Helicobacter pylori multiple-epitope fusion protein and multiple-epitope vaccine prepared by helicobacter pylori multiple-epitope fusion protein
A technology of Helicobacter pylori and fusion protein, which is applied in the field of fusion protein and multi-epitope vaccine, and can solve problems affecting the therapeutic effect of the vaccine
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1 Construction of recombinant plasmid
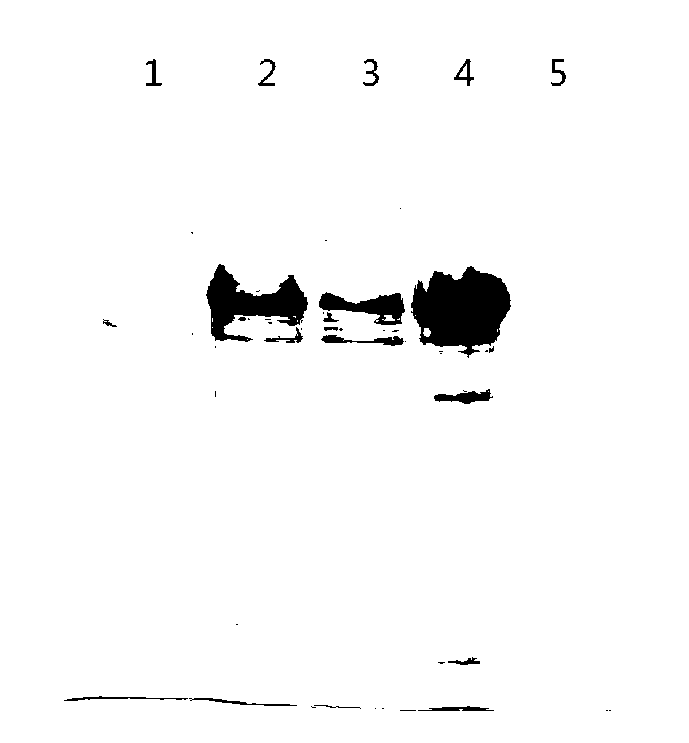
[0039] E. coli preferred codons are used to synthesize the vaccine protein coding gene EpiVac, and its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:1. Insert EpiVac into the plasmid vector pET 30a to obtain a recombinant plasmid named pET 30a-EpiVac. Transform the recombinant plasmid into E.coli DH5α competent cells, inoculate the transformed competent cells on LB plates containing a final concentration of 30μg / ml kanamycin for resistance selection, pick a single clone, and use whole bacteria PCR method and restriction enzyme digestion of recombinant plasmids identify recombinants. Recombinant plasmid was identified correctly by restriction enzyme digestion, and it was also correct by sequencing. Please refer to the restriction enzyme digestion electropherogram figure 1 .
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2 Induced expression of vaccine protein and identification of expression form
[0041] The recombinant plasmids prepared in Example 1 were respectively transformed into E.coli BL21(DE3) competent cells, and single clones were picked and inoculated in 10ml LB medium containing a final concentration of 50μg / ml kanamycin at 37°C , 200rpm / min shaking culture overnight, and then inoculating in fresh LB medium at a volume ratio of 1:100, 37℃, 200rpm / min shaking culture, until the cell density OD 600nm When it reached about 0.6, IPTG was added to a final concentration of 1 mmol / L, and the culture was induced for 5 hours. The cells were collected and sonicated and centrifuged at 12000rpm / min for 30min. The supernatant and precipitate obtained were analyzed by SDS-PAGE to determine the expression form of the target protein. The results show that the recombinant protein EpiVac is an inclusion body protein. The expression and expression form of the recombinant protein EpiVac...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Example 3 Purification of vaccine protein
[0043] Centrifuge the 1L of the induced recombinant bacteria and collect the cells, wash them once with PBS, then resuspend the bacteria in 100ml A solution (20mM Tris, 5mM EDTA), break it with a high pressure homogenizer, and centrifuge at 800×g for 20min at 4℃ , Discard the precipitate, centrifuge the supernatant at 8000 rpm / min for 30 min, discard the supernatant to obtain inclusion bodies. The inclusion bodies were dispersed with liquid B (20mM Tris, 5m MEDTA, 1% Triton) and stirred for 1h. Centrifuge at 8000 rpm / min for 30 min. Disperse the pellet with solution C (20mM Tris, 5mM EDTA, 2M urea) and stir for 10 min. Centrifuge again to dissolve the pellet in the lysate (20mM Tris, 8M urea, pH 8.5). Filter with a 0.22um membrane, and the filtrate is purified by affinity chromatography. Using Invitrogen's Ni-NTAAgarose column, the protein was purified by the affinity between the 6×His tag at the N-terminal of the recombinant p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com