Efficient ceramic core removal device for hollow blade
A ceramic core and hollow blade technology, which is applied in the field of hollow blade ceramic core removal equipment, can solve the problems of long time for core removal, complex inner cavity structure, ceramic core removal or low removal efficiency, and achieve faster The effect of removal speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
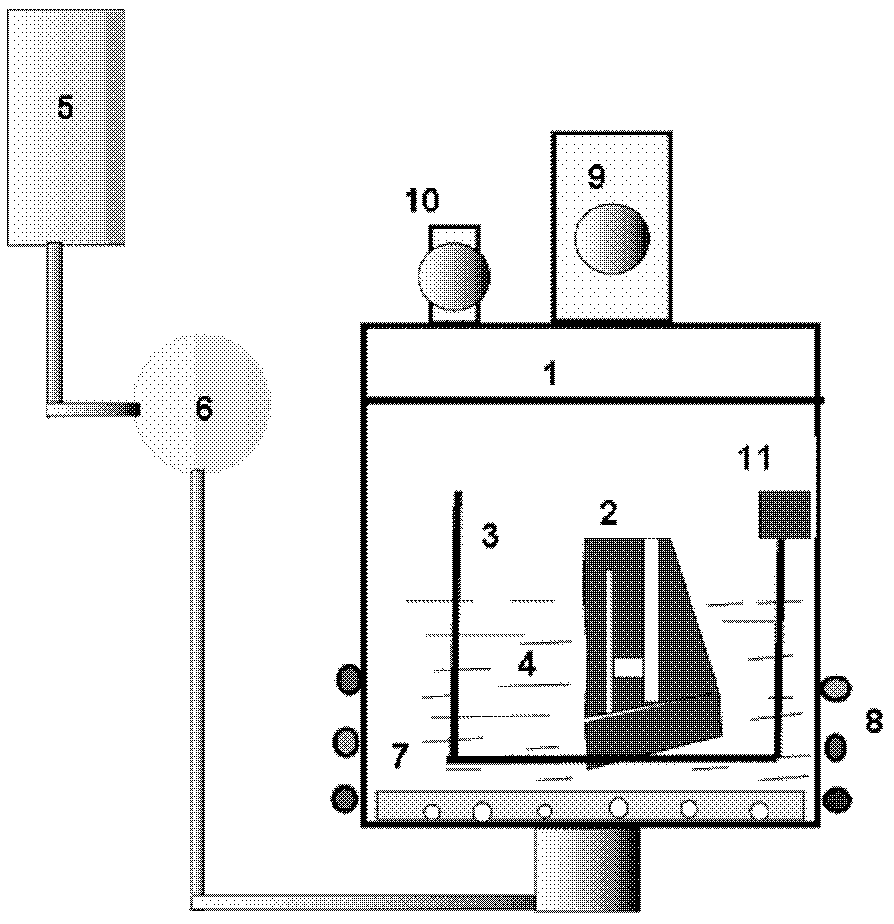
[0019] In the autoclave 1, the NaOH alkali solution 4 with a concentration of 30% is prepared, and the hollow blade 2 after casting is placed in the stainless steel basket 3 by using the lifting mechanism 11. The ceramic core for the blade is a silica-based ceramic core, which is resistant to alkali. Solution 4 is heated to a temperature of 250°C. At the same time, the pressure pump 5 is turned on to blow bubbles into the autoclave 1 for 30 minutes. When the pressure in the autoclave 1 rises to 4 atmospheres, the pressure is released. The valve 9 is depressurized to the normal pressure state, and then the above process is repeated 10 times. After the ceramic core is removed, the hollow blade 2 is synthesized with a hydrochloric acid solution with a concentration of 2-10% after the core is removed, and then cleaned with water. Hollow vane with ceramic core removed 2 see figure 2 .
[0020] Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that by adopting the equipment of the present inven...
Embodiment 2
[0022] In the autoclave 1, the KOH alkali solution 4 with a concentration of 35% is prepared, and the cast hollow blade 2 is placed in the stainless steel basket 3 by using the lifting mechanism 11. The ceramic core for the blade is a silica-based ceramic core, which is resistant to alkali. The solution 4 is heated, and the heating temperature is 170°C. At the same time, the air pressure pump 5 is turned on, and the air bubbles are blown into the autoclave 1 for 25 minutes. The pressure relief valve 9 releases the pressure to the normal pressure state, and then repeats the above process until the removal of the ceramic core is completed. After the blade is removed from the core, it is synthesized with a hydrochloric acid solution with a concentration of 3%, and then cleaned with water, and finally The casting after removing the core is obtained.
Embodiment 3
[0024] In the autoclave 1, the KOH alkali solution 4 with a concentration of 30% is prepared, and the cast hollow blade 2 is placed in the stainless steel basket 3 by using the lifting mechanism 11. The ceramic core for the blade is a silica-based ceramic core, which is resistant to alkali. The solution 4 is heated, and the heating temperature is 230°C. At the same time, the air pressure pump 5 is turned on, and the air bubbles are blown into the autoclave 1 for 20 minutes. The pressure relief valve 9 releases the pressure to the normal pressure state, and then repeats the above process until the removal of the ceramic core is completed. After the blade is removed from the core, it is synthesized with a hydrochloric acid solution with a concentration of 3%, and then cleaned with water, and finally The casting after removing the core is obtained.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com