Method for assisting in identifying resistance of soybeans to soybean mosaic viruses
A technique for soybean mosaic virus and auxiliary identification, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbe measurement/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problems of marker-gene genetic distance and small application range, and achieve saving Experimental cost and effect of saving experimental time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Embodiment 1, the design and preparation of primer pair
[0056] Design and synthesize the following three pairs of primers:
[0057] SSR23 primer pair (F stands for upstream primer, R stands for downstream primer):
[0058] SSR23-F (sequence 1 of the sequence listing): 5'-TCGGTCCTATCCCCCTCCTAA-3';
[0059] SSR23-R (SEQ ID NO: 2 of the Sequence Listing): 5'-CGAGTCGCTTTTTCTCTTCTGT-3'.
[0060] SNP9 primer pair:
[0061] SNP9-F (sequence 3 of the sequence listing): 5'-GCTGGCTACACCAACGAAC-3';
[0062] SNP9-R (SEQ ID NO: 4 of the Sequence Listing): 5'-TATTAGAATGTGGACGGCAAA-3'.
[0063] SNP11 primer pair:
[0064] SNP11-F (sequence 5 of the sequence listing): 5'-TATCATGGCTAGTAGGCATAGATAGA-3';
[0065] SNP11-R (SEQ ID NO: 6 of the Sequence Listing): 5'-CCTTTATGAAAATTTTGTGATTGGAAC-3'.
Embodiment 2
[0066] Embodiment 2, the acquisition of the gene locus (RsmvN1-1) of the anti-SMV-N1 strain and the gene locus (RsmvN3-1) of the anti-SMV-N3 strain
[0067] 1. Construction of recombinant inbred lines
[0068] 1. The first generation of hybrids (F 1 generation).
[0069] 2. Put F 1 Generation self-pollination obtains 130 seeds, namely the second generation of children (F 2 generation).
[0070] 3. Put F 2 Each generation was subcultured 6 times by offspring single seed pass method (SSD), and 130 F 2:6 generation of recombinant inbred lines.
[0071] will be 130 F 2:6 Recombinant inbred lines, Dongnong 93-046 (female parent) and Hefeng 25 (male parent) were identified in Step 2 and Step 3, respectively.
[0072] 2. Identification of Plant Anti-SMV-N1 Strains and Anti-SMV-N3 Strains
[0073] The identification of the anti-SMV-N1 strain and the anti-SMV-N3 strain of the plants in each group were carried out in an independent aphid-proof net room. The experiments were ca...
Embodiment 3
[0089] Application of three pairs of primers prepared in embodiment 3 and embodiment 1 in the selection of hybrid offspring
[0090] 1. Construction of recombinant inbred lines
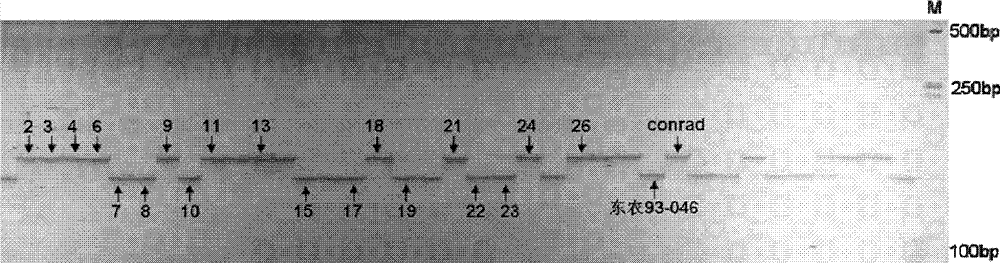
[0091] 1. Crossbreed Dongnong 93-046(♀) and conrad(♂) to obtain the first generation of hybrids (F 1 generation).
[0092] 2. Put F 1 Generation self-pollination obtains 150 seeds, namely the second generation of children (F 2 generation).
[0093] 3. Put F 2 Generations were subcultured for 6 times by single-seed seed transfer method (SSD) respectively, and 150 F 2:6 generation of recombinant inbred lines.
[0094] will be 150 F 2:6 Recombinant inbred lines, Dongnong 93-046 (female parent), conrad (male parent) and Hefeng 25 (susceptible control) were identified in Step 2 and Step 3, respectively.
[0095] 2. Identification of Plant Anti-SMV-N1 Strains and Anti-SMV-N3 Strains
[0096] The identification of the anti-SMV-N1 strain and the anti-SMV-N3 strain of the plants in each group were car...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com