Load sharing method of non-equivalent route and equipment
A load sharing, non-equivalent technology, applied in the field of communications, can solve the problems of low link utilization, waste of bandwidth, and no support for non-equivalent path load sharing, and achieve the effect of increasing network bandwidth and improving utilization.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the solutions of the present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and examples.
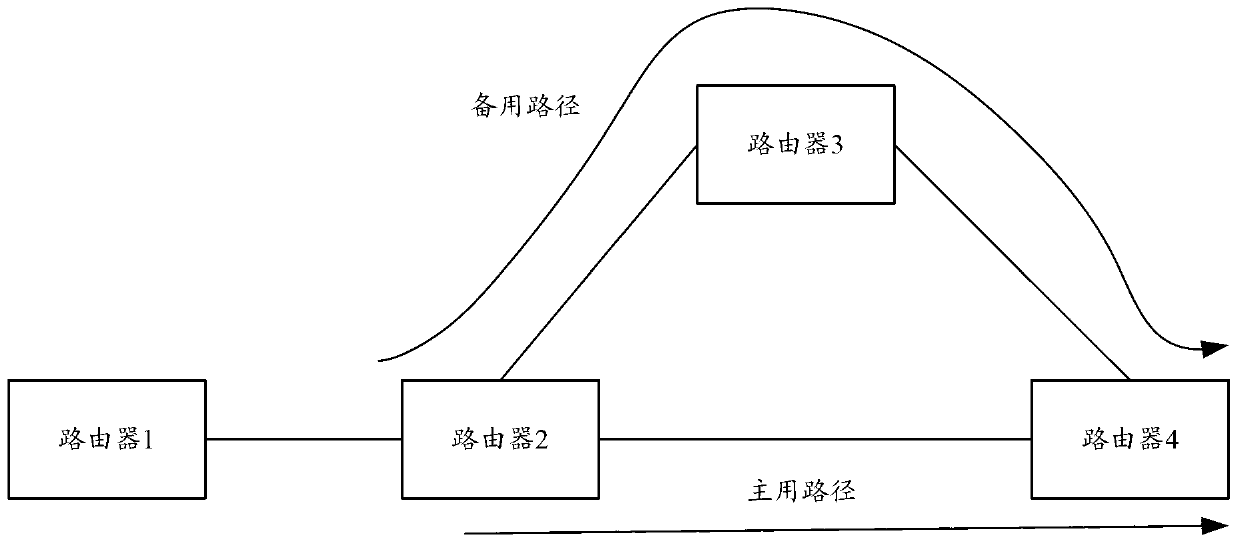
[0019] In the embodiment of the present invention, a load sharing method for non-equivalent routing is proposed, which is applied to any router in a network based on a