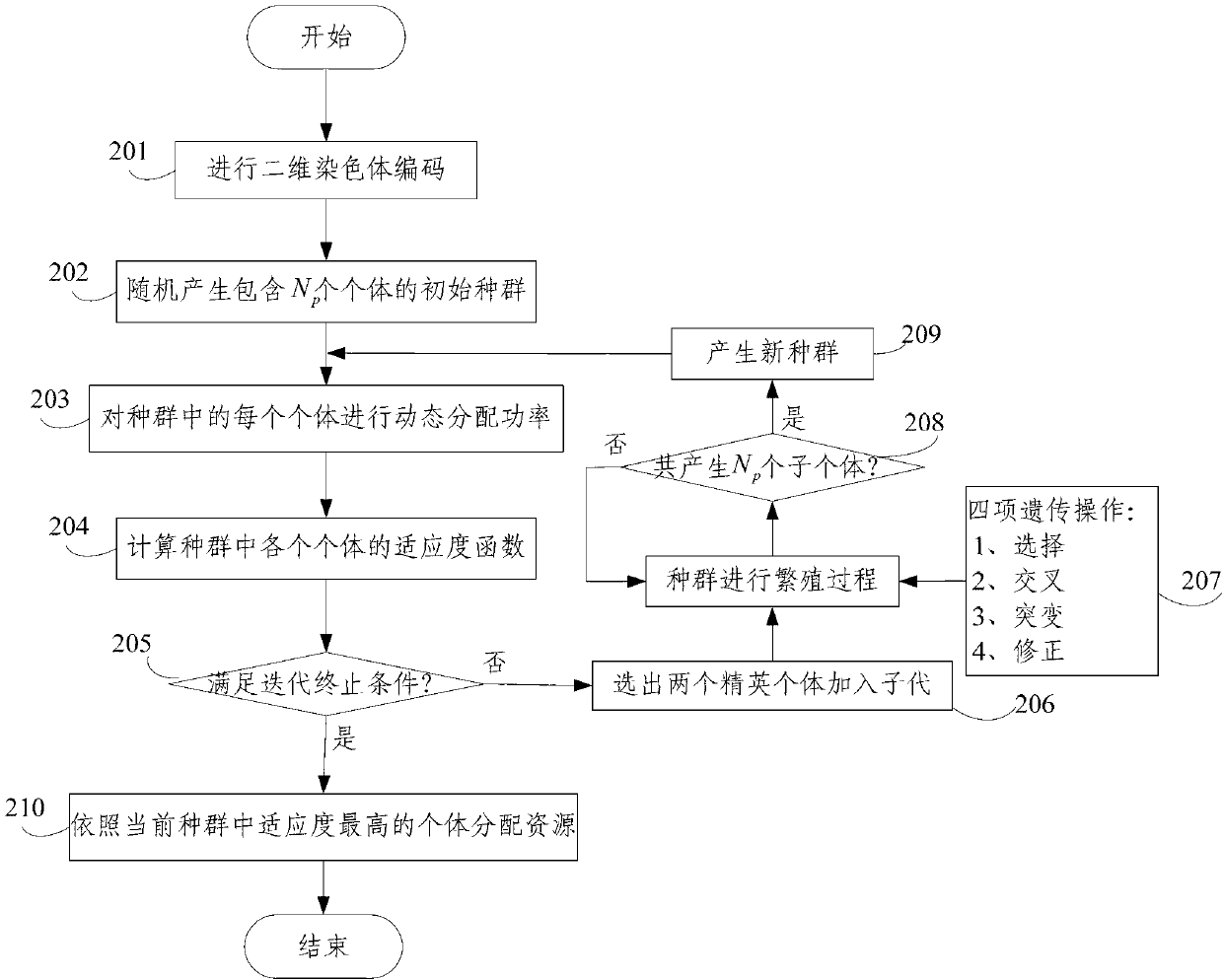
[0064] like figure 1 As shown, this embodiment describes a centralized resource management method based on a genetic algorithm, and the method includes the following steps:
[0065] S1. Integrate network resources in the system and users in the system, perform two-dimensional chromosome coding for resource allocation, and randomly generate N individuals as the initial population, where N is an integer greater than 2;
[0066] S2. Perform dynamic power allocation for each chromosome, and construct an individual fitness function based on the power allocation and user requirements;
[0067] S3. Carry out population reproduction, including: selection, crossover, mutation and revision process, to maintain the same number of offspring individuals as the number of parent individuals;
[0068] S4. Replace the parent with the child, and repeat the population reproduction process until the iteration termination condition is met;
[0069] The network resources refer to other network re...
