Important-protein inhibitor in severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome
A platelet and syndrome technology, applied in the direction of non-central analgesics, antipyretics, anti-inflammatory agents, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
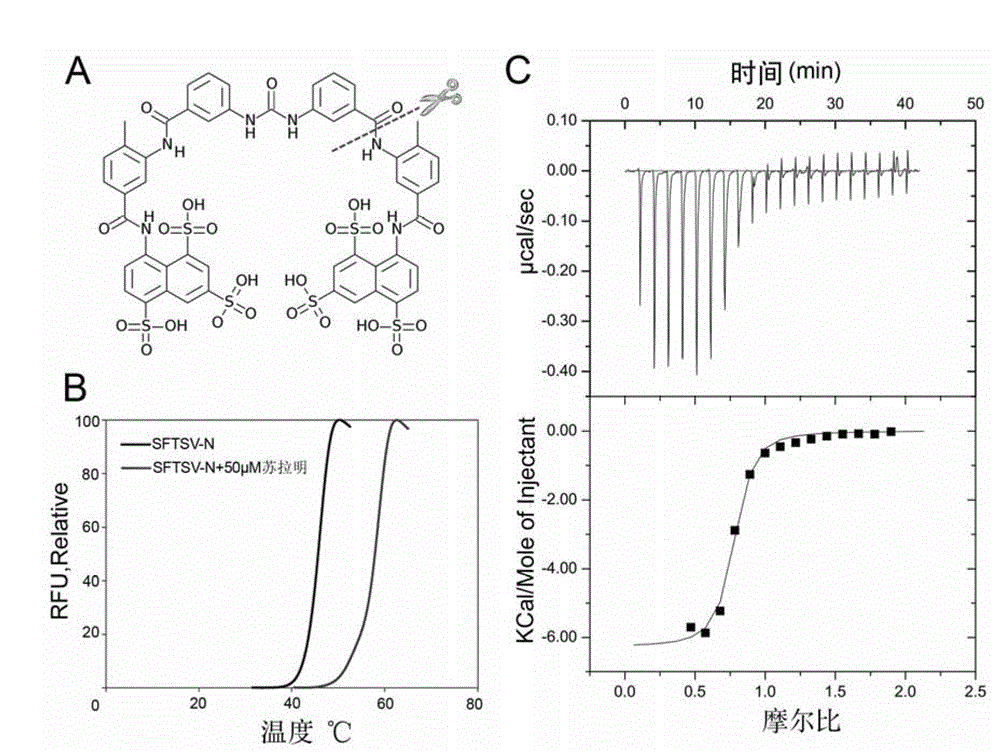
[0024] Embodiment 1, preparation of SFTSV-N protein (SFTSV N protein, SFTSV nucleoprotein) and SFTSV-N / suramin complex
[0025]The gene sequence encoding SFTSV-N (GI: 395406763) (see SEQ ID NO.1 for the amino acid sequence of SFTSV-N, and SEQ ID NO.2 for its encoding nucleic acid sequence) was constructed into the pMCSG7 vector (see reference [11]) The positive recombinant plasmid pMCSG7-SFTSV-N was obtained, and it was transformed into the expression strain (Novagen) of Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3), and spread on fresh LB plate medium with ampicillin resistance, 37°C After culturing overnight, pick a single clone and insert it into 5ml of LB liquid medium, and culture it at 37°C for about 12 hours. Then it was transferred to 500ml LB medium at a ratio of 1:100 for expanded culture. When the OD600 of the bacteria reaches 0.6-0.8, lower the culture temperature to 16°C, add IPTG to a final concentration of 0.2mM, continue to cultivate for about 20 hours, and collect the bacteria...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Example 2. Screening potential inhibitors of SFTSV-N by fluorescence-based thermal shift assay
[0028] Fluorescence-based Thermal Shift (FTS) experiment is a newly developed experimental detection method based on fluorescence technology. The working principle of the detection is to use fluorescent dyes that are sensitive to environmental changes, such as Sypro Orange, to monitor the thermal stability of the protein itself in the system and related factors that may affect the thermal stability of the protein, such as interacting proteins, buffers, and ligands. . This technology combines the high sensitivity of Sypro Orange dye, which can reflect the protein folding state, and the characteristics of reaction and detection in a small volume, with the real-time PCR of high-throughput operation and fluorescent signal detection. This technology can realize rapid high-throughput screening and detection of the above-mentioned proteins and their stability-related factors by de...
Embodiment 3
[0030] Embodiment 3, ITC (isothermal titration calorimetry) verify the interaction of SFTSV-N and suramin
[0031] The interaction between suramin and SFTSV-N protein was further verified by ITC method. The buffer of the SFTSV-N protein sample prepared as described in Example 1 was exchanged with Tris buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 200 mM NaCl, 2 mM DTT) by dialysis. Protein concentration was determined by A280nm light absorption method. Before titration, protein and suramin (Sigma) were centrifuged at 4°C, 18,000×g for 10 minutes to remove possible debris and air bubbles. Calorimetric titrations were performed on a MicroCalITC200 instrument (Microcal Inc., Northampton, MA) at a reaction temperature of 25°C. 50 μM SFTSV-N protein reaction was placed in a 300 μl sample chamber, and 500 μM suramin was injected 20 times, 2 μl each time (the first injection was 0.5 μl), with an interval of 120 seconds. The data were analyzed by ORIGIN software, and the binding constant (Ka), h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com