unicast routing protocol. The path information of the cost path is sent to the FIB, and the traffic is forwarded proportionally through two non-equal-cost paths according to the metric value included in the path information, which can support the load sharing of non-equal-cost paths on the unicast routing protocol, improving Bandwidth utilization, increase network bandwidth.
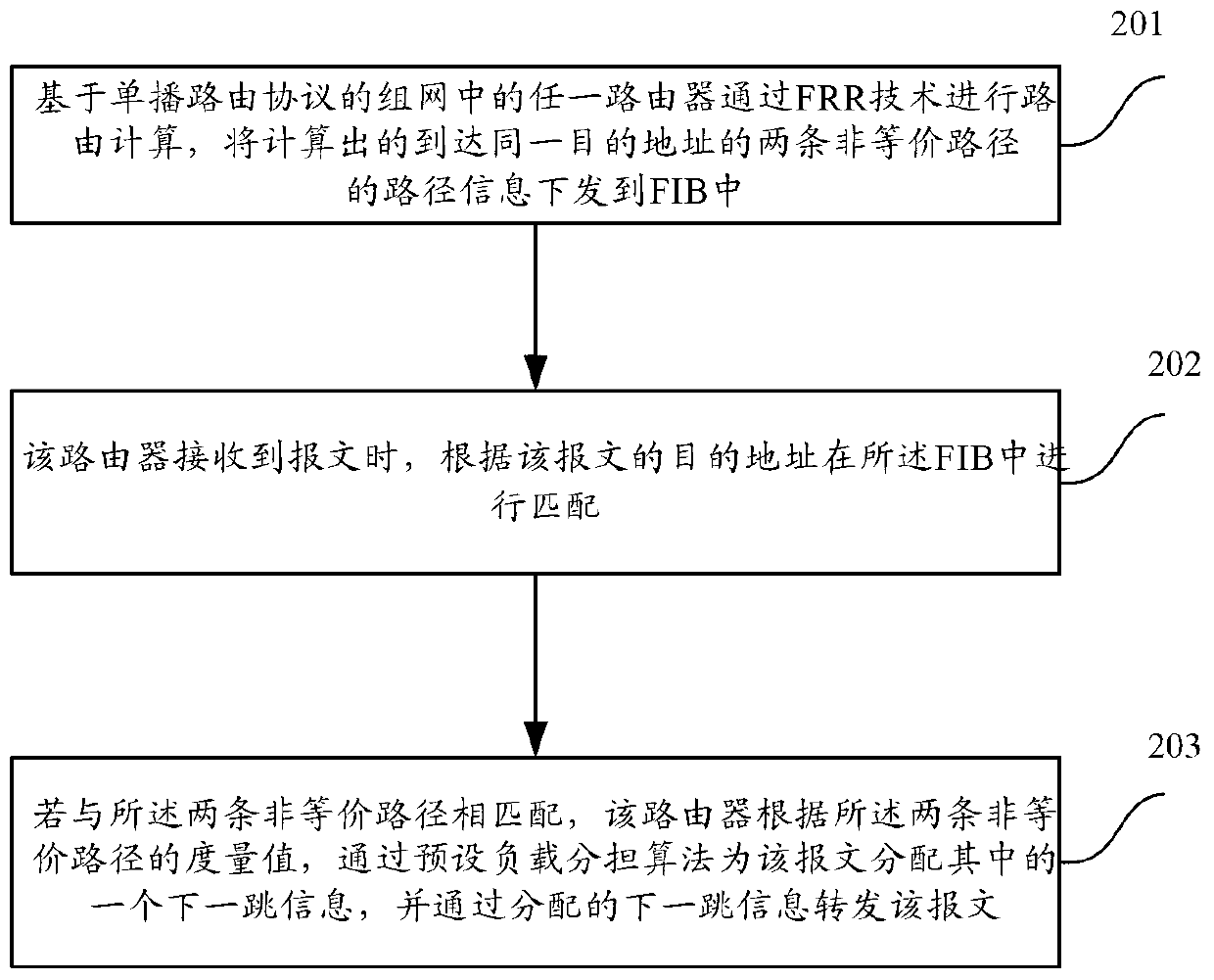
[0020] see figure 2 , figure 2 It is a schematic flowchart of a non-equivalence routing load sharing method in a specific embodiment of the present invention. The specific steps are:
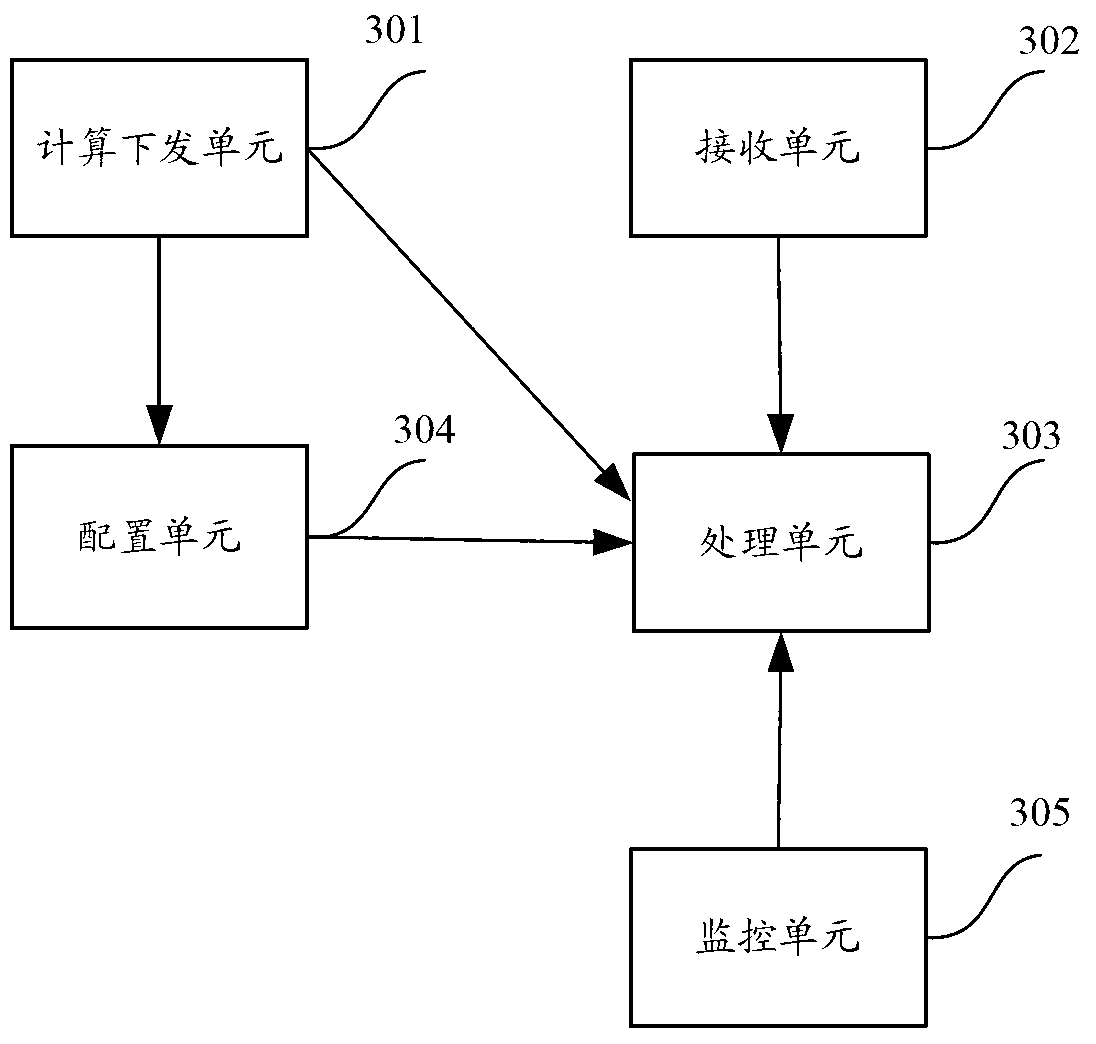
[0021] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com