Embodiment 2
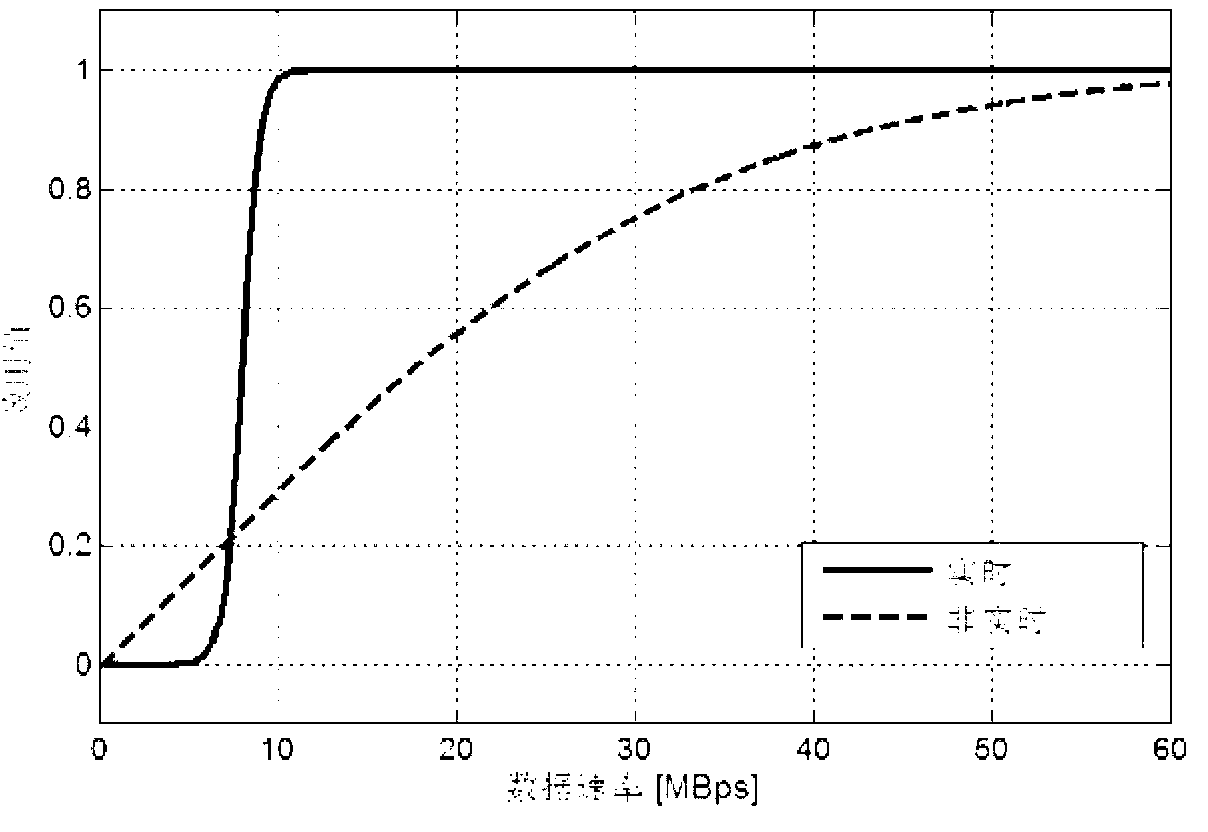
[0153] This embodiment further provides the matlab simulation experiment and results of the first embodiment. Set the experimental value of the parameters of Example 1: set the number of users in the system K=10, where the number of real-time users is K 1 =4, the number of non-real-time users K 2 =6; the number of antennas is I=7, which are randomly distributed in the system; the number of sub-channels is M=20. Each user has at most N a = 3 antenna services, occupying at most N s =4 subchannels. The channel response between the base station and the user considers large-scale fading, shadow fading, and Rayleigh fading. For the genetic algorithm, each generation of the population contains N p =50 individuals, a total of N g = 100 generations of search, the iteration is terminated, and the mutation probability is p m =0.05.
[0154] For the user's utility function, let C in the real-time user's utility function 1 = 2, C in the utility function for non-real-time users 2 ...
comparative approach 1
[0157] Comparison scheme 1: The antennas are allocated according to the path loss, and the sub-channels are randomly allocated
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com