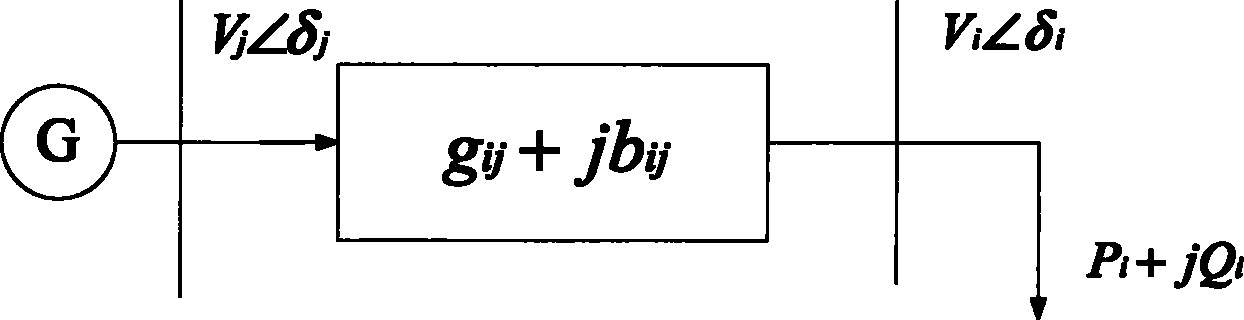Method for identifying cascading failure of power system
A power system and cascading failure technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, circuit devices, AC network circuits, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Such as figure 1 Shown is the geographical wiring diagram of the two-node system. This is to illustrate the voltage stability index VSI and the voltage critical value V of the power system by taking the two-node system as an example. th derivation process. symbol in the figure represents the generator, the vertical solid line represents the transmission bus, |g ij +jb ij | indicates the impedance of the transmission line, and the arrow indicates the load.
[0052] (1) For any two-node power system:
[0053] S i * = Y ii ‾ V i 2 + V ‾ * j V j ‾ Y ij ‾ ...
Embodiment 2
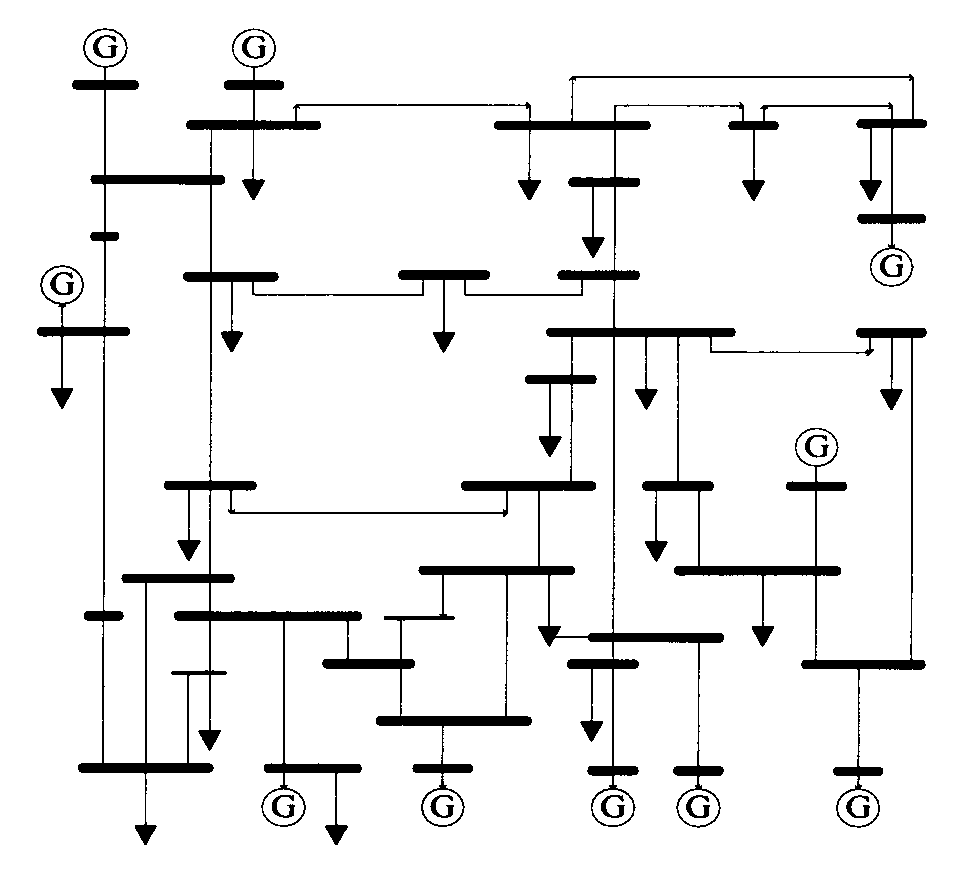
[0089] Such as figure 2 Shown is the geographic wiring diagram of IEEE-39 node system, which is used as the research standard power grid of the present invention, including 10 generators and 34 transmission lines. symbol in the figure Indicates the generator, the thin solid line indicates the transmission line, the thick solid line indicates the node bus, and the arrow indicates the load.
