High-power semiconductor laser with non-absorbing windows
A non-absorbing, laser technology, applied in the structure of optical waveguide semiconductors, the structure of active regions, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the output power of lasers, achieve simple and easy manufacturing process, increase output power, and increase optical catastrophe damage threshold Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
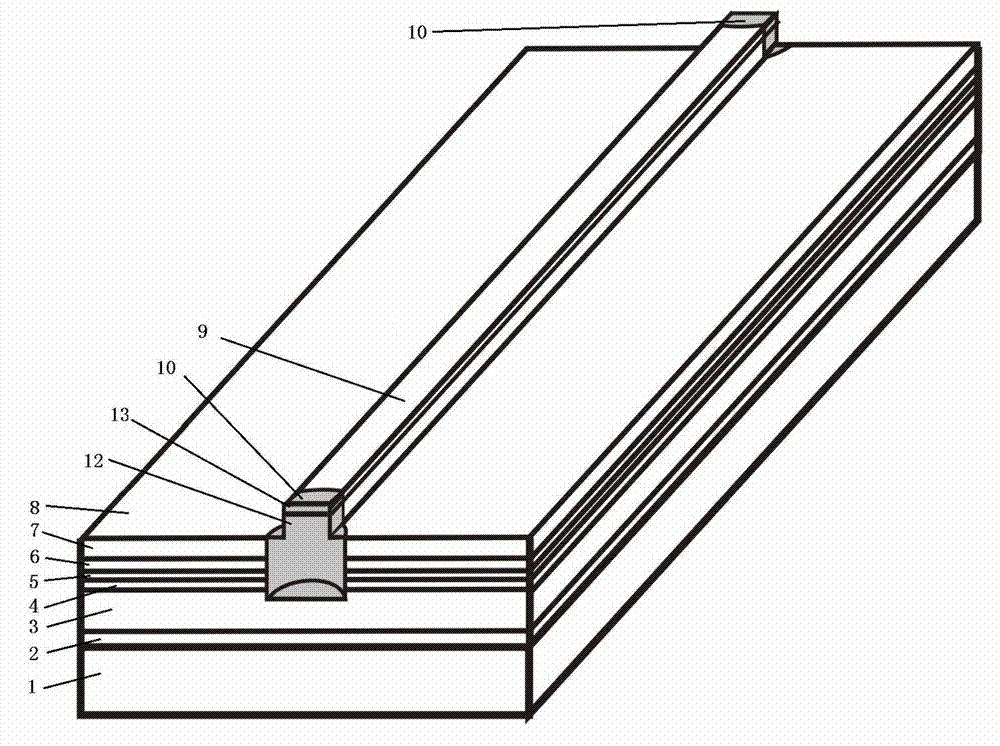
[0017] refer to figure 1 , is a schematic structural diagram of a high-power semiconductor laser with a 670nm non-absorbing window in Example 1 of the present invention. The non-absorbing window 10 is distributed on the upper surface of the epitaxial wafer structure of the laser. 1. Epitaxially grown buffer layer 2, lower confinement layer 3, lower waveguide layer 4, quantum well and quantum barrier region 5, upper waveguide layer 6, upper confinement layer 7 and upper contact layer 8, longitudinal centerline of upper contact layer 8 A ridge waveguide 9 and a semi-cylindrical non-absorbing window 10 are arranged on it, the non-absorbing window 10 includes a semi-cylindrical planar portion 12 and a semi-cylindrical arc portion 13, the planar portion 12 is used to serve as the light-emitting surface of the laser, The arc portion 13 is used as the interface between the non-absorbing area and the normal area; the central area of the non-absorbing window 10 coincides with the cen...
Embodiment 2
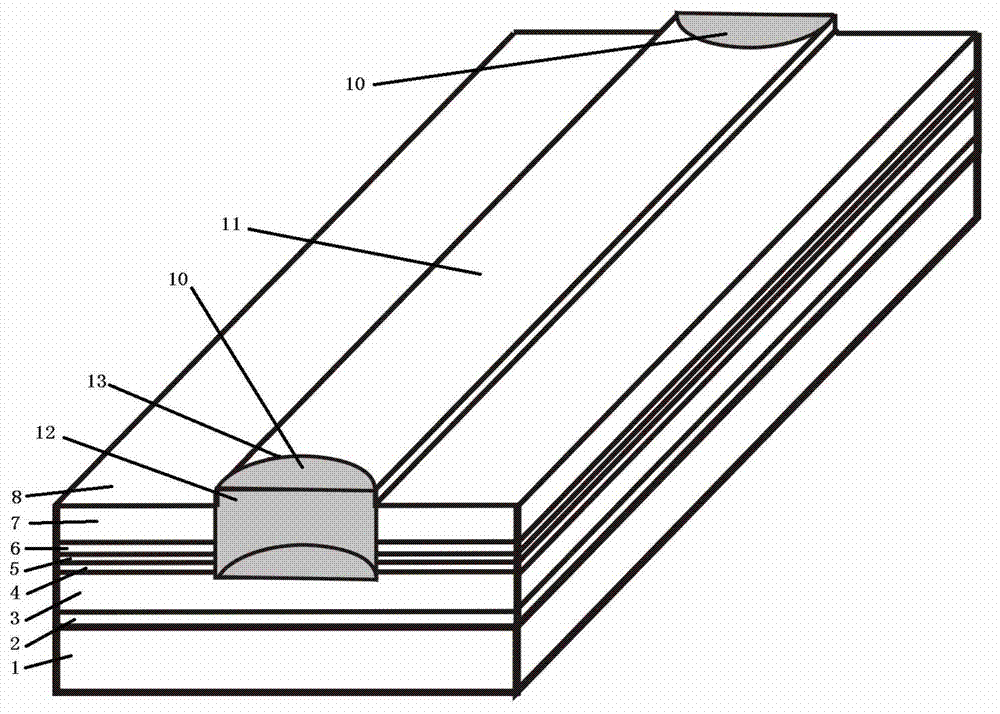
[0023] refer to figure 2 , is a schematic diagram of the structure of the 808nm non-absorbing window high-power semiconductor laser in Example 2 of the present invention. The difference from Example 1 is that the laser in Example 2 is a strip structure, and the width of the strip area is 60 microns. The non-absorbing window 10 is distributed on the surface of the laser epitaxial wafer structure, and the described epitaxial wafer structure is sequentially provided with a substrate 1, an epitaxially grown buffer layer 2, a lower confinement layer 3, a lower waveguide layer 4, a quantum well and The quantum barrier region 5, the upper waveguide layer 6, the upper confinement layer 7 and the upper contact layer 8, the longitudinal center line of the upper contact layer 8 are provided with a strip region 11 and a non-absorbing window 10, and the non-absorbing window 10 includes a semi-cylindrical Planar portion 12 and semi-cylindrical arc portion 13, semi-cylindrical planar portio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com