Farad capacitor charger
A technology of Farad capacitors and chargers, applied in current collectors, battery circuit devices, electric vehicles, etc., can solve problems such as charger damage, and achieve the effects of preventing overcharging, saving energy, and protecting Farad capacitors.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
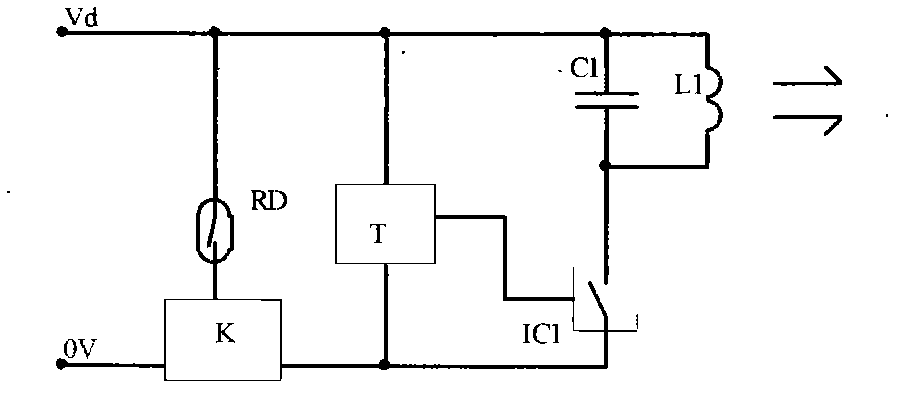
[0022] Example 1. The working principle of the farad capacitor charger
[0023] in the attached figure 1 Among them, the farad capacitor charger, which includes the following structure: a L1C1 resonant transmitting circuit, a transmitting driver IC1, a timer T, a reed switch RD and a group of electronic switches K; the resonant transmitting circuit L1C1 is controlled by the transmitting driver IC1, the transmitting driver IC1 is controlled by the timer T, and the timer T is controlled by the magnetic switch. The specific structure and working principle are as follows:
[0024] in the attached figure 1 And attached figure 2 Among them, the L1C1 resonant transmitting circuit is a parallel resonant transmitting circuit. One end of this circuit is connected to the positive pole Vd of the power supply, and the other end is connected to the output terminal of the transmitting driver IC1. The power supply terminal of the transmitting driver IC1 is connected to the output terminal ...
example 2
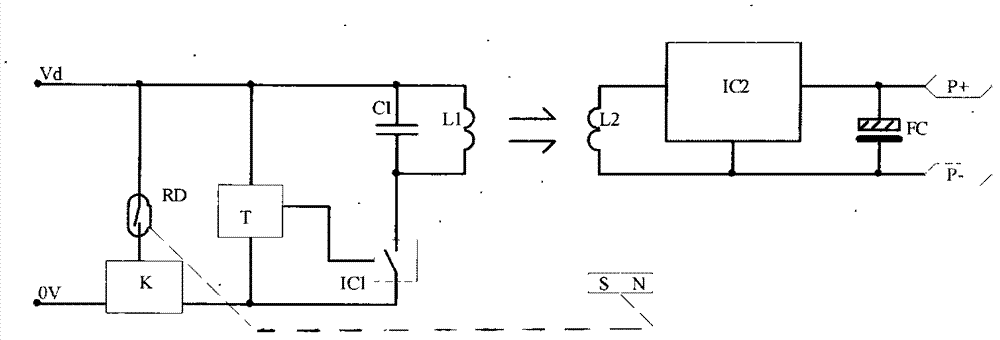
[0029] Example 2. Another principle of Farad capacitor charger
[0030] There are other options for implementing the Farad capacitor charger of Example 1:
[0031] Solution 1: Use a single-chip MCU to write the timing program and the oscillation and driver required for the launch, and add a power output tube outside the MCU to replace the timer T and launch driver IC1 in Example 1.
[0032] Solution 2: Use Hall (Hall) sensor instead of reed switch RD to realize the magnetic control function.
example 3
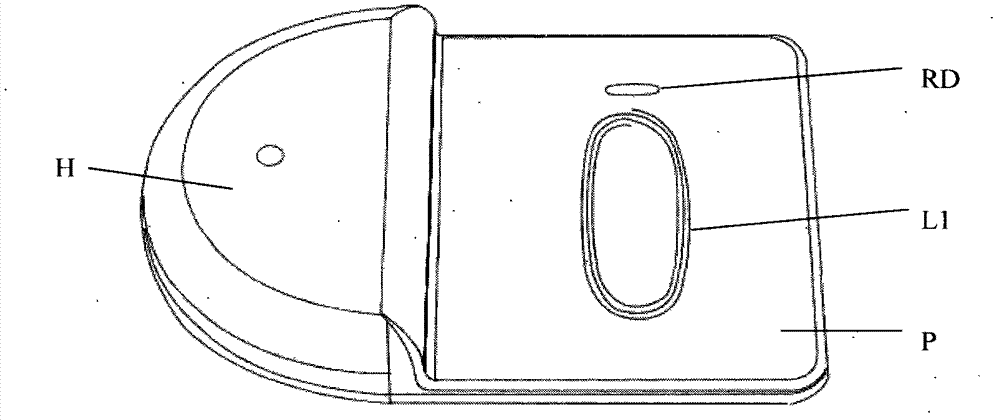
[0033] Example 3. Structural layout of Farad capacitor charger
[0034] like image 3 , the plastic shell P is divided into upper and lower shells, and the cavity H is used to place a PCB. The components on the PCB include: electronic switch K, timer T, resonant capacitor C1 and transmitting driver IC1, etc., transmitting coil L1 and dry reed Tube RD is placed on the other side of the cavity;
[0035] The position requirements of the transmitting coil L1 and the reed switch RD: the position of the transmitting coil L1 is aligned with the receiving coil L2 up and down, and the position of the reed switch RD is aligned with the magnet SN up and down, so as to ensure that the reed switch RD is connected when the magnet SN is close. At the same time, when the transmitting circuit is working, the receiving coil L2 can well receive the energy from the transmitting coil L1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com