Graphite/barium ferrite composite wave-absorbing material and preparation method thereof
A composite wave-absorbing material, barium ferrite technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, other chemical processes, etc., can solve problems such as the toxicity and hazards of composite materials, achieve the effects of reducing operating costs, good application prospects, and avoiding toxicity hazards
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0008] Specific implementation mode 1: This implementation mode is a graphene / barium ferrite composite absorbing material. The graphene / barium ferrite composite absorbing material is composed of barium ferrite suspension and concentration of 0.5mol / L~5mol / L of graphite oxide aqueous dispersion prepared.
[0009] The mass ratio of the barium ferrite in the barium ferrite suspension described in this embodiment to the graphite oxide aqueous dispersion with a concentration of 0.5 mol / L-5 mol / L is 9:(1-2).
[0010] Barium ferrite is a typical magnetic loss absorbing material with better absorbing performance but higher density.
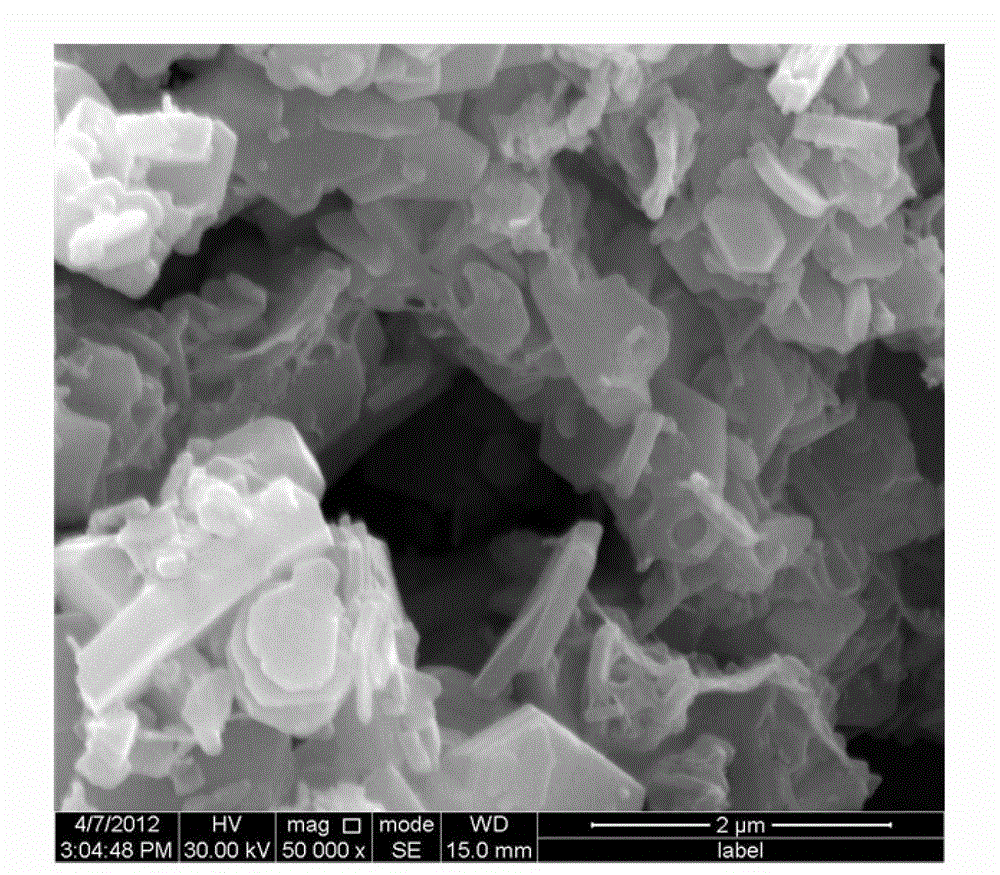
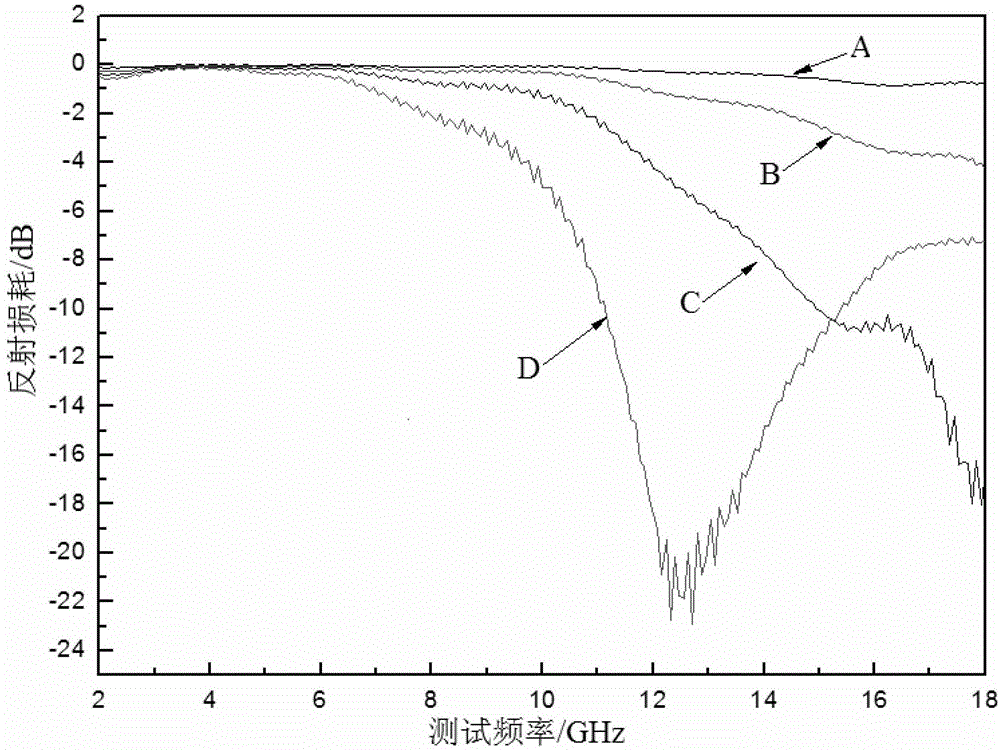
[0011] Using a scanning electron microscope to characterize the morphology of the graphene / barium ferrite composite wave-absorbing material described in this embodiment, and using a vector network analyzer to evaluate the wave-absorbing performance of the graphene / barium ferrite composite wave-absorbing material, It can be seen that the graphene / barium ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0012] Specific embodiment two: This embodiment is a preparation method of graphene / barium ferrite composite wave-absorbing material, which is completed according to the following steps: 1. Prepare graphite oxide aqueous dispersion: put graphite oxide into deionized Perform ultrasonic dispersion in water to obtain a graphite oxide aqueous dispersion with a concentration of 0.5mol / L~5mol / L; 2. Preparation of barium ferrite suspension: put barium ferrite with a particle size of 50nm~2μm into deionized water Perform ultrasonic dispersion to obtain a barium ferrite suspension uniformly dispersed by ultrasonic; 3. Ultrasonic treatment: add the barium ferrite suspension to the graphite oxide aqueous dispersion with a concentration of 0.5mol / L~5mol / L for ultrasonic dispersion , to obtain the ultrasonic blend; 4. Hydrothermal treatment: transfer the ultrasonic blend to the reactor for hydrothermal treatment to obtain the reduced product; 5. Drying treatment: The reduced product is firs...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0019] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 2 is: the specific operation of the ultrasonic dispersion described in step 1 is as follows: Ultrasonic dispersion is performed for 60 min to 300 min with the assistance of ultrasound at a frequency of 20 KHz to 100 KHz. Others are the same as in the second embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com