Method for distinguishing marine red tide algaes by using MODIS ocean color remote sensing data
A discrimination method, a technology of remote sensing data, applied in the measurement of color/spectral characteristics, etc., which can solve problems such as application failure and complex optical properties of water bodies.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
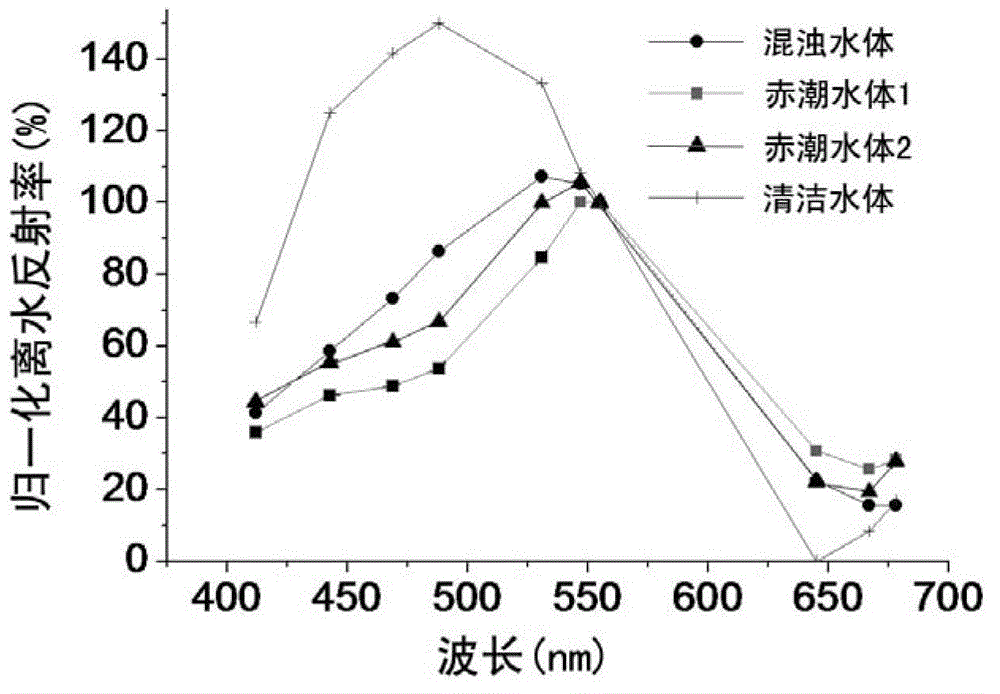
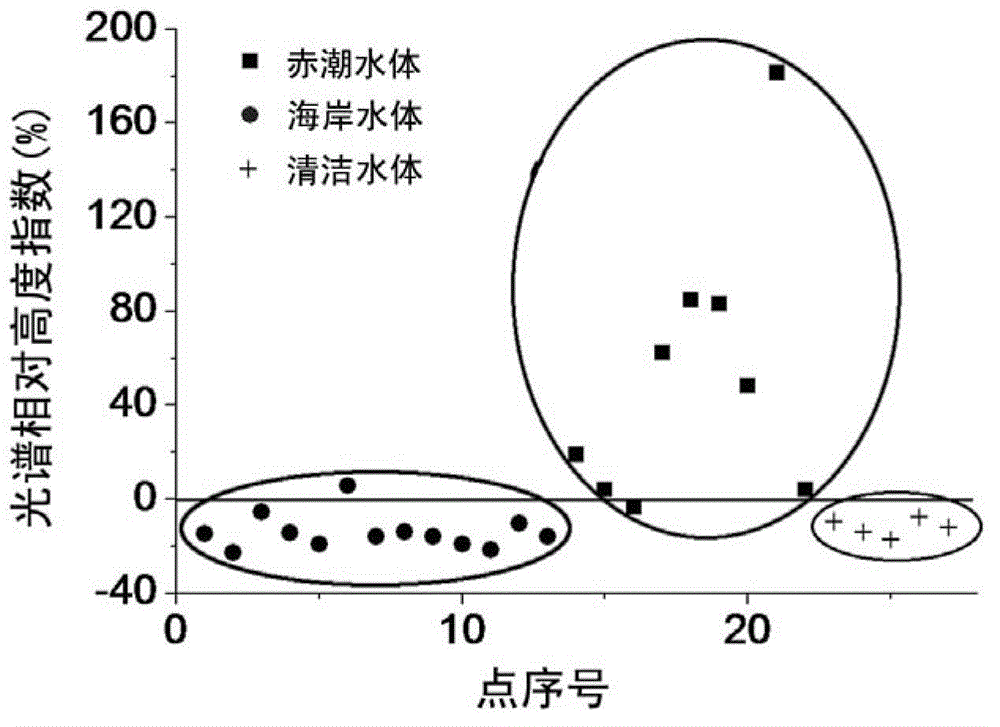
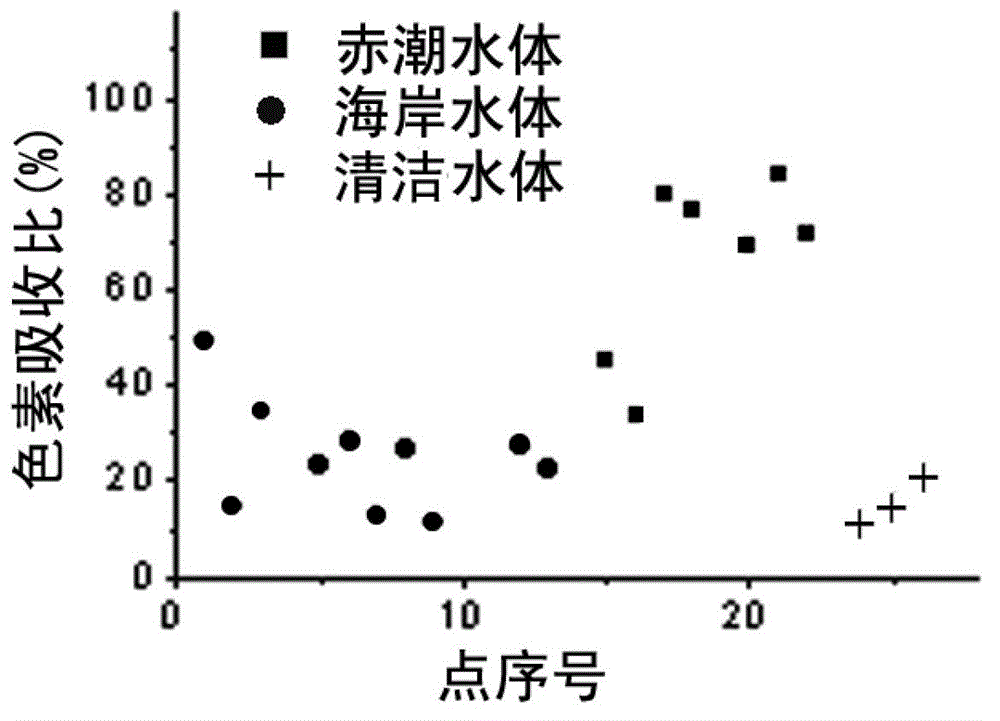
[0018] The invention can directly reflect the physiological and biochemical characteristics of water body substances by using the inherent optical quantity, and show differences with the change of water body substances, effectively eliminate the interference of nearshore water body substances, and realize the effective distinction between red tide water bodies and non-red tide water bodies and the identification of red tide algae species has huge potential. Therefore, starting from the inherent optical quantity of the water body, the red tide and non-red tide water bodies of the ocean, as well as the red tides of dinoflagellates and diatoms are analyzed, and a red tide extraction method suitable for marine areas is established.
[0019] Such as Figure 4 Shown, the present invention utilizes the marine red tide algal discrimination method of MODIS water color remote sensing data, comprises the following steps:
[0020] Step 1. Obtain MODIS water color remote sensing secondary...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com