[0090] The inventive method is described in detail below:
[0091] (1) Basic parameter setting: load characteristic parameter k i = 1.5, a i =0.85,b i =0.1,c i =0.05, k' i = 1.5, a' i =0.8, b' i =0.15, c' i =0.05, generator speed regulation parameter: K G =20,K D = 1.5. The basic Newton method is used to calculate the power flow of the system; the partial power flow distribution of the IEEE-39 node system is shown in the table below, and the benchmark value is 1000MW:
[0092] node number
node voltage
Node injected power
1
0.982
(0.663008934734...
Embodiment 3
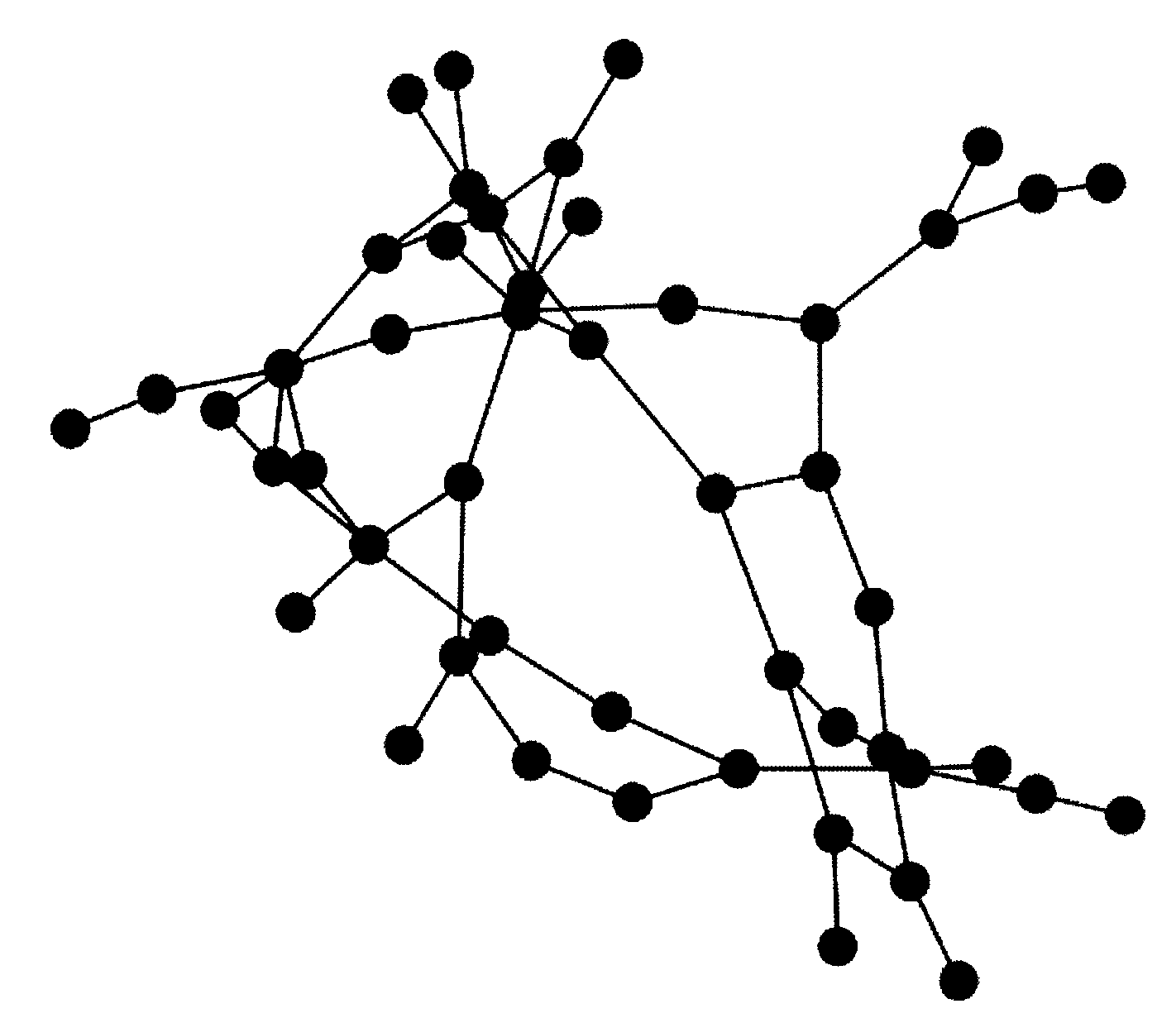
[0119] Such as image 3 Shown is a topological structure diagram of the 500kv side of a power grid in Guangdong, which is used as the actual power grid studied by the present invention. Nodes in the figure represent buses and substations, and thin lines represent transmission lines.
[0120] The inventive method is described in detail below:
[0121] (1) Basic parameter setting: load characteristic parameter k i = 1.5, a i =0.85,b i =0.1,c i =0.05, k' i = 1.5, a' i =0.8, b' i =0.15, c' i =0.05, generator speed regulation parameter: K G =20,K D = 1.5, using the basic Newton method to calculate the system power flow as shown in Table 3;
[0122] node number
Node voltage p.u
Node injection power (1000MW)
1
1.006
(27.2326710998-30.0611882767j)
2
1.053763
(-19.931-1.272j)
3
1.019433
(15.716+1.154j)
4
1.042896
(-9.739+0.788j)
5
1.068123
(-24.554+4.374j)
6
1.055256
-